The working capacity of an office worker depends on the indoor microclimate. According to medical research, the temperature in the office should not exceed 26 degrees, whereas in practice in buildings with panoramic windows and an abundance of equipment it can go off scale at 30 degrees. In the heat, the reaction of employees is dulled, fatigue increases. Also cold affects the ability to work and causes drowsiness and lethargy. Lack of oxygen and high humidity create unbearable conditions for employees, lowering labor productivity, and hence the profitability of the enterprise.
To maintain the optimal temperature and humidity conditions, an office ventilation system is equipped.
Office ventilation requirements
The ventilation of the office building must meet the following requirements:
- providing an influx of fresh clean air;
- removal or filtration of exhaust air;
- minimum noise level;
- accessibility to management;
- low power consumption;
- small size, the ability to harmoniously fit into the interior.
The load on office climate systems is much higher compared to household ones. It is required to qualitatively remove excess heat and carbon dioxide emitted by technicians and employees, to supply clean and filtered air of a given temperature.
Previously used natural ventilation systems of offices today are not able to provide conditions regulated by sanitary standards. The operation of natural ventilation cannot be controlled; its effectiveness is very dependent on the parameters of the air outside. In winter, this method threatens to cool the room, and in summer drafts.
Widely used in the construction of office buildings, modern hermetically sealed windows and doors, continuous panoramic glazing impede the passage of air from the outside, causing it to stagnate and impair people's well-being.
All office ventilation requirements are specified in SanPiN (Sanitary rules and regulations) 2.2.4.
According to the document, the humidity in the rooms should be:
- at a temperature of 25 degrees - 70%;
- at a temperature of 26 degrees - 65%;
- at a temperature of 27 degrees - 60%.
Recommended Air Temperature 22 - 24 degrees at humidity 40 – 60%.
The following ventilation standards have been developed in offices, taking into account the purpose of the room, in cubic meters per hour for 1 person:
- manager's office - from 50;
- conference room - from 30;
- Reception - an average of 40;
- meeting room - 40;
- offices of employees - 60;
- corridors and lobbies - at least 11;
- toilets - from 75;
- smoking rooms - from 100.
SanPiN ventilation of office premises also regulates the air speed of 0.1 m \ s, regardless of the time of year.
As a rule, ventilation of small office premises is realized with the help of several air handling units. If in the hot season, the office supply ventilation is not able to lower the air temperature below 28 degrees, additional air conditioning is required.
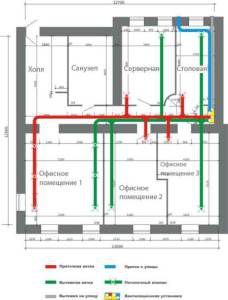
Separate air handling units are needed in conference rooms. Additional exhaust devices - in toilets, smoking rooms, corridors and vestibules, copy rooms. A mechanical extract from office rooms is necessary if the area of each is more than 35 square meters. meters.
If the total area is not more than 100 square meters.meters and 1-2 toilets in it are allowed natural ventilation in the office through the window. Supply and exhaust ventilation is installed in offices of medium and large sizes.
Office ventilation project
The ventilation system of the office building has a number of functions. Therefore, when designing, many factors are taken into account, which are regulated by the SNiP rules for ventilation of office premises No. 2.09.04.87 and 2.04.05.91. The system is assembled from nodes of various cost, functionality and design. The task of designers to choose them correctly.
The following points are agreed with the customer:
- location of the ventilation unit;
- location of ventilation ducts;
- power of the electrical system, the ability to supply water;
- the need and ways of the drainage system;
- access to equipment after installation;
- the possibility of changing the design.
Design of ventilation systems for offices includes:
- calculations of heat influx for each individual room, depending on the architectural features, purpose, taking into account the terms of reference for the project;
- calculation of air exchange;
- axonometric diagram of communications;
- aerodynamic calculation, which allows you to determine the cross-sectional area of the ducts and pressure loss over the network;
- selection of all necessary equipment to complete the ventilation system in the office;
- calculation of heater power in the supply unit;
- preparation of a package of design documents.
Technical equipment is selected simultaneously with the preparation of the project and takes into account all the requirements of the customer. A properly arranged ventilation system of any office increases the productivity of employees by 20% and higher.
