In order for the car to be in good condition, it is necessary to ensure not only proper operation, but also its appropriate storage. This is especially true in climatic zones of high humidity and zones of subzero temperatures in winter. High humidity, aggressive reagents used against icing the road surface, are the main cause of corrosion of metal parts of the car.
Naturally, storing a car outdoors is not the best way to keep a car. Therefore, most motorists build garages. Garages are of two types: heated and unheated. In those garages where there is the possibility of obtaining cheap heat, they perform heating. If this is not possible, build a "cold" garage.
Why ventilation is needed
 After a trip in the rain or in winter during snowfalls, the car brings a lot of moisture and snow to the garage, which increases the humidity in the room. When the engine starts, a large amount of harmful and aggressive substances are thrown into the air along with exhaust gases. Such a “cocktail” immediately begins its destructive work. In order to exclude these factors, the supply and exhaust ventilation is performed. Ventilation provides air exchange in the garage room, the influx of external air, removes water vapor and toxic fumes, exhaust gases.
After a trip in the rain or in winter during snowfalls, the car brings a lot of moisture and snow to the garage, which increases the humidity in the room. When the engine starts, a large amount of harmful and aggressive substances are thrown into the air along with exhaust gases. Such a “cocktail” immediately begins its destructive work. In order to exclude these factors, the supply and exhaust ventilation is performed. Ventilation provides air exchange in the garage room, the influx of external air, removes water vapor and toxic fumes, exhaust gases.
Possible system options
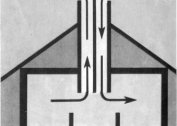
In most cases, the following ventilation systems are used: natural, forced, combined (mixed). The simplest is the natural ventilation system. The draft is created due to the difference in the heights of the supply and exhaust openings; it works like an ordinary stove. A continuous airflow is generated from the air inlet to the air outlet. The creation of such a system requires minimal costs.
The most effective system is forced ventilation. It provides incentive devices for air exchange - fans. The system effectively provides a calculated air exchange rate, which depends on the performance of the supply and exhaust fans. The forced system, as a rule, has a duct system that provides air intake from the most dangerous areas of the room. Supply fans take in the outside air, which passes through the air heater in winter and heats up. Since this system has equipment, air ducts, it requires large, compared with other ventilation systems, costs.
The combined system provides a natural flow of air into the room and its forced removal. Fans and ducts provide exhaust only. The combined system is the most common type of garage ventilation system.
Natural ventilation system
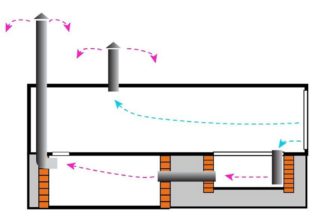 The air intake hole is made as close as possible to the planning level of the earth, focusing on the "wind rose". The hole may be rectangular or circular. The inlet is equipped with a louvre grille, which allows you to adjust the flow of air into the room. From two pipe sections and a branch, a supply pipe can be made, which is equipped with an umbrella to protect against rainfall. One or more exhaust openings are made in the ceiling and roof. The upper section of the exhaust pipes is discharged above the roof ridge. Pipes are protected from rainfall by umbrellas. The most effective measure is the installation of deflectors.The natural ventilation system works efficiently if the ratio of the areas of the inlet and outlet openings is observed. To ensure normal air exchange, an exhaust opening of 1.8 cm2 must be provided. per cubic meter of ventilated volume. The area of the air inlet, per one cubic meter of volume, is assumed to be 5.4 cm square. It is very simple to determine the area of the inlet and outlet openings. For example, for a garage with a volume of 100 m3: an exhaust opening of 1.8x100 = 180 cm2, a supply opening = 5.4x100 = 540 cm2.
The air intake hole is made as close as possible to the planning level of the earth, focusing on the "wind rose". The hole may be rectangular or circular. The inlet is equipped with a louvre grille, which allows you to adjust the flow of air into the room. From two pipe sections and a branch, a supply pipe can be made, which is equipped with an umbrella to protect against rainfall. One or more exhaust openings are made in the ceiling and roof. The upper section of the exhaust pipes is discharged above the roof ridge. Pipes are protected from rainfall by umbrellas. The most effective measure is the installation of deflectors.The natural ventilation system works efficiently if the ratio of the areas of the inlet and outlet openings is observed. To ensure normal air exchange, an exhaust opening of 1.8 cm2 must be provided. per cubic meter of ventilated volume. The area of the air inlet, per one cubic meter of volume, is assumed to be 5.4 cm square. It is very simple to determine the area of the inlet and outlet openings. For example, for a garage with a volume of 100 m3: an exhaust opening of 1.8x100 = 180 cm2, a supply opening = 5.4x100 = 540 cm2.
Combined ventilation system
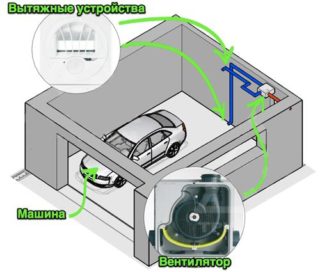 The air inlet for the combined ventilation system is calculated in the same way as for natural ventilation. The hood is forced, for which they install an exhaust fan. As a rule, such a system is switched on periodically, especially in winter. If it works continuously, the room will be very cold due to the constant increased influx of cold outside air.
The air inlet for the combined ventilation system is calculated in the same way as for natural ventilation. The hood is forced, for which they install an exhaust fan. As a rule, such a system is switched on periodically, especially in winter. If it works continuously, the room will be very cold due to the constant increased influx of cold outside air.
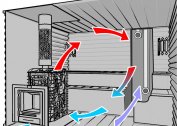
Mechanical (forced) ventilation
Compulsory ventilation systems have fans for supply and exhaust. Fresh air passes the filter for cleaning from mechanical impurities and is heated in winter by an electric air heater or air heater connected to the heating system. Forced ventilation systems are used in garages with large volumes of premises, as well as in heated garages. The ventilation system justifies its creation by extending the life of the car and providing safe comfortable conditions for humans.