Before installing heating equipment in a private house, first of all, it will be necessary to allocate a separate room for it and organize an efficient exhaust in the boiler room. High-quality ventilation for a gas boiler guarantees the removal of combustion residues from the room and the maintenance of normal climatic conditions in it. When arranging it, the requirements of regulatory documents (SNiP) are also taken into account, according to which special organizations should deal with the development of the project and its implementation. If the user decides to do this with his own hands, he will need to coordinate the issue with the local gas services.
The importance of ventilation in a boiler room
The ventilation in the boiler room in a private house, which meets the requirements of the standards, performs the following important functions:
- provides the flow of oxygen into the room and creates normal conditions for the combustion of gas or solid fuel;
- guarantees the safety of operation of boiler equipment;
- the remains of carbon monoxide are completely removed from the room.
With a deficiency of oxygen, any fuel does not burn completely, and also produces less heat. This reduces the efficiency of the heating system. Other consequences of a lack of fresh air include:
- without ventilation, more fuel is consumed in the boiler room to maintain a comfortable temperature;
- the process of equipment wear is accelerated;
- a lot of burning accumulates in the chimney.
Ventilation, equipped in accordance with the requirements of the MCH 2.02-01-1997 of the year “Fire safety of buildings and structures”, provides the following advantages:
- the likelihood of a fire or gas explosion is reduced;
- excludes the possibility of carbon monoxide poisoning;
- the normal operation of the boiler without failures and failure of individual nodes is guaranteed;
- equipment loads are reduced, and fuel is also saved.
It is important to constantly monitor the tightness of the joints in the gas main and chimney, in violation of which gas will begin to accumulate in the room.
Mandatory Requirements
The requirements for a room equipped with ventilation for a gas boiler in a private house, primarily relate to the location. According to current standards, it is allowed to equip it in the following rooms:
- separate building or extension;
- a room inside the house;
- the kitchen of the building with a boiler power of not more than 30 kW;
- attic space.
In private houses, the furnace unit, as a rule, is arranged either in a room specially designated for this purpose on the ground floor, or in the neighborhood of a garage.
In accordance with the main provisions of SNiP 42-02-2002, the following requirements are imposed on such boiler rooms:
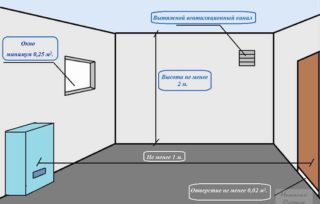
- when placing the equipment in a separate room, its total volume cannot be less than 7.5 m³, and the area - 6 m² with a ceiling height of 2.5 meters;
- a special room is reserved for boilers with a capacity of more than 30 kW, with a lower rate they can be placed in the kitchen;
- the kitchen area must be at least 15 m²;
- in the boiler room d. a separate exit is provided.
When determining the size of the openings for fresh air supply, it is assumed that, in accordance with SNiP, the cross-sectional area of the ventilation duct connected to the street is selected at the rate of 8 cm² for every 1 kW of power. If the boiler room is connected to a neighboring room, and the supply air comes from it, this indicator is selected equal to 30 cm² per 1 kW.
Ventilation options
According to the method of organizing air exchange, known ventilation systems are either working by the principle of natural influx or forced. The first method relates to relatively simple options, however, the ventilation efficiency of the room in this case is markedly reduced. However, because of its simplicity, these systems are widely used in private households and apartment buildings.
Natural ventilation
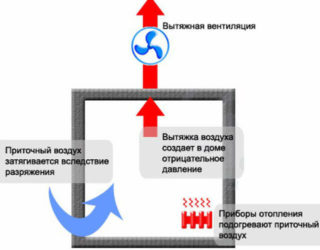
The principle of operation of the natural inflow system is based on the following natural laws:
- layers of warm air always rush up;
- over time, they move towards lower pressure;
- Earth’s density is always higher than at altitude.
For the organization of natural air exchange, it is enough to provide a certain pressure difference in the room. This can be done in several ways, the choice of which depends on the specific conditions and preferences of the owner:
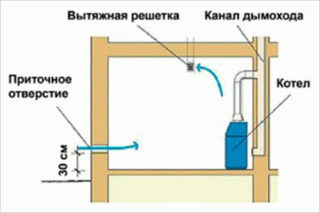
- a small hole is made between the street and the room, which is the point of influx of external air;
- an exhaust pipe is drawn from the room to the roof, the outlet of which is higher than the inflow point - at its end the pressure will be lower.
As a result, the air masses will move from the inflow site from the street towards the outlet of the exhaust pipe.
The distance between the sampling point and the end of the exhaust duct is selected to the maximum possible. This ensures high-quality ventilation of the room, as air flows cover the entire room. Particular attention is paid to ensuring that no closed doors are located between these two points. Varieties of this method of air exchange are exhaust or supply ventilation systems, dispensing without forced exposure.
Forced air exchange
If the natural circulation is not enough for a good ventilation of the boiler room, forced ventilation will be required. It is equipped through the use of special equipment, through which the forced movement of air masses is organized. Usually these are duct fans of various capacities installed in the following places:
- on the outside of the house;
- directly above the boiler itself in the form of a hood;
- inside the channel of the supply and exhaust system.
In the latter case, according to current standards, cleaning filters, water heaters and noise absorbers are installed in the same air channels.
A set of equipment for forced ventilation guarantees high-quality cleaning and dosing of air masses, ensuring their constant updating.
How to make a hood
Before equipping the hood in your home, it is important to correctly determine the necessary equipment (including the type of boiler), the materials used and the type of branch ducts. You should start with a set of equipment, selected taking into account the following factors:
- area of the future boiler room;
- safe distance to flammable objects;
- type of premises;
- estimated costs.