Office Ventilation Components
Air ducts
Air delivery to the room and its removal is carried out through the duct system. The duct network contains directly pipes, adapters, splitters, turns and adapters, as well as diffusers and distribution grilles. The diameter of the ducts, the resistance of the entire network, the noise from the ventilation and the power of the installation are closely interconnected. Therefore, for optimal ventilation performance in the design process, it is necessary to balance all indicators. This is a difficult job that only professionals can do right.
Air pressure is calculated taking into account the total length of the air channels, the branching network and the cross-sectional area of the pipe. Fan power increases with a large number of transitions and branches. The speed of air movement in office ventilation systems should be about 4 m \ s.
Ducts are assembled from flexible corrugated pipes or rigid metal or plastic. Flexible pipes are easier to install. But they are more resistant to air movement and buzzing. Therefore, flexible pipes are used in offices of a small area. Sometimes the main channels are made of rigid pipes, and the layering to the cabinets is made of flexible pipes. But large systems are assembled from rigid pipes.
Air intake grilles
They are installed at the place of air intake from the street to the ventilation duct. Lattices protect against insects, rodents, and precipitation from entering the pipe. Made of plastic or metal.
Air valves
They prevent wind blowing when the ventilation system is off. Often, an actuator controlled by automation is connected to the valve. In order to save money, manual drives are used. Then the check spring valve or “butterfly” adjoins the valve in order to block the ventilation duct outputs for the whole winter.
Air filter
Cleans supply air from dust. As a rule, coarse filters are used that trap up to 90% of particles with a size of 10 microns or more. In some cases, it is supplemented with a fine or very fine filter.
Periodically, the filter surface (wire mesh or artificial fibers) needs to be cleaned.The degree of contamination of the filters is determined by pressure sensors.
Heater
It is used to heat street air in winter, are electric or water.
Electric heaters have some advantages compared to water heaters:
- simple automatic control;
- easier to mount;
- does not freeze;
- easy to maintain.
The main minus - high price of electricity.
Water heaters operate on water at a temperature of 70 - 95 degrees. Disadvantages:
- complex automatic control system;
- bulky and complex mixing circuit;
- the mixing circuit requires special care and supervision;
- may freeze.
But with proper operation, it provides significant cost savings compared to an electric heater.
Fans
One of the most important components of the entire ventilation system. The main parameters when choosing: performance, pressure, noise level. There are radial and axial types of fans. For powerful and branched networks, radial fans are preferable. Axial are more productive, but give out weak pressure.
Sound attenuator
Installed after the fan to suppress noise. The main source of noise in the office ventilation system is the fan blades. Silencer filler is usually mineral wool or fiberglass.
Distribution grilles or diffusers
Installed at the exits of the air ducts into the premises. They are in full view, so they must fit into the interior and ensure the spread of air flows in all directions.
Automatic control system
It controls the operation of ventilation equipment. It is usually installed in an electrical panel. It starts the fans, prevents freezing, warns about the need to clean the filters, turns fans and heaters on and off.
Climatic equipment for offices
-
Supply ventilation unit for office. It pumps fresh air from the street directly into the office building. Outflow of air occurs by forcing it into the corridors and vestibules. With an area of more than 40 square meters. meters air is evacuated directly from it. Supply units for office ventilation are used in areas up to 100 square meters. meters;
- Supply and exhaust office ventilation systems. This is the most widely used type of equipment, providing outflow, purification and delivery of air. The kit may include cooling or heating appliances, humidifiers. The equipment is the most diverse, but the supply and exhaust ventilation of the office should be calculated and installed by professionals. Automatic control over functionality reduces power consumption and increases efficiency;
- Office ventilation system. Channel air conditioners with a mixture of air from the street are installed in offices of small and medium size. Combined with supply and exhaust equipment, bringing the temperature of the street air to the required. After which he is served in the room;
- Central air conditioning and ventilation in a large office. In large office buildings, climate controlled chiller-fan coil systems and multi-zone VRF systems are controlled. The latter consist of many indoor units, providing different temperature and humidity in the rooms. Central air conditioners are supply and exhaust ventilation in offices with cooling and heating units. This type of climate system is suitable for large offices that are not divided into separate rooms.
Supply and exhaust ventilation of the office
Channel ventilation of the inflow-blowing system is used for rooms up to 600 square meters. meters, since the productivity of supply and exhaust ventilation of the office is up to 8 thousand cubic meters per hour.
