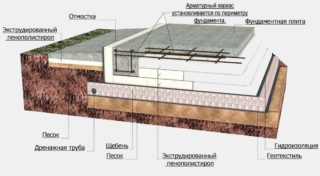
The Swedish insulated plate is a monolithic base of a small deepening for the house. A USP foundation is built on a heat-insulating layer, therefore it does not come into contact with the ground. The slab is built on any soil, the mark of the standing groundwater and the depth of freezing do not matter. Additionally, it becomes possible to conduct communications in the thickness of the base.
The device of the insulated Swedish stove
The complex structure is insulated with thermal insulation with water-repellent characteristics. The top of the monolithic slab is prepared for laying the floor of the first level of the house. Stiffening ribs are arranged under the walls around the perimeter.
The warmed Swedish plate (USP) includes:
- soil drainage system;
- geotextiles;
- sand pillow;
- crushed stone bedding;
- insulation (extruded polystyrene foam);
- concrete slab with reinforcement, heating and communications inside.
Sewerage, water supply are laid in the foundation body, and floor heating is done using water pipes connected to the boiler. Warming up is carried out evenly, so radiators are not required on the ground floor of the building. A warm floor is usually hidden in a screed, but in the case of an economical base, pouring is not needed.
The soil under the house does not freeze in winter, the soil does not swell with the onset of heat or in severe frosts. For concreting, an insulated fixed formwork is used, which additionally saves the internal energy of the room. The findings of communications are calculated accurately and protrude from under the floor in the right places.
A perimeter drainage system is installed in conditions of increased soil moisture. Water drainage is done in marshy areas and in areas with high moisture conditions. The USP plate is on a dry basis, and the effluents enter the general sewage system or accumulate in separate containers.
Swedish designers have calculated the options for the plates depending on the type of soil, the load on the plate, taking into account other factors of influence. Data on the selection of versions for constructing a warmed foundation is collected in technical catalogs with tables and drawings. The regulatory framework with a description has been compiled by German manufacturers of the KNAUF product line. You can use the catalog or entrust the design and calculation of UWB to specialists.
Application area
Insulated structures are universal foundations; different types of buildings are being built on them. Monolithic slabs on the insulation layer work well on unstable soils.
Types of soil for the construction of slab bases with insulation:
- sandy, sandy loamy soils;
- rocky views;
- clay soils, loams;
- water saturated areas;
- wetlands;
- weakly bearing layers, for example, peat bogs;
- permafrost areas.
The type of soil is considered before installation. The vegetative layer of soil is completely removed and is changed by sand and gravel bedding. In areas with a slope of the ground, you need a pit device or a leveling of the soil on the lower part, the work is fixed with a reliable supporting wall. The Swedish foundation will serve as a support for one-story and two-story buildings.
Cost-effective slabs work well under buildings made of materials:
- logs and glued or rounded timber;
- wood lumber, SIP panels;
- billboards (frame construction);
- brick, concrete;
- aerated concrete, foam concrete, cinder block.
Heat losses through the base are reduced with the use of a slab foundation with fixed formwork, usually up to a third of the heat is removed in this way. The USP is a battery that maintains the temperature in the home and heats the floor in the first tier. It is important to insulate with extruded polystyrene foam with a thickness of about 100 - 200 mm and perform the installation of a warm floor.
Advantages and disadvantages
 The USP scheme has enough groundwork to relate to proven systems in the construction of foundations. The top of the slab remains flat after the completion of concrete work and is a good basis for ceramic coating, laminate, linoleum. Convenience is that the floor level in all areas of the house will be on the same level. This is important when decorating and operating housing.
The USP scheme has enough groundwork to relate to proven systems in the construction of foundations. The top of the slab remains flat after the completion of concrete work and is a good basis for ceramic coating, laminate, linoleum. Convenience is that the floor level in all areas of the house will be on the same level. This is important when decorating and operating housing.
Advantages of applying the USP technology
- saving money on heating the house by isolating the foundation from the cold and reducing energy losses;
- there are no cold bridges, so the corners of the house and the basement do not freeze;
- there is no shrinkage of the building during construction on soft soils; there is the possibility of building on any soil;
- reduction of construction time due to an integrated approach to laying communications and finishing work.
Difficulties in choosing UWB or strip foundations arise due to the high price of materials and installation work. The installation of the slab is carried out by qualified personnel, since accuracy is needed in the production of communications, insulation, concrete pouring and reinforcement. The mistakes of the builders cannot be fixed, since a house has already been erected on the foundation. With your own hands you can make such a foundation for a small structure, for example, a workshop, a garage or a bathhouse.
