The ventilation system of the production room creates and maintains climatic indicators, the norms of which are regulated by the sanitary and epidemiological supervision instructions.
Humidity, temperature and air flow rate are important for the health of employees and compliance with the process. Unlike household objects, such indicators as the amount of mechanical and chemical impurities in the air are also controlled at production facilities.
In some cases, the indoor microclimate should provide optimal storage conditions (for example, in museums or libraries), then the convenience of the staff fades into the background.
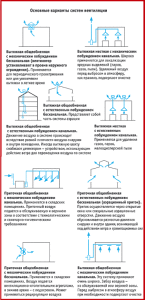
Classification of ventilation systems in the workplace
Industrial ventilation systems and installations can be divided into the following properties:
- Way of movement of air masses: on free and compulsory;
- Nature of action: exhaust or supply;
- Serviced area: local or general exchange;
- Design features: channelless or channel.
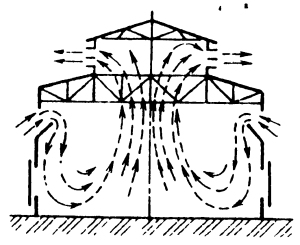
Natural impulse
Ventilation with natural flow movement has the following properties:
- air flow is provided by aeration;
- due to the pressure difference between the workshop and the end of the exhaust channel located above the roof of the structure;
- due to wind pressure.
According to the fundamentals of ventilation of premises of a production type, the natural impulse is realized in factories with powerful heat generation and content of mechanical impurities of not more than 30% of maximum permissible concentration in the workplaces of personnel.
If it must be treated before the air is supplied, a method such as aeration is not suitable.
For the stable movement of air masses due to the pressure difference, the height difference between the points of intake and discharge should be from 3 meters. In ventilation calculations for rooms of this type, the maximum duration of horizontal ventilation ducts is 3 meters. The air in the system moves at a speed not exceeding one meter per second.
The ventilation system of the premises, built according to this principle, is cheap, it is simply mounted and operated. However, its effectiveness is unstable and varies from many external factors.
Mechanical motivation
In ventilation systems of rooms operating on mechanical traction, devices are used that transport air masses to the required distances.
Air is supplied and discharged from the working area in the required volumes under any environmental conditions. If required, the supply air can be filtered, cooled, heated, drained or humidified. Natural ventilation does not allow for optimal air performance. Inflow parameters are similar to atmospheric air.
The most common ventilation systems with mixed motivation.
Supply equipment delivers fresh air to the serviced building. At the same time, exhaust mechanisms draw contaminated, hot or wet fumes.
When calculating the ventilation of rooms, it is important to correctly balance the volume of supplied and discharged used air.
Local ventilation
The fundamental difference between the local air exchange scheme is that the air is supplied pointwise to a specific place (local inflow) and is discharged in the same way (local exhaust).
Here is a list of local fresh air components used in industrial premises:
- air showers (streams of air going to a specific place at high speed);
- areas fenced off from the total area where a special atmosphere is created;
- air curtains.
Due to the high efficiency and cost-effectiveness of local ventilation, it is very widely used in various types of industries.
Exhaust local ventilation is necessary when toxic substances or heat are released pointwise and their distribution must be prevented.
Elements of local exhaust ventilation:
- exhaust umbrellas;
- side hoods;
- covers over the equipment;
- air curtains.
When calculating the ventilation of a room, the following requirements are taken into account:
- local exhaust should not interfere with the process;
- the entire surface of the release of hazards should be covered;
- secretions are discharged in the course of their physical movement (cold ones go down, and hot ones, up according to the laws of physics).
The exhaust air must be cleaned before being released into the environment. Sometimes only one coarse filter is enough, if necessary, a cascade of filters of different degrees of purification is installed. Despite the effectiveness of local systems, they do not always cope with maintaining the necessary microclimate.
General ventilation
General ventilation system is needed when harmful impurities, moisture and heat are distributed throughout the room.
A supply general exchange system reduces the concentration of harmful substances and displaces polluted air masses.
Exhaust ventilation is a system of ducts and a fan. If the length of the ventilation duct is not more than 40 m, an axial fan is installed, otherwise it is centrifugal, as it is more powerful.
Features of calculations of ventilation systems
Calculations and the type of ventilation of the room depend on its purpose. Ventilation of the production room should remove the following types of pollution, emitted during the operation of the equipment and by people:
- hot air;
- explosive and toxic impurities in the air;
- water vapor.
The calculation of ventilation is carried out for each type of pollution present in the air.
The calculation is based on the amount of supply air required for normal operating conditions.
