Strict requirements are imposed on working conditions in industry and industry. Various regulations must be observed. The correct fulfillment of many requirements affects the quality of the air. It provides the correct air exchange. At most industrial enterprises, it is impossible to provide due to natural ventilation, so the installation of special hoods is required. In order to properly set the air exchange, it is necessary to calculate the ventilation.
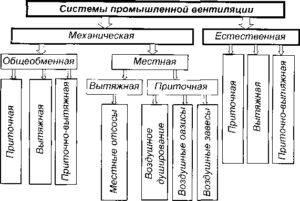
Types of air exchange used in industrial enterprises
Regardless of the type of production, quite high requirements are imposed on air quality at any enterprise. There are standards for the content of various particles. In order to fully comply with the requirements of sanitary standards, various types of ventilation systems have been developed. The air quality depends on the type of air exchange used. Currently, the following types of ventilation are used in production:
- aeration, i.e. general ventilation with a natural source. It regulates air exchange throughout the room. It is used only in large industrial premises, for example, in workshops without heating. This is the oldest type of ventilation, it is currently used less and less, as it copes poorly with air pollution and is not able to regulate the temperature regime;
- local exhaust, it is used in industries where there are local sources of emissions of harmful, polluting and toxic substances. It is installed in the immediate vicinity of the discharge sites;
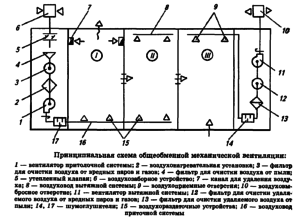
- supply and exhaust ventilation with artificial motivation, used to regulate air exchange in large areas, in workshops, in various rooms.
Ventilation functions
Currently, the ventilation system performs the following functions:
- removal of industrial harmful substances released in the process. Their content in the air in the working area is regulated by regulatory documents. Each type of production has its own requirements;
- removal of excess moisture in the working area;
- filtering polluted air taken from the production room;
- emission of removed pollutants to the height necessary for dispersion;
- temperature regulation: removal of air heated during production (heat is released from working mechanisms, heated raw materials, substances that enter into chemical reactions);
- filling the room with air from the street, while filtering it;
- heating or cooling drawn air;
- humidification of the air inside the production room and drawn in from the street.
Types of Air Pollution
Before you begin the calculation work, you need to find out what sources of pollution are available. Currently, the following types of harmful emissions are found in production:
- excess heat from operating equipment, heated substances, etc.
- fumes, vapors and gases containing harmful substances;
- explosive gas emission;
- excess moisture;
- discharge from people.
Typically, in modern plants there are various types of pollution, for example, working equipment and chemicals. And not one of the industries can do without discharge from people, because in the process of activity a person breathes, tiny particles of skin are showered from him, and so on.
The calculation must be performed for each type of pollution. At the same time, they are not summarized, but taken as the final largest calculation result. For example, if air is most needed to remove chemical air pollution, then this calculation will be adopted to calculate the necessary amount of general ventilation and exhaust capacities.
Settlement
As can be seen from the foregoing, ventilation performs many different functions. Only a sufficient number of devices can provide high-quality air purification. Therefore, during installation, it is necessary to calculate the required power of the installed hood. Do not forget that for various purposes they use different types of ventilation systems.
Calculation of local exhaust
If harmful substances are emitted at the factory, they must be captured directly at the closest possible distance from the source of pollution. This will make their removal more effective. As a rule, various technological capacities become emission sources; working equipment can also pollute the atmosphere. To catch the emitted harmful substances use local exhaust devices - suction. Usually they have the form of an umbrella and are installed above a source of vapor or gas. In some cases, such installations are included with the equipment, in others, the capacities and sizes are calculated. It is easy to execute them if you know the correct calculation formula and have some initial data.
To make the calculation, it is necessary to conduct some measurements and find out the following parameters:
- the size of the ejection source, the length of the sides, the cross section, if it has a rectangular or square shape (parameters a x b);
- if the source of pollution has a round shape, it is necessary to know its diameter (parameter d);
- air velocity in the zone where the emission occurs (parameter vv);
- suction speed in the area of the exhaust system (umbrella) (parameter v3);
- the planned or existing installation height of the hood above the pollution source (parameter z). It should be remembered that the closer the hood is to the source of emission, the more efficiently the pollutants are captured. Therefore, the umbrella should be placed as low as possible above the tank or equipment.
