The standards for ventilation of chemical laboratories are quite stringent. This is explained by the fact that they work with reagents that cause toxic, explosive emissions, smoke.
Laboratory Ventilation Design Rules
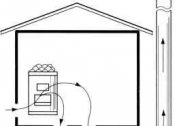
The ventilation of chemical laboratories is equipped so that the products released during the reactions are completely drawn out of the room. These toxic components must be blown out of the room in such a way that they disperse in the atmosphere without entering the windows or air ducts.
When designing laboratory ventilation, it is necessary to provide lower pressure in ventilation ducts compared to other rooms. This measure is taken to block toxic substances directly in the ventilation system.
In the laboratory, it is necessary to provide heating or cooling, as well as humidification. Calculations of supply and exhaust ventilation in the laboratory are similar to calculations for industrial workshops with light types of work. It is important to provide access to system management directly from the laboratory.
Laboratory ventilation specifications
Laboratory ventilation design is carried out in accordance with existing standards and requirements. Opening indoor windows and windows should be equipped in the room. If there are a number of laboratories in one building, all of them can be connected to one ventilation system.
A sufficiently powerful blow provides a guarantee of quick evacuation of toxic or explosive substances to the outside and their non-entry into the ventilation ducts of other rooms.
Exhaust power must be stronger than the supply. This ensures a reduced pressure in the system.
Only forced supply and exhaust ventilation of laboratories is installed.
The main requirements for the projects:
- Air exchange should be carried out at a speed of 4 to 8 liters per hour;
- There must be at least three meters between the air intake grille and the intake grille;
- The exhaust system of the laboratory is not connected to the emergency conclusions of the fire alarm;
- If the laboratory is located in a multi-story building, air blowing should be located one meter or higher than the height of the upper floor;
- Ducts for the outflow of air are mounted from stainless steel or from a neutral material that does not oxidize under the influence of aggressive exhausts;
- The efficiency of the exhaust system is monitored using special sensors installed in the laboratory.