According to the norms of SanPiN ventilation of office premises, 60 cubic meters of air per hour must be supplied per person.
SNiP ventilation of office premises requires air exchange:
- inflow of 3.5 times per hour;
- outflow 2.8 times per hour.
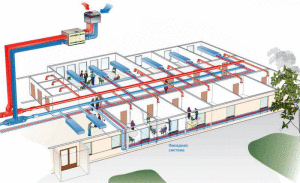
Equipment is usually hidden behind a suspended ceiling in a utility room. At offices, air is distributed by a system of ventilation ducts, the outputs of which are hidden behind diffusers or grilles.
Air inflow from the street with the supply ventilation of the office is carried out at a height of two meters above the soil surface. Air is passed through the cleaning system, if necessary, its temperature decreases or rises (electric or water heater).
Outflow of exhaust air is carried out into the ventilation shaft or through a pipe, the end of which is located 150 cm above the roof.
To reduce energy consumption, the supply air is heated by a recuperator. It is a heat exchanger in which heat from the exhaust air is transferred to fresh. Recuperators for office ventilation use rotary and plate. The former have an efficiency of more than 75%; they work in crackling frosts. But in the process, about 5% of the exhaust air enters the room.
Lamellar recuperators are inexpensive, their efficiency is not more than 65%. But they freeze, it is necessary to provide their heating.
All the necessary equipment for air treatment in the supply and exhaust system is located in one relatively small building. Office ventilation is a combination of several modules.
In order to ensure the necessary temperature in the office space, the supply and exhaust ventilation is supplemented with air conditioning. Depending on the characteristics of the building, these can be several split systems or multisplits.
Office ventilation
The ventilation of a small office building can be provided by duct air conditioning. In addition to cooling and heating the air, duct systems supply a certain amount of fresh air from the street to the halls. To implement this function, the duct air conditioner is equipped with additional air-mixing equipment. That is, the equipment and air conditioning, and ventilates the office in accordance with the standards.
This scheme works like this:
Outside air is supplied to the mixing chamber located in front of the air conditioner, here it is mixed with exhaust air. The mixture is supplied to the air conditioner, cleaned, brought to the required temperature and sent through ventilation channels to the offices. The air from here moves into the mixing chamber and further in a circular cycle.
The air conditioner enclosure is hidden above the false ceiling or in the utility room.
The advantage of the channel scheme of ventilation of office premises in its invisibility. But it eliminates the possibility of varying the temperature in different rooms.
Air handling units combined with office VRF systems
On large areas, the installation of channel equipment is difficult, therefore, large buildings are serviced by supply and exhaust ventilation units for offices in combination with chiller fan coil units and VRF systems.
The power of such equipment can reach 60 thousand cubic meters per hour. Ventilation and climatic equipment is installed on the roof of the building or in separate rooms.
The installation consists of many modules, which are assembled depending on the needs of the enterprise and taking into account the ventilation standards of offices. The kit may include:
- fan chamber;
- recuperator;
- sound absorber;
- mixing chamber;
- block with filters.
Air movement is carried out through a branched duct system. The air temperature in the building is maintained by chiller fan coils or VRF systems.
VRF- is a multi-zone climate system that can maintain the microclimate of an entire building. It is possible to differentiate the temperature in different rooms. In each room, an internal module is mounted that holds the temperature in a given framework.Temperature differences characteristic of domestic air conditioners are absent. Indoor modules can be of any type (floor, cassette, ceiling).
The chiller warms or cools the refrigerant - ethylene glycol. Which is fed to the heat exchanger - fan coil with forced air movement. Fancoils are located directly in office rooms. In order for the coolant to move at a given speed, the system is supplemented by a pumping system. To one ventilation and air conditioning scheme, many cabinets and halls can be connected. And not all at once, but as the need arises.
Central air conditioning for office ventilation
Central air conditioners are industrial climate technology. They are installed according to SNiP and provide ventilation and air conditioning of office premises. In the air conditioner module, the air is brought to the required temperature and humidity parameters. Air recirculation (mixing of used and fresh) is carried out, including partial with a mixture. After processing, air is supplied to the premises through a duct system.
The advantage of central systems in the absence of internal modules. At the same time, the air conditioner itself is a rather bulky structure, requiring a separate room. Ducts are also quite voluminous. In this case, the temperature throughout the building will be maintained at the same level.