The disadvantage of USP is that it is almost impossible to make a basement or garage under the house. If the thickness of the monolith is chosen incorrectly, over time, the slab is sold and the building settles. Sewerage and water supply in the base body cannot be repaired, and the durability of the insulation layer is difficult to predict in advance.
List of necessary materials and tools
The plate can be arranged independently if you thoroughly study the USP technology, choose tools and modern materials. For the construction, quality components are selected, because the Swedish insulated foundation is the basis of the entire structure and the convenience of operating the house depends on its execution.
Materials for work:
- sand of medium size, sifted;
- crushed stone of fraction 10 - 20;
- geotextiles made of polyester or polypropylene yarns;
- stove insulation polystyrene foam up to 200 mm thick;
- collectors for the drainage system;
- boards or fixed formwork;
- armature for the frame;
- knitting wire or welding machine with consumables;
- sewer pipes, water pipes;
- material for the underfloor heating system.
On the market there is a sale of insulation from manufacturers of brands URSA, TechnoNIKOL, Penopleks, Styreks. Insulators that are pressed by extrusion are suitable, because of this, PSB-S insulation is not used. The material must be reliable, durable, environmentally friendly and not absorb water.
Tool List:
- shovels, wheelbarrows, scrap, buckets;
- building or water level, level;
- drill, grinder, screwdriver, vibrator;
- hacksaw, hook for knitting wire, knife, pliers;
- concrete mixer.
To reinforce stiffeners, a volumetric frame is made of reinforcement with a diameter of 16 mm, and clamps from a rod of 6 - 8 mm are placed after 30 cm. The metal does not protrude beyond the concrete. The plate is reinforced with two steel grids of rods with a diameter of 12 - 16 mm, while the cell size is 15 x 15 cm. Communication pipes are not placed in the stiffeners.
The main stages of the installation of the USP base
 Before starting work, calculations and soil studies are done to select the thickness of the bedding and the slab itself.On each side of the monolith, 2 m is provided to establish a system for draining water from the site.
Before starting work, calculations and soil studies are done to select the thickness of the bedding and the slab itself.On each side of the monolith, 2 m is provided to establish a system for draining water from the site.
USP do it yourself, step-by-step instructions:
- Soil development. The vegetation layer with a thickness of 30 - 40 cm is removed. After mechanical excavation of the soil, the bottom of the pit is cleaned to the mark.
- Geofabric is spreading to prevent mixing of the earth with sand, overlaps are made at the connection of 10 - 15 cm.
- Sand 7 - 15 cm is laid in the pit, crushed stone is poured on it up to 15 - 25 cm. The layers are spilled with water and compacted.
- Mounted drainage system.
- The insulation is laid at the bottom and mounted around the perimeter from the finished factory elements cut to size, or pieces are selected in place. For fixing, angular and rectangular fasteners are used. Wooden props are installed from the outside of the fixed formwork.
- The frame is cooked directly in the pit or prefabricated blocks are made of reinforcement, which are welded separately. They are installed in the formwork in parts and connected.
- Headers are mounted communication pipes, a warm floor is installed. Collectors are laid between the grid rods.
- Concrete is fed in layers and each layer is vibrated by a power tool to rid the mass of air.
The insulation layer is mounted in a checkerboard pattern with a shift of the joints in a vertical and horizontal plane. End plates of insulation are fixed with plastic dowels with wide hats (mushrooms). The seams are filled with foam-adhesive for polystyrene foam. The insulation is laid under the stove in 2 - 3 layers, and under the stiffening ribs is made in one sheet.
Recommendations for the construction of the foundation
During installation, attention is paid to the quality of each layer to obtain a durable and durable structure. Sometimes the thickness of the sand and gravel bedding reaches 600 mm and depends on the bearing capacity of the soil itself.
Communications pipes are attached to the frame elements with plastic clamps. Under the supporting walls and doorways, the collectors are worn in corrugated sleeves or polyethylene pipes. Communications are laid out strictly according to the project in accordance with the height indicated in the drawing. Elements are temporarily fixed with supports until subsequent concreting.
The heating system is checked before concreting. The pipes are filled with energy, the system is pressed to identify areas of leaks. Concrete is kneaded or ordered after all work is done, and the grade of the mixture is indicated in the design. The mass is evenly distributed over the area of the plate with the use of shovels, and with a trowel it is driven into difficult places.
Vibration is necessarily done for each layer to reduce voids in the concrete solution. The mixture is kneaded in such a volume that it can be worked out in a couple of hours. You can not add water to increase ductility, because it will reduce the strength of concrete.
If concreting stops before tomorrow, a step transition is made for the subsequent connection of the layers, a vertical seam is not allowed. It is moistened with water and cement milk before pouring.