A strong, reliable foundation is the key to the durability of any building. For the construction of houses choose the types of foundations that correspond to the size, geometry and weight of the house. The design should correspond to the type of soil on the site, hydrological and climatic conditions.
Building Features

The foundation is the foundation on which the main part of the building is placed - enclosing, bearing and interior walls, bridge supports, overpasses.
Under the capital facilities equip the fundamental foundations that perform the following tasks:
- Distribute the weight of the building evenly over the surface of the site. Prevent more massive parts from sinking stronger than the lungs.
- Create an even horizontal base for the walls.
- Prevent moisture from entering the basement or the technical floor.
- Save some heat from leakage to the ground.
- Prevent displacement on heavy heaving soils.
- Protect buildings from destruction in seismically active areas.
Capital foundations are suitable for bridges and overpasses, advertising structures and tanks with oil products, silos and bunkers.
The influence of soil on the choice of foundation
 Soil features directly affect the types of foundations used in construction. Foundations are natural and artificially created.
Soil features directly affect the types of foundations used in construction. Foundations are natural and artificially created.
Important characteristics of the land:
- mechanical (geological) composition;
- freezing depth;
- maximum and minimum groundwater level;
- seismic situation in the area.
The choice of the type of foundation depends on the combination of soil properties.
Mechanical composition
Builders distinguish between soils:
- Rocky. They contain a minimum of moisture, are resistant to heaving, retain their properties when changing climatic conditions. Suitable for shallow surfaces.
- Sand is easy to develop. Water does not stay, which reduces the cost of waterproofing. The freezing depth in the Midland does not exceed 1 meter, which allows the use of most varieties of foundations.
- Cartilaginous contain sand, clay, earth and gravel in the composition. Resistant to heaving. Suitable for anyone to deepen the bases.
- Loams with various proportions of clay and sand. A higher clay content can contribute to heaving, imposes increased requirements for the preparation of pillows, waterproofing, installation of the blind area.
- Clay requires careful attention to the preparation of the site. Not suitable for shallow laying of foundations, as they freeze by more than 1.5 meters and change shape (hesitate).
- Peat cooked. If necessary, remove peat and bring in new soil. Constructed without preliminary measures, houses can be "occupied" in the soil.
To find out what soil is on the site, it is possible only during geological studies or by the methods of making pits, digging a pit. Even in neighboring areas, the composition and properties may vary.
Freezing depth
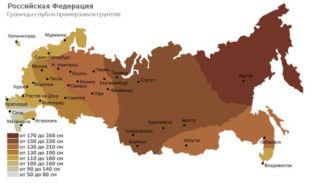 The ability of the soil to heave depends on the characteristics. Moisture permeates the earth during the thaw. When frost returns, it expands, destroys the foundation, and mechanical movements destroy the walls.
The ability of the soil to heave depends on the characteristics. Moisture permeates the earth during the thaw. When frost returns, it expands, destroys the foundation, and mechanical movements destroy the walls.
The bases are made either below the freezing depth, or they are finely buried with the preparation of the place according to the technologies.
Humidity and groundwater
If water rises to the surface of the soil, the house is built without basements, use a slab or shallow foundation.
Moisture impregnates the foundation material and can lead to the rapid destruction of the building structure.
Classification of grounds
Conventionally, all types of bases are divided into bearing, combined, special.
Carrier type perceives and evenly distributes the load.
Combined species are used on heavy, floating soils. The base compensates for horizontal and vertical movements of the earth layers, resists seismic phenomena.
TO special include swinging and floating foundations, as well as bases that distribute part of the load through the side walls and ends. This type includes deep supports, pile piles, pillars, lowering wells, caissons, anchor and slotted design options.
Types of structures
Foundations are:
- tape
- columnar
- pile;
- plate;
- continual.
In some cases, various technologies are combined. The reason may be complex soils, number of storeys, seismic conditions, and stability requirements.
Tape
The foundation passes at the location of the bearing walls and partitions.
There are prefabricated and monolithic reinforced concrete structures.
Deep laying allows you to get basements and ground floors.
Under a shallow foundation, dig a trench up to 80 cm deep. Sand is poured at the bottom and along the side walls of the tape. Pillows prevent the destruction of the base in winter from soil heaving.
In houses with basements, a monolithic tape and walls of separate blocks are combined.
The strip foundation is suitable for the erection of buildings of any height, geometry, mass.
Columnar
Column foundation is used for buildings of small mass. Supports made of wood, concrete, metal are deepened to the level of freezing.
The upper ends of the posts are connected with a grillage.
For small structures, the columns are built of ceramic brick or concrete blocks. The rubble and concrete poles are made by pouring.
Columnar bases are suitable for heaving lands and for places with high groundwater.
Pile
Foundations on piles are installed on soils that are compressible and peat bogs with a depth of more than 4-6 m.
Piles are:
- Hanging - located in the thickness of soft rock, not reaching hard soils. The load is transferred to vertical planes. At the lower end, there is sometimes a screw thread with wide blades, which makes the base more stable.
- Standing piles run through the entire thickness of light soil and rest on a solid foundation.
According to the installation technology, they are driven or stuffed.