It is also important to determine the type of boiler selected for heating a private home. The best option for this case are electric, gas or solid fuel (pellet) units. In case of frequent power outages, it is recommended to install combined boilers using several types of fuel.
An average power gas unit was chosen as an example, which is explained by the comparative cheapness of the energy carrier used in them and the efficiency of the heating method itself. The operating temperature in the combustion chamber of such a sample is significantly lower than in other models.
Materials for hoods
When choosing a material for the arrangement of the hoods, they proceed from the capabilities and specific conditions of the work. Most often for these purposes are selected:
- brick;
- ceramics;
- metal.
Brick is usually used to make hoods in solid fuel boilers. Despite the fact that it is quite difficult to clean, the service life of units with such an extract is quite long. This material is not suitable for gas units, because condensate will accumulate in the pipe at low temperatures of fuel combustion.
Ceramics are much better suited for gas - can withstand temperatures up to 650 ° C. But in this case, it is necessary to provide protection against soot fire in the chimney, having foreseen the condensate drain channel. As an option - insulation of the output channels with mineral wool.
Steel pipe is a good choice for solid fuel and gas heating systems. At relatively high temperatures with solid pellets, an extract from heat-resistant metal with thicker walls (up to 1 mm) is selected, and when using gas, this indicator is taken 0.6 mm.
Fan duct type selection
 Next, you should choose a suitable outlet channel with a fan for the given conditions, which guarantees the required performance. This indicator is determined by the simplest calculation according to a formula that takes into account the volume of the boiler room (even if it is 10 m³) and the need for three-fold air renewal in it during the day. Multiplying these two numbers, you get 30 m³ / h - this is the minimum capacity of the required fan.
Next, you should choose a suitable outlet channel with a fan for the given conditions, which guarantees the required performance. This indicator is determined by the simplest calculation according to a formula that takes into account the volume of the boiler room (even if it is 10 m³) and the need for three-fold air renewal in it during the day. Multiplying these two numbers, you get 30 m³ / h - this is the minimum capacity of the required fan.
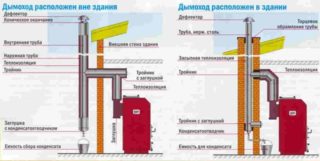
Coaxial chimneys have two different designs: horizontal and vertical. The former are traditionally mounted along the walls, and the latter is laid in any acceptable place with the output through the ceiling to the attic and roof.
When choosing a vertical chimney, you should be prepared for the fact that the costs will increase, since it has a large length and is more difficult to install. It will also require a separate capacitor bank. The disadvantages of horizontal design include the risk of freezing of condensate in the outward part. To solve this problem without high costs, it is enough to insulate it with mineral wool or similar heat-insulating material - with not very severe frosts this partially helps. To prevent ice formation, a trellised head is mounted at the end of the pipe.
For proper installation of a horizontal chimney, it is important to adhere to the following recommendations:
- the output of the pipe is done approximately at a height of 2 meters from the ground;
- the distance from the output channel to the window located above it is at least 1 meter;
- when laying a pipe at an angle of 3-12 degrees, it is not necessary to make a condensate collector;
- it is forbidden to take the highway to the next room;
- the distance from the exit point of the chimney to a nearby gas pipe should be 0.2 meters or more.
The classic equipment of the horizontal outlet includes the pipe itself, adapters of various types, as well as a set of decorative pads and crimp rings with fixing bolts.
Ventilation calculation
 When designing ventilation systems, it is important to consider that wall-mounted gas boilers of limited power (up to 30 kW) are calculated according to a formula slightly different from the standard. This is due to the fact that the requirements for them take into account the size of the heated room. As an example, consider the calculation of natural ventilation for a 3 by 5 room with a height of 3 meters.
When designing ventilation systems, it is important to consider that wall-mounted gas boilers of limited power (up to 30 kW) are calculated according to a formula slightly different from the standard. This is due to the fact that the requirements for them take into account the size of the heated room. As an example, consider the calculation of natural ventilation for a 3 by 5 room with a height of 3 meters.
To obtain the necessary parameters of the supply system at a given power, the following calculations will be required sequentially:
- The volume of the room is determined (in this case it will be 45 m3).
- To determine the highest point of the chimney exhaust, proceed from the fact that it is supposed to be located a quarter above the ceiling of the room (at a height of 3.75 meters).
- It is taken as an indicator or coefficient of air exchange efficiency.
- Next is the volume of air circulating through it: the found coefficient is multiplied by the area of the room.
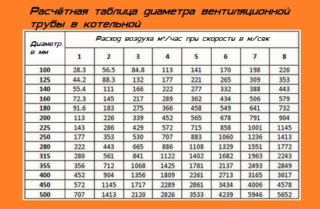
For the case under consideration, the obtained value is 168.75 m3.Taking it as the basis of calculation, on the Internet there is a table according to which the desired duct diameter is determined. In this situation, it is 225 mm.
In heating systems operating entirely on gas, a scheme or ratio is used in which for every 10 kW of power there is 0.01m3 of supply air per second. With the stated indicator of 30 kW from ventilation, a productivity of about 0.03 m3 / s with a small margin will be required. After that, from the table given in SNiP, the diameter of the hood is at least 130 mm. If this indicator does not provide normal air exchange, a forced air supply system is equipped in the room.
Making reliable and efficient ventilation in a private house is not at all as simple as it seems at first glance. It will require the help of specialists involved in the design of ventilation systems and well versed in these issues.