Emergency ventilation - the combined design of mechanical devices and elements, in general, representing a general forced ventilation system for the period of emergencies, regardless of the cause of their occurrence.
Emergency ventilation at industrial and office facilities of a public kind is designed to provide acceptable conditions for the evacuation of people for the period of an emergency situation.
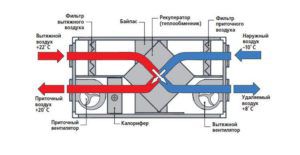
The principle of the ventilation system
The emergency type ventilation system operates using a special control panel in automatic mode. The console connects the operation of the system and the blocking elements: in the event of an accident, the general ventilation systems are instantly blocked, and then shut down.
Elements of an emergency ventilation system respond to:
- the smallest occurrence of smoky formations;
- sources of fire or excessive gas contamination.
Exceeding the permissible values is detected by a high sensitivity sensor. This installation, which sensitively reacts to sources of danger, provides guaranteed regulation and gradual neutralization during the emergency period of any formed substances, smoke, impurities and other things.
As a rule, the ventilation system for emergency neutralization is designed in the form of a chimney, which ensures independent switching on and a constant air exchange process in the respective rooms.
Key Features
In case of emergencies at the time of construction of buildings or at the stage of major repairs, installation of special structures is provided. Such designs are called supply systems, which allow you to quickly clean the room of odors, gas, smoke and other hazardous compounds.
Supply systems provide an uninterrupted supply of clean air (during an accident), evenly distributing the clean flow along the length of all production aisles, rooms, halls and office buildings.
If the accident is characterized by emissions of toxic impurities, chemical compounds with an increased hazard class for life and health and people, then through the operation of such a system, a stream of fresh air flows into all smoky rooms and is redistributed across all areas of the facility.
Reasons for connecting ventilation during an accident
Only a correct and reliable analysis regarding the danger of an emergency will ensure that all production facilities are equipped with an appropriate and productive range hood.
During an emergency, the non-standard nature of the whole process should be considered. During the period of its operation, including the beginning of the system until the moment of completion, the complete elimination, stabilization and balancing of all smoky and gas formations within the premises should be ensured.
Causes of industrial accidents can be caused by such reasons as:
- uncontrolled sources of fire;
- spontaneous ignition of individual elements and devices;
- a single emission of gaseous impurities of a sharp nature;
In such cases, it is necessary to provide not only a safe and planned exhaust system, but also draw up and display its operating mode, a schedule of inspections of the ventilation system for emergency cases.
Calculation of emergency ventilation: methodology
In the case of calculations for the operation of the emergency ventilation system, two methods are available:
Option number 1. In this case, we are talking about unsteady changes in the concentration of harmful substances formed in the room. The calculation condition is the switched off general ventilation systems for the entire period of the accident (climate systems).
The balance of the total mass of harmful substances polluting the premises by volley emissions during the depressurization of production plants, equipment, in the event of a violation of technological processes, in the form of a differential equation, is as follows:
Gpdτ - Vndс = 0
Option number 2. In this case, all changes of a non-stationary type are neutralized. The removal of an increased concentration of harmful toxic substances occurs. The working condition of the hood is working (included) general exchange emergency ventilation systems.
The formula for the mass balance of all harmful substances formed in the perimeter is as follows:
Gbpdτ + LetcWITHetcdτ – LuhWITHuhdτ – Vndc = 0where
Гврdτ - the mass of substances whose release occurred during the accident;
LппПрдτ - the value of all harmful substances accumulated in the premises during the time interval τ, arriving with the flow of the supply air masses;
LuxDhdτ - the mass of harmful substances removed from smoky rooms over a period of time τ using exhaust general exchange designs.
Normative documents of equipment
Emergency ventilation and air curtains are regulated by the document: “SNiP 2.04.05 - 91”, which specifies such standards as the temperature of the air coming in through the operation of air-to-air curtains.
In these situations, you must take:
- no more than 50.S near entrance doors and walkways;
- no more than 70.S near street gates and main external openings.
The estimated temperature of the air flows entering the smoky rooms through doors, gates, open openings should be taken as the value C, but not lower than the values:
- C = 14, if an accident occurred on the territory of production, in the perimeter of the premises during light work;
- C = 12, in the event of emissions within production during medium-load work, for vestibules in public institutions, in office buildings.
- C = 8. Premises of a production type with a heavy workload;
- C = 5. For production facilities with hard work, in the absence of permanent places for employees.
The duration of the emergency combines the time of two time periods:
- tа1 - duration of the initial stage of the accident;
- ta2 - the duration of the emergency phase, during which a complete stop of emissions and injections of harmful toxic substances into the premises is ensured.
The general formula for the duration of the accident with the automatic inclusion of the ventilation system:
ta = ta1 + ta2
Thus, during an emergency, absolutely all system elements must operate automatically and provide the fastest possible neutralization of all emissions regardless of the characteristics of the systems.