Earlier, overhead power lines used exclusively unprotected conductors without an insulating layer. They were less reliable, had a short lifespan and could lead to a short circuit when the line broke, but in general they coped with their work. Now there is a transition to more reliable insulated conductors. Such products include SIP cable. It is presented in various forms, each of which has its own characteristics, advantages and disadvantages. It can be used both on the street and inside houses to create electrical wiring.
SIP varieties
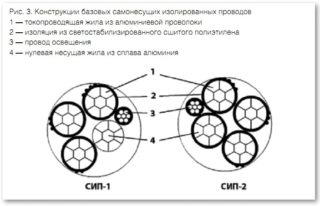
SIP wire can be divided into several different categories depending on the material from which it is made, and design. The differences include conductor diameter, number of cores, insulation material. All types of SIP cables necessarily have an insulating layer. Explanation of the name: C - self-supporting, And - isolated, P-wire.
SIP-1
 Aluminum is used as a material for veins. The cores are coated with an insulating material PET - polyethylene terephthalate in the form of a synthetic film. This coating protects the wire from the negative effects of ultraviolet radiation. The cable has a zero core. It can be isolated (then the letter A appears in the marking - SIP-1A) or without zero insulation (SIP-1).
Aluminum is used as a material for veins. The cores are coated with an insulating material PET - polyethylene terephthalate in the form of a synthetic film. This coating protects the wire from the negative effects of ultraviolet radiation. The cable has a zero core. It can be isolated (then the letter A appears in the marking - SIP-1A) or without zero insulation (SIP-1).
SIP-2
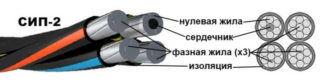 It has a similar SIP-1 design, but another material is used as insulation - polyethylene film. It is used in power lines up to 1000 V and in summer cottages with a network voltage of up to 380 Volts. Suitable for use as main and auxiliary lines. Recommended for use in northern and temperate regions.
It has a similar SIP-1 design, but another material is used as insulation - polyethylene film. It is used in power lines up to 1000 V and in summer cottages with a network voltage of up to 380 Volts. Suitable for use as main and auxiliary lines. Recommended for use in northern and temperate regions.
Also divided into SIP-2 and SIP-2A. Able to withstand temperatures up to 90 ° C. The minimum bending radius is 10 diameters.
SIP-3
This modification has significant differences from the previous two types. Structurally consists of a steel core with a braid of aluminum, silicon and magnesium. PET is used as insulation material. Single core. Applicable in conditions of up to 20 kV. Suitable for work in any climate, except for the Arctic and continental. Operating temperature range from -20 ° С to + 90 ° С.
SIP-4
A conductor is created from several pairs of cores without a neutral wire. On the marking there is a letter H, indicating that an alloy is used as the core material. If there is no sign, you can judge that the cores are made of pure aluminum. Insulation - thermoplastic PVC that protects the wire from ultraviolet rays.
SIP-5
It is similar in design to SIP-4, but PET is used as the insulation material. Due to this, it is possible to increase the maximum permissible temperature by 30%, which expands the climatic zone of application. It is used in power lines with voltages up to 2.5 kilovolts and leads to various buildings, street lighting, branches to cottages. It is recommended for use in the regions of cold and temperate climatic zones.
Conductor marking
CIP cables can be indicated by the classic alphanumeric code and the color of the insulating layer. An example of decryption will be considered on the basis of SIP-1 - 3x50 + 1x70 - 0.6 / TU 16-705.500 - 2007
The first letters indicate that the SIP-1 modification is used without an isolated zero core. There are 3 phase conductors with a cross section of 50 sq. Mm. and one zero core with a cross section of 70 sq. mm. The following indicates the operating voltage, which is 0.6-1 kV.Then, the number of technical conditions, in accordance with which it is fulfilled, and the year of manufacture (2007) are registered. There should also be a manufacturer's label with the name of the plant.
Rules for marking:
- Phase veins are marked with numbers, stripes by inscription or embossing.
- Zero is not indicated.
- Color coding in the form of a strip from 1 mm wide can be used instead of the alphanumeric code or at the ends of the wire.