In the first embodiment, the finished metal, concrete or wooden pile is hammered with special devices or mechanisms. As it deepens, the soil around the product is compacted, which makes the foundation stable.
For printed models, a pit is made in the ground, which is clogged with concrete mortar.
Pile foundation applications:
- peatlands and subsidence soils;
- quicksand;
- swamps;
- slopes.
At the last stage, the ground part of the piles is leveled and connected by a grillage.
Screw piles up to 1.5 meters long are used for small buildings.
Tiled
The slab foundation is a continuous monolithic reinforced concrete platform, which is equipped under the entire area of the future building.
On stone and granite foundations, the design is impractical and unprofitable.
Technological holes for communication are left at the filling stage. Before starting work, pipes for water supply and sewage are laid.
Continual
Continental foundations are designed for tall, heavy buildings, monuments, bridge supports.
The design has several levels and is similar in shape to a pyramid, combines elements of columnar, tape slab types.
Continental types of substrates are redundant in properties for private construction and are rarely used.
Foundation materials
For the construction of using a variety of materials that are resistant to the effects of climatic factors.
Wood
The foundation of wooden foundations is advisable for the construction of houses from timber or cylindrical logs, frame buildings.
It is advisable to use larch, which does not decay and up to 50 years old serves even in wet soil. Oak is used less often because of the high cost, in addition, the wood of this breed is quickly cracked.
The tree is suitable for columnar (pile) and strip foundations.
The advantages of wooden bases include a small price, quick construction. Repair consists in replacing the crown. Sometimes not the entire beam is replaced, but the insert (insert) of a part of a worn log is made.
The tree withstands deformations and weakly transmits heat.
The disadvantage is the short overhaul due to the rapid destruction of wood under the influence of moisture - high-quality treatment with water-repellent and antifungal impregnations is required. Do not use wood in houses with basements. A small bearing capacity does not allow the construction of massive multi-story buildings and other structures.
A rock
Stone types of foundations used in construction are made from the following materials:
- rubble rock - limestone, calcareous tuff, granite, dolomite;
- ceramic bricks;
- concrete blocks.
The natural boot is divided into several types: ragged (uneven edges), cobblestone (round shape), bedded with two parallel faces and a flat flagstone.
The technology consists in laying individual elements of the foundation with filling the joints with cement-sand mortar.
Tape and columnar bases are built from stone.
The advantages of stone foundations:
- increased strength and bearing capacity;
- environmental friendliness;
- long service life;
- resistance to temperature extremes and high humidity.
The complexity of the erection and the large amount of manual labor, the difficult painstaking adjustment of individual stones to the configuration of the foundation, unsuitability for high-rise buildings are the disadvantages of using the material.
Prefabricated foundations are made of FBS (building blocks). They are made of concrete or expanded clay concrete.
Reinforced concrete
Concrete reinforced with steel and composite reinforcement is called reinforced concrete.
Composite reinforcement is not intended for the manufacture of foundations.
The composition includes sand, cement, gravel and additives that improve physical and mechanical characteristics. These additives include plasticizers and compositions for working at low temperatures.
For small buildings, claydite concrete is allowed. It is important to provide moisture protection for part of the foundation located in the ground. This is achieved by the blind area equipment and waterproofing of the outer walls.
Tape, columnar, slab, clogged types of bases are built from concrete.
Advantages of concrete:
- manufacturability;
- strength, ability to withstand any load;
- the ability to give the base any geometric shape;
- availability on sale of ready-to-use composition of any brand;
- resistance to any climatic conditions;
- resistance to moisture;
- ease of finishing (if necessary).
The disadvantages of reinforced concrete include the need to withstand the period to gain strength, the complexity and difficulties with maintaining proportions in self-manufacturing.
Foam concrete
A new material with improved consumer properties - cellular concrete is used for private homes and public buildings. The maximum height of buildings should not exceed three floors.
Foam concrete is not used for pouring monolithic bases.Prefabricated foundations are erected from finished blocks.
Aerated concrete is divided into several classes according to density. The specific gravity varies from 300 to 1200 kg / m3.
The blocks are dried naturally or autoclaved. For the bases, products made by the second method are selected.
For the construction of the foundation, only structural foam concrete with a density of D1000 – D1200 is suitable.
Material Advantages:
- low thermal conductivity;
- mechanical strength with the right choice of density;
- exact geometry;
- simple processing and cutting at home;
- durability, resistance to the spread of fungus and rot.
The disadvantages are associated with the properties of the material:
- the cellular, porous structure facilitates the penetration of moisture into the block;
- multiple wetting-drying cycles quickly destroy the material;
- the impossibility of erecting multi-story buildings;
- the need for high-quality waterproofing.
The main distribution of cellular concrete blocks received during the construction of houses made of foam concrete. This is convenient when ordering and delivering building materials that are manufactured in one enterprise.
It is better to entrust the calculation of the foundation to specialists if the building has non-standard architectural solutions. Based on the parameters of the soil, the hydrological features of the area, the mass of the building, you can make the foundation yourself. Compliance with the rules of arrangement will ensure the integrity of the building for the entire period of operation.