The calculation formulas for rectangular hoods are as follows:
A = a + 0.8zwhere A is the side of the ventilation device, a is the side of the source of pollution, z is the distance from the source of exhaust to the exhaust.
B = b + 0.8zwhere B is the side of the ventilation device, b is the side of the source of pollution, z is the distance from the source of exhaust to the exhaust.
If the exhaust system will have a round shape, then its diameter is calculated. Then the formula will look like this:
D = d + 0.8zwhere D is the diameter of the hood, d is the diameter of the source of pollution, z is the distance from the source of exhaust to the hood.
The exhaust device is made in the form of a cone, and the angle should not be more than 60 degrees. Otherwise, the efficiency of the ventilation system will decrease, since at the edges zones are formed where air stagnates. If the air velocity in the room is more than 0.4 m / s, then the cone must be equipped with special folding aprons to prevent dispersion of the released substances and protect them from external influences.
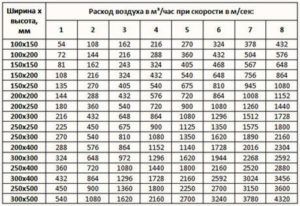
It is necessary to know the overall dimensions of the hood, since the quality of air exchange will depend on these parameters. The amount of exhaust air can be determined by the following formula: L = 3600vz x Szwhere L is understood as air flow (m3/ h), vz is the air velocity in the exhaust device (a special table is used to determine this parameter), Sz is the opening area of the ventilation unit.
If the umbrella has a rectangular or square shape, then its area is calculated by the formula S = A * Bwhere A and B are the sides of the figure.If the exhaust device has the shape of a circle, then its size is calculated by the formula S = 0.785Dwhere D is the diameter of the umbrella.
The results obtained should be taken into account in the design and calculation of general ventilation.
Calculation of general exchange of supply and exhaust ventilation
When the necessary volumes and parameters of local exhaust are calculated, as well as the volumes and types of pollution, you can proceed to calculate the required volume of air exchange in the production room.
The simplest option is when during work there are no harmful emissions of various types, but there are only those pollutants that people emit. The optimal amount of clean air will ensure normal working conditions, compliance with sanitary standards, as well as the necessary purity of the process.
To calculate the required amount of air for working people, use the following formula: L = N * mwhere L is the required amount of air (m3/ h), N - the number of working people at the production site or in a specific room, m - air flow for breathing 1 person per hour.
The specific air consumption per 1 person per hour is a fixed value indicated in special SNiPs. The standards indicate that the volume of the mixture per 1 person is 30 m3/ h, if the room is ventilated, if there is no such possibility, then the norm becomes twice as much and reaches 60 m3/ h
The situation is more complicated if there are various sources of emissions of harmful substances on the site, especially if there are a lot of them and they are dispersed over a large area. In this case, local extracts will not be able to fully get rid of harmful substances. Therefore, in production, they often resort to the next technique.
Emissions are dispersed, and then removed using general ventilation. All harmful substances have their own MPCs (maximum permissible concentrations), their values can be found in the specialized literature, as well as regulatory documents.
The amount of harmful substances in the air can be calculated using the following formula:
L = Mв / (yпом - yп)where L is the required amount of fresh air, Mv is the mass of the emitted harmful substance (mg / h), the specific concentration of the substance (mg / m)3), yn is the concentration of this substance in the air entering through the ventilation system.
If several types of pollutants are released, it is necessary to calculate the required amount of clean air mixture for each of them, and then summarize them. The result is the total volume of air that must enter the production room to ensure that sanitary requirements and normal working conditions are met.
Calculation of ventilation is a complex matter, requiring great accuracy and special knowledge. Therefore, for independent calculations, you can use online services. If you have to work with hazardous and explosive substances in production, it is better to entrust the calculation of ventilation to professionals.