Calculation of ventilation by excess heat:
Q = Qu + (3.6V - cQu (Tz - Tp) / c (T1 - Tp),
WhereQu - the volume of air discharged by local suction in cubic meters \ h,V - the amount of heat generated by equipment and products, in watts,c - heat capacity, taken from reference books, equal to 1.2 kJ,Tz - temperature of the exhaust air discharged from the workplace, in degrees Celsius,Tp - supply air temperature, in degrees Celsius,T1 - temperature of air removed by general exchange ventilation.
Calculation for explosive and toxic industries
When calculating ventilation for plants with explosive or toxic emissions, the task is to dilute them to the maximum permissible level.
Q = Qu + (M - Qu (Km - Kp) / (Ku - Kp),
WhereM - mass of toxic substances released into the air in 1 hour, in mg,Km - the content of toxic substances in the air discharged by local systems, in mg \ cubic meter,Kp - the content of toxic substances in the supply air, mg \ cubic meter,Ku - the content of toxic substances in the air discharged by the general exchange system, mg \ cubic meter.
High Moisture Calculation
Q = Qu + (W - 1.2 (Om - ABOUTp) / (O1 - Op)),
hereW - the amount of moisture entering the workshop air in 1 hour, in mg / h,OM - the amount of steam discharged by the local system, in g \ kg,Or - humidity of supply air, gr \ kg,O1 - the amount of steam in the air discharged by the general exchange system, g / kg.
Calculation of discharge from staff
When calculating the ventilation of some rooms, it is important to consider every gram of moisture that enters the air. Then the calculation is carried out according to the number of employees:
Q = N * m,
hereN - number of employeesm - air consumption per 1 person per hour.
Categories of premises for fire safety
Premises for any purpose: industrial, storage, residential or public are divided into categories for ventilation and fire safety:
- AND - increased danger of explosions, fires. Buildings in which flammable gases and substances or substances are used or emitted, which, in contact with air (water), can catch fire or explode with a flash point of up to 28 degrees;
- B - danger of fire or explosion. Buildings in the atmosphere of which there is dust or steam, flammable and having a flash point above 28 degrees;
- B1 - B4 - danger of fire. Buildings in which liquids, solids or volatile substances are emitted or present that are not readily flammable when in contact with air, water or other substances;
- G - moderate risk of fire. Premises in which substances are present in heated or molten form, an abundance of heat, flame. As well as substances used in the form of fuel or utilized by burning;
- D - low probability of fire. Buildings in which non-flammable substances are present at ambient temperature.
Creating ventilation of warehouse or industrial premises, a unified system is provided in the following cases:
- for residential buildings;
- for office buildings, domestic, public or industrial premises with ventilation category D;
- industrial premises with ventilation category B or A, occupying up to 3 floors;
- industrial with a single category D, G or B;
- warehouse, occupying up to 3 floors, having category B, A or B.
Features of warehouse ventilation
Choosing the ventilation of the warehouse, it is necessary to be guided by SNiP “General sanitary and hygienic requirements for the air of the working area”, “Warehouse buildings”, “Fire safety of buildings and structures”.
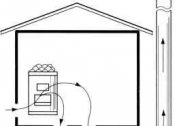
If typical room ventilation with natural draft is not able to create the required microclimate, mechanical motivation is used. For example, aeration is not recommended for ventilating warehouses with food storage. Street air is polluted, and there is often no way to clean it.
In some cases, aeration cannot be organized due to the architecture of the building or its location. Then resort to the mechanical type of ventilation of the warehouse.
If substances emitting harmful or explosive gases (vapors) are stored in the warehouse, mechanical ventilation is arranged.
However, in the vast majority of storages, a general exchange system with natural draft and a single air exchange is organized.
Before calculating the ventilation of the warehouse, it is necessary to determine the nature of the stored materials. So, when calculating air exchange, the type and amount of harmful emissions is taken into account.
Infiltration
As a rule, warehouses are not tight. The process of air exchange between the warehouse and the street is called infiltration. With a large temperature difference, infiltration can be 1.5 to 2 air exchanges. This parameter is certainly taken into account when designing the basics of storage ventilation.
If 1-time air exchange is sufficient for a warehouse, it is only possible to organize exhaust air blowing. The inflow will be replenished by infiltration.
More often in warehouses are installed channel-free systems. It is advisable to use channels with natural draft in small auxiliary buildings with a design air exchange of not more than 1.
During aeration, the air flow is ensured by open vents. If the concentration of impurities in the air is more than a third of the MPC, aeration is not applied.
In the warm season, air is supplied to the warehouse through openings in the walls located at a height of not more than 1.5 meters from the ground. It can be gates, windows, sliding partitions.
In winter, openings for inflows are equipped at an altitude of 3-4 meters from the ground. They must be covered with visors from rain and snow.
