To maintain a normal water-ground "microclimate" in the suburban area, you need to install a drainage system. Moreover, it is desirable to make a hidden option. Then groundwater will freely leave the site, thereby ensuring the safety of the foundation of the house, healthy growth of cultivated plants. In order for the communication to work properly, it is important to take care of the correct slope of the drain pipe by 1 meter according to SNiP.
Conditions for creating a drainage system
The need for a groundwater drainage system arises when the water treatment plant in the area in the spring rises to the level of 1.3-1.5 meters. This situation threatens swamping of lands, flooding of basements, basement floors.
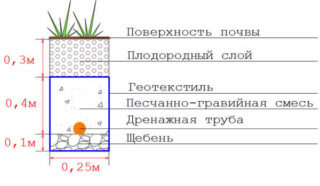
The main elements of the hidden drainage system are perforated tubular drains, which are additionally wrapped with geotextiles. Sand and gravel sprinkles are also important. They play the role of a kind of filter that prevents the ingress of earth into the sleeves of the line.
According to SNiP standards, any drainage circuit must be equipped with inspection wells. This allows you to control the operation of the system in any part of it.
Recommended Grade Levels
In addition to the diameter of the drainage pipes, an important parameter in the design of the system is the level of inclination of the drains. As a rule, these norms are regulated by SNiP with an indication of the minimum acceptable values. It is important to consider the lowest groundwater flow rate along the branches. According to the regulations of an official document, for a smaller cross section of drains, a larger angle of inclination is provided.
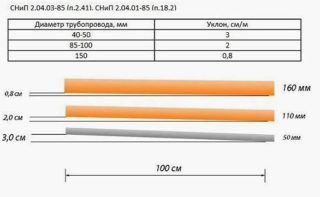
Minimum slopes for drainage pipes of different diameters according to SNiP:
- open (external) trays and ditches of water discharge - 3 mm per mp;
- freestanding gutters - 0.005 mm per mp;
- cobblestone or paved blind area with trays - 3 mm per mp;
- the device of paving stones or crushed stone with gutters of the open type - 4 mm per mp;
- pipes with a cross section of 40-50 mm - 3 cm / mp;
- sleeves with a diameter of 85 mm - 2 cm / mp;
- drains 100 mm - 1-1.5 cm per mp;
- 150 mm - 8 mm on mp;
- 200 mm - 7 mm per meter
Always consider the type of soil on the site. In sandy ones, the level of filling the contour with water and its movement will be faster than in clay ones. Therefore, the slope should be made slightly larger than with denser strata of soils.
What threatens the wrong bias
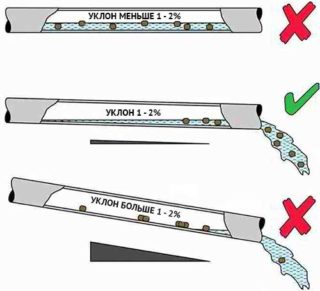
It is important to correctly calculate what inclination angle the drainage pipe should have. If the recommended norms are not followed, emergency situations may occur.
- With a slight slope, a pressureless drainage system will cause water to stagnate in the sleeves. The garbage present in it in the form of small grains of sand will be deposited. Sooner or later, their number will lead to clogging in the pipe. You will have to dig out a portion of the system and carry out repair work.
- With insufficient slope, groundwater will fill the entire drainage gap, but will not be able to leave in the right direction. As a result, the water supply system will remain at the same level, and the installation of a drainage system will be simply meaningless. The site will remain marshy.
- If the recommended slope increases, the water flow rate will be too high. This threatens to rupture the drain with time in any area under the influence of pressure. Either the water will go to the discharge point with high speed, and heavier impurities (grains of sand, clay particles) will settle at the bottom of the circuit. Sooner or later this will lead to blockage.
In case of insufficient slope of the drainage pipes and stagnation of groundwater, permanent washing of the soil will occur. The natural strength of the upper layers of the earth will decrease.
How to calculate the correct angle
In order to install the drainage system on the site and at the same time calculate the optimal angle of inclination, it is necessary to take into account the following parameters:
- Cross section of drains. It directly depends on the type of drained soil. The more loose it is, the larger the diameter of the contour should be.
- Type of drains used: with or without geotextiles. The first option is optimal for loose soils with lots of sand. For coarse-grained soils it is allowed not to use geotextiles.
- Depth of the contour.
- The relief of the site: differences in its heights.
- Groundwater level in the area - it is advisable to conduct preliminary hydrogeological surveys.
- Soil type - information is taken from the table “Classification of soil types.
To correctly determine the slope of the entire highway from the upper point of the first drain to the point of water discharge, you need to do the following:
- From the highest point of the first pipe to the final receiver of groundwater, the total length of the drainage circuit is measured. In total it turns out, for example, 20 m.
- Measure a straight line from the top of the system to the bottom. It turns out, for example, 10 m.
- Both numerical values need to be added: 10 + 20 = 30 m.
- To calculate the differential height between the upper and lower points, a value of 1% of the total amount is taken. In this case, it is 0.3 m (30x1% = 0.3). Thus, the master must lay the drainage system on the site so that the difference between the upper part of the communication and the lower one is 30 cm. This will be considered the correct slope.
Such communication will function smoothly.