- For lighting, auxiliary conductors are used, which are marked as B1, B2, B3.
- According to the requirements of GOST, all designations must be applied along the entire length at a distance of 50 cm from each other.
- The standard sizes of signs are a width of more than 2 mm, a height of 5 mm.
- Auxiliary cores may not be labeled.
- The quality of the marking should be at a high level, it should not be erased, respond to ultraviolet rays and change during the entire period of operation.
By marking, you can understand which conductor is used, what properties and operating conditions it has. Similar information is also duplicated in the passport of the conductor.
Cable properties
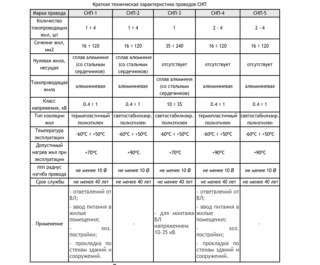 All technical properties of the wire are regulated by GOST R 52373-2005. According to the described standard, SIP can be used on power lines up to 35 kilovolts. The section should be no higher than 240 sq. Mm. In sections of the mains of power lines, the diameter of the main cable must exceed the cross-section of the conductors of the branch conductors.
All technical properties of the wire are regulated by GOST R 52373-2005. According to the described standard, SIP can be used on power lines up to 35 kilovolts. The section should be no higher than 240 sq. Mm. In sections of the mains of power lines, the diameter of the main cable must exceed the cross-section of the conductors of the branch conductors.
SIP cable is also suitable for creating street lighting. The best option is a product with 25 square mm wires.
The main parameters of the conductor according to GOST standard:
- The maximum permissible load. Directly depends on the cross-sectional area of the sip. Determined in kW.
- Operating temperature limits.
- Permissible humidity limits, resistance to water and ultraviolet rays.
- Critical temperature limit.
- Bend radius.
- Warranty (usually 3 years).
- Lifetime. Subject to compliance, is 40 years or more.
There may be differences depending on the cable manufacturer. But they must be within the limits established by GOST.
By name, SIP is a wire, but by its characteristics - a cable.
SIP cable armature
Mounting the wire requires the purchase of additional accessories. They allow you to fix the product on the surface, lengthen it as necessary. All details must be selected specifically for the selected cable in order to perform its work efficiently.
The following equipment is needed for the SIP wire:
- Piercing clamps. They allow you to make the connection of conductors in such a way that removal of insulation from the cable is not required.
- Branch details.
- Anchor hardware. Helps secure the clamps.
A bandage tape is also used. All necessary components must be resistant to rust, ultraviolet radiation and temperature changes.
Mounting Features
SIP is an occasion that is used mainly for conducting electrical lines in the open air. Connection is made on a centralized line.
For independent connection and cable management, it is required to obtain permission from the relevant organizations that are involved in energy supply. It is mandatory to develop a project plan indicating the conductors used. To work, you need professional equipment.
Insertion of the wire is carried out using piercing clamps. After that, you need to connect the tips. Suspension is carried out using cables that are pulled between the posts (for lengths over 25 meters). Holders are made to install the cable on poles.
If you need to stretch the cable along the facade of the building, use anchor fasteners. Their number should correspond to the number of opening cores. The cable can be inserted into the house no more than 1 meter, after which wiring is carried out inside the building.With non-combustible material at home, the cable on the wall is conducted in an open way. This can be done in a corrugated pipe or plastic box.
For air laying, the SIP 2x16, 4x16 brand is used. The first is also used to branch lines in the room and connect to machines and meters.
Advantages and disadvantages
The positive points include:
- No need to install powerful insulators.
- Good current performance.
- Safety for professionals conducting its maintenance.
- Small line width.
- Great ultimate power.
- Long service life.
- Performance in all weather conditions.
- Resistance to corrosion.
- The absence of harmful components in the composition, which guarantees environmental safety for humans and animals.
- Cable overlapping does not affect performance.
- Easy styling, easy to connect.
Cons of the power cable:
- Great weight 1 meter. Frequent installation of supports is required.
- Improved insulation is required for use on an industrial scale.
Despite its shortcomings, the cable is actively used for laying power lines. The calculation of the required length and cross section depends on the connected load.