The exhaust air is extracted through exhaust shafts or vents. The traction in the system is enhanced by installing a deflector at the outlet of the exhaust shaft. And the draft intensity is regulated by various dampers, gates, shutters.
The height of the head of the exhaust shaft must exceed the height of the roof ridge by 50 cm or more. Otherwise, with strong winds, reverse thrust is observed.
Supply air volume calculation:
Odd = 3600 *S*m*n,
WhereS - window area in sq.m,m - air velocity in m \ sec, is 1 - 1.5 with natural traction,n - the flow coefficient depends on the angle of the window opening: at 90 degrees 0.65, at 45 - 0.44, at 30 degrees - 0.32.
| Distances between centers of exhaust and supply shafts, cm | The volume of air passed 1 square meter window, in thousand m | ||
| Opening angle 90 degrees or fully open | 45 degree opening angle | 30 degree opening angle | |
| 600 | 2,5 | 1,7 | 1,2 |
| 1000 | 4,1 | 2,8 | 2 |
| 1500 | 6,1 | 4,1 | 3,2 |
Table 1. The volume of air penetrating through 1 sq.
Features of ventilation of retail premises
All retail premises can be divided into 2 types:
- Warehouses (large metro-type hypermarkets);
- Zoned shopping complexes (malls such as Mega).
Warehouse stores
In the first case, it is not necessary to supply air to separate rooms. Therefore, the ventilation of a retail space of the first type most often represents a powerful supply and exhaust installation without zoning of climatic indicators.
The standard solution for warehouse stores are roof air conditioners. This is a one-piece equipment that is installed on the roof of the building and is connected to the hall with air ducts. Ducts are distributed under the false ceiling. In addition to ventilation, the rooftop performs the function of heating and conditioning.
Sometimes several rooftops of lower power are installed instead of one large one.
Roof air conditioners are reliable, durable, quiet, and quite economical. The only minus of the use of ventilation of a retail space of this type is the impossibility of zoning air indicators.
Shopping malls
In shopping malls there are areas for various purposes: boutiques, beauty salons, cafes, warehouses. Which need to create a different microclimate. Therefore, for each type of room, a calculation is made depending on the number of visitors, the release of heat, moisture (spas), smoke (smoking rooms).
An additional difficulty is the location of shopping complexes at several levels, as well as the architectural features of each room.
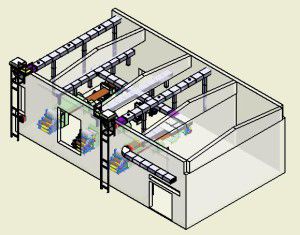
The standard choice for ventilation of commercial premises of this type are central air conditioners. This is a sectional equipment, including sections:
- heating;
- noise reduction;
- fans;
- moisturizing;
- filtering.
The modules are enclosed in a common building, which is located in a special compartment of the building. Since the central air conditioner does not include sources of cold and heat, it must be combined with a chiller-fan coil. This combination of equipment allows you to set individual air parameters for each room, serves buildings of any area. And this type of equipment for ventilation can be used simultaneously to heat the water in the pool and freeze the ice on the ice rink.
Such complex climatic equipment is controlled only automatically through a central console.
Features of cleanroom ventilation
The main task of ventilation in a clean room is to provide such indicators:
- The concentration of dust particles in 1 cubic meter. m of air. To do this, air is driven through absolute filters, maintaining a given purity class. Supply air is cleaned on four-stage filters that capture inclusions up to 0.01 microns;
- Temperature, humidity and air velocity. The microclimate is important not only for the work of personnel, but for the technological process. If the air is too dry, it causes static electricity. If it is too wet, condensation may settle;
- Pressure difference between clean and adjoining rooms. To prevent dust and moisture from entering neighboring rooms into a clean room, a slightly increased pressure is maintained inside. Cleanroom ventilation ensures the predominance of the inflow over the hood;
- The presence of fresh air. People work in the room, so they should be provided with clean air in volumes regulated by sanitary standards.
Creating Clean Zones
Using a directed or laminar air flow, you can create a clean area in the room. Air moving in one direction without turbulence displaces dust particles from the necessary zone. Then they are pulled out by the duct system. Due to the special direction of flow, the particles are removed instantly. The effect is achieved through the use of special laminar air distributors.
As a rule, the basis of ventilation of a clean room is a central air conditioning of a special modification.
It is controlled automatically. And the necessary air parameters are supported with the help of a whole network of sensors and a control unit, also fully automated.
Design and installation of industrial ventilation is a complex multi-stage process. Many companies offer comprehensive services: from design to after-sales service. Such a solution removes from the customer all problems with the microclimate of the enterprise.
Video about automation of cleanroom ventilation control: