Water supply is the process of providing hot and cold water to the population, production facilities, agriculture and fire extinguishing installations. If the set of organizational and technical measures for water supply is organized correctly, consumers receive quality water on time and in the required volume, and the ecosystem is not disturbed.
Application area
Water goes to different needs, which are reduced to three parameters:
- for household and drinking consumption;
- for the operation of industrial facilities;
- to extinguish fires.
Such classification as intended applies to all water supply systems. The fire network is additionally equipped with special equipment and hydrants. Usually they make it a dead end, so that the highway can be combined with household and industrial supplies.
Drinking water supply is not compatible with facilities that transport technical water.
According to renewable sources, water supply networks are divided into circulating and single use. The classification of water supply also involves the division into cold water supply and domestic hot water systems.
Current requirements
The quality of drinking water is regulated by SanPiN 2.1.4.1074-01. The main requirement of sanitary standards - water should not be dangerous in the epidemiological and radiation terms. It should be harmless in chemical composition and have pleasant organoleptic characteristics. The quality of the aquatic environment must comply with hygiene standards before being supplied to the distributors and at the water distribution points of the water supply network.
With regard to technical standards, the SNiP and TKP impose the following requirements on aquifers:
- the supply of specified volumes of fluid to the points of water consumption under the necessary pressure;
- high level of reliability and uninterrupted water supply;
- accessibility of utilities for water consumers;
- cost-effectiveness of water supply systems projects, which implies a minimum of costs for the arrangement and operation.
The fulfillment of the requirements is achieved by a competent selection of the configuration of the water supply system and pipe material, as well as the correct determination of the technological and economic characteristics of all the details of the pipeline.
Water sources
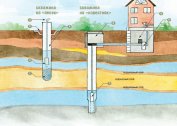
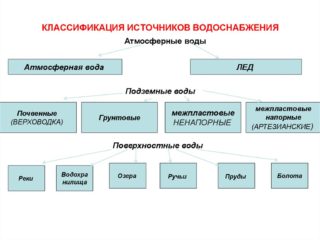 Sources can be superficial or deep. The former include lakes, rivers, ponds, reservoirs, and the latter include wells and wells.
Sources can be superficial or deep. The former include lakes, rivers, ponds, reservoirs, and the latter include wells and wells.
Requirements for water supply sources:
- obtaining the required volumes of water, taking into account the increase in possible water consumption;
- uninterrupted provision of the population;
- achieving maximum quality by simple and inexpensive cleaning;
- low-cost water supply;
- minimal impact on the ecosystem.
They are responsible for selecting a source, because it determines the nature of the system, which determines the costs of its installation and operation.
The device of water supply systems
 The central water supply system is used to mass supply consumers from a single grid. It is used in cities and urban settlements. However, it is possible to connect houses in the countryside, but this rarely happens.
The central water supply system is used to mass supply consumers from a single grid. It is used in cities and urban settlements. However, it is possible to connect houses in the countryside, but this rarely happens.
Centralized systems, as a rule, are executed in the form of ring networks, supplied with water from two or more water towers. This allows you to ensure the provision of all water intake points in case of emergency or to carry out repairs on a separate section of the water supply line.
Facilities for the purification, intake and lifting of water are supplied to consumers in their area of operation according to an agreed schedule in advance. If it is impossible to connect to the citywide pipeline, there is a need to equip an autonomous water supply network of a private house.
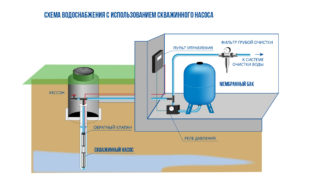
The creation scheme looks like this:
- A well or a well is equipped with a submersible pump; a water main is connected to it.
- The pipeline is laid and carried into the house.
- The water supply network is connected to the filtering treatment element, the automation unit and the accumulator.
From this system, the water supply system distributes clean water among consumers.
In places with regular power surges in the electric network, the arrangement of water supply is carried out using a storage tank. The principle of operation of a decentralized system of this type is as follows:
- In the elevated part of the structure, for example, in the attic, a storage tank is installed, equipped with a float valve.
- The water supply is connected to a submersible pumping device, which is placed in the well or well.
- A branch from the source leads into the building.
- The home line is brought down and connected to the bottom of the tank to store moisture.
- By means of pumping equipment, liquid is injected into the container. When it is completely filled, the pump is automatically turned off.
- When the water drops to the lowest level, the valve is triggered and the pump device starts working again.
Non-centralized types of water supply are suitable for private houses with a small number of consumers. They are winter and summer. In the first case, the installation of the water supply is carried out thoroughly in houses with permanent residence. The second option is suitable for seasonal work: automation of garden watering, water supply to the shower room, country house, bathhouse. The installation cost here is much less.
Turnkey capital plumbing costs at least 85,000 rubles - perhaps for a summer residence it is worth stopping at the summer option. Realistically equip it ten times cheaper.
Types of water supply
 Water networks are divided into external and internal. The first are necessary for the delivery of water from sources or storages to the user. They are laid above the surface of the earth or buried in the ground. The surface mounting method is inexpensive and quick. The pipeline is fixed on elevated supports and perform insulation. If the laying plan provides for a trunk intersection, the water supply is installed in a closed way - underground in tunnels or trenches.
Water networks are divided into external and internal. The first are necessary for the delivery of water from sources or storages to the user. They are laid above the surface of the earth or buried in the ground. The surface mounting method is inexpensive and quick. The pipeline is fixed on elevated supports and perform insulation. If the laying plan provides for a trunk intersection, the water supply is installed in a closed way - underground in tunnels or trenches.
The external system is assembled from devices that are responsible for the purification, storage of water and pumping equipment. Filtration is performed not only upon suction, but also in the outermost water main.
If the water supply branches are carried out in an area with large relief differences, the device of a single network is irrational. When draining the water from the highest point on a low section, a strong pressure occurs, which can damage the communication facilities. In this case, a zone pipeline is equipped. The number of zones and methods of installing pumping equipment are determined depending on the terrain and the pressure of the water flow in each section.
The internal water supply system consists of a main line and branches departing from it, which pass inside the building and are connected to water intake points. To trace it, you need to carefully study the floor plans of the structure, basement or technical underground.
Since the external water supply can have different pressure, the water supply network inside the building is equipped according to two schemes:
| Network device | Water supply | Mandatory Elements | Operational Features |
| Without booster pumps. | Due to pressure in the external line. | Input, water meter, pipes, riser and eyeliner. | In most country houses and low urban buildings. |
| With pumps operating periodically or continuously. | Due to the action of pressure equipment. | In addition to the above - booster pump or pressure station. | In buildings more than 50 m high, hotels, holiday homes and industrial facilities. |
The option with boosting equipment is used when the necessary pressure is not available in the external line for moving the liquid, or if it is required to transfer it to elevated and remote water intake points.
Drainage Schemes
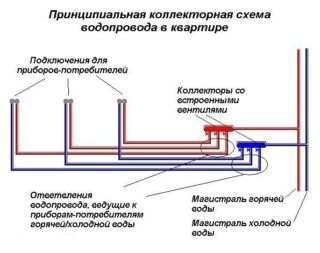 Water distribution according to the method of execution can be:
Water distribution according to the method of execution can be:
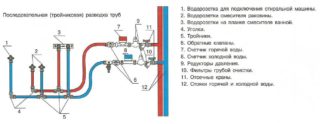
- sequential or tee;
- fan or collector;
- mixed - when combining the first two types in one room.
Each water supply scheme has advantages and disadvantages. In the first case, the advantage is ease of installation and profitability, and the minus is the dependence on the pressure of the water when it is distributed to consumers. The second type provides uniform pressure in all branch pipes. Each conclusion can independently overlap without disrupting the work of other consumers. The downside is the expense of funds for building materials and the time spent on installation. The best option is the third type of distribution of trunk branches.
 When organizing a water supply system, the compliance with GOST of all building materials, especially pipe segments and fittings, must be taken into account. Particular attention is paid to valves. It is placed on eyeliners for faucets, a toilet bowl, flushing cisterns and wash basins. For the proper functioning of the network, a plunger should also be installed - a device for bleeding air bubbles. It is recommended that retrofitting the network bypass - an emergency pipeline for emergency situations.
When organizing a water supply system, the compliance with GOST of all building materials, especially pipe segments and fittings, must be taken into account. Particular attention is paid to valves. It is placed on eyeliners for faucets, a toilet bowl, flushing cisterns and wash basins. For the proper functioning of the network, a plunger should also be installed - a device for bleeding air bubbles. It is recommended that retrofitting the network bypass - an emergency pipeline for emergency situations.
Water supply is a complex multifunctional process. For all systems and devices to work smoothly, you need to responsibly approach the design work, choose high-quality building materials and clearly observe the technology for installing highways.