The organization of the heat supply system in non-residential buildings and premises can be very different from that for residential buildings. The difference lies in the required parameters and, therefore, in the choice of air heating method and equipment. How to make heating non-residential premises: methods, calculations, tariffs are mandatory for analysis.
Rules for organizing heating of non-residential premises
First of all, it is necessary to determine the optimal characteristics of the future heat supply scheme. Heating large rooms requires significant costs both for the purchase of equipment and for maintenance after installation.
First you need to conduct an initial analysis of the characteristics of the building. The results obtained are verified with the calculated parameters. Based on these values, heating of non-residential premises is knocked out. For the correct implementation of this design phase, the following is required:
- Purpose of the room. Based on this, the thermal mode of operation of the heating is selected, as well as the schedule for its functioning - daily, weekly or monthly;
- Dimensional characteristics - area and volume. In most cases, storage space heating should be designed to maintain the desired temperature level in relatively large buildings;
- Available energy - gas line, electrical network with the required power parameters or cheap fuel. The latter includes firewood, coal or diesel fuel.
Based on these data, heating methods are selected. It is from the analysis of possible options for heat supply that any project of an administrative or industrial building should be read.
During the preliminary assessment of the house or premises, it is necessary to take into account its heat loss. If necessary, install an additional layer of thermal insulation.
The choice of heat supply for buildings
It must be remembered that the heating of livestock buildings is different from a similar heating system of a commercial or industrial building.
Currently, there are many methods to ensure that indoor air is heated to the desired level. For this, various equipment and accessories for it are used. The difference lies in the schemes and methods for ensuring a normal temperature level.
Water heating of non-residential buildings
Among all the methods of heating the premises, this is one of the most common. The heat supply scheme consists of a heat source (boiler), pipelines through which the heated coolant passes, as well as radiators, batteries and registers.
The heating of the commercial premises made in this way can be easily adapted to various types of energy carrier - gas, solid or diesel fuel. To do this, you only need to replace or upgrade the boiler. In this case, you do not need to change the complete set of the rest of the system.
However, along with this, it is necessary to take into account the features of the operation of heating large rooms of this type. It consists in high maintenance costs, since it is necessary to constantly maintain a comfortable temperature in a significant amount. In addition, when organizing heating of non-residential premises, the following factors should be taken into account:
- Possible coolant effect negative temperatures in the winter. This can lead to freezing and damage to the pipeline;
- System inertia. The air heating time is directly dependent on the volume of the room;
- Possible heat distribution problems. The air temperature will be higher for heating appliances.
This method is applicable for heating livestock buildings if the level of heating in them must be constant. In all other cases, it is best to consider other heat supply options.
For autonomous water heating of warehouses, it is necessary to make the correct arrangement of the boiler room. Her work should not interfere with the main production process.
Air heating of buildings
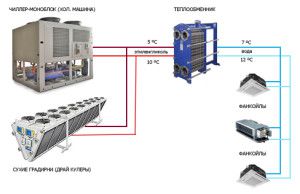
One of the new and effective ways of heating a retail space is to install an air circuit. It is called the chiller-francoil system.
This type of heat supply consists of two elements - a chiller and francoils installed in the building. The first is not mounted inside the house, but on its roof. The operation of the chiller is based on the principle of a heat pump. In its first circuit, refrigerant circulates, the temperature of which rises with increasing pressure. The energy received through the heat exchanger is transferred to the internal circuit, which is connected via pipelines to the mains. They, in turn, are connected to francoils.
Before installing such a system, an accurate and rigorous calculation of the heating of the room will be required. During its implementation, internal and external factors are taken into account - the climatic features of the region, the characteristics of the building, etc. This task should be performed by special design bureaus.
The main advantages of heating an air-type retail space:
- The system can work both for heating (in winter) and for air cooling (in summer);
- The ability to install additional francoils in other areas of the building;
- High speed of air heating and organization of zone heating of rooms;
- Adjustment of the operation mode of each francoil. This allows you to set the optimal mode of heating the air in individual rooms.
It is important to correctly calculate the heat for heating the room, since depending on this a chiller of a certain power and performance will be selected. According to the type of coolant used, it can be with a water circuit or air. The latter can be used for heating small and medium-sized buildings and production halls.
The cost of the chiller-francoil system can be from 700 thousand rubles. Therefore, it is so important to calculate the feasibility of its installation.
Spot heat supply for production facilities
How to optimize the cost of heating non-residential premises? To do this, you can apply a fundamentally different scheme of air heating. At the same time, despite the high heating tariff for non-residential premises, significant energy savings will be observed.
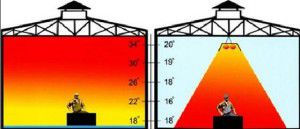
It is primarily about spot heating. Its difference from the traditional one is the distribution of heat in a certain volume of the room, and not over its entire area. This applies to heating warehouses, where it is necessary to create an individual thermal regime in separate zones.
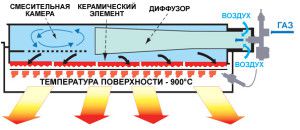
There are several ways to organize this type of heating. The most effective is the installation of gas infrared emitters. In them, during gas combustion, the formation of infrared radiation occurs, which, with the help of a reflector, focuses on a certain area.
Using similar electrical devices, it is possible to organize heating of livestock farms, where it is necessary to maintain the desired temperature level in only one area of the room. In this case, experts take into account such moments:
- Use of IR heaters as an auxiliary system for operational heating of a room.For further work, it is possible to install electric boilers for space heating or their solid fuel and gas analogues;
- During operation of the heaters, air heating does not occur. The temperature on the surface of objects that fall into the range of the instrument rises;
- When calculating the heating of a room, the ventilation system must be taken into account. In particular, the intensity and frequency of a complete air change. This refers to the inevitable heat loss of heating.
In addition, it is important to choose the right power of devices, as well as ensure the safety of their work. Safety precautions are a priority when planning heating.
If the location of the heating area will constantly change - the purchase of mobile infrared heaters is recommended. They are convenient for organizing heating of a trading floor with a different assortment of goods.
Electric heating for commercial premises
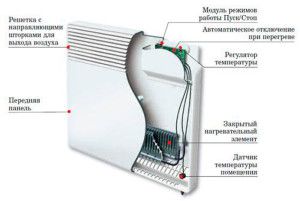
For rooms with a small area, you can install electric heat supply. For this, special electric boilers are installed for heating non-residential premises - electrode or induction. They are characterized by small size and the ability to install in limited areas.
Given the heating tariffs of non-residential premises, they will not be the most appropriate. In any case, you will have to make a piping system, install radiators and batteries. Alternatively, consider installing electric heaters.
With their help, it is impossible to make heating of large rooms and premises, since this will entail too high costs. Installation of electric convectors is relevant only if the following conditions are met:
- There is no possibility of organizing gas or infrared heating;
- The power grid is designed for the maximum power of all electrical appliances;
- Installation of two tariff meters to optimize costs. With good thermal insulation, heating of non-residential premises can be arranged at night. In the afternoon, turn on the radiators only at a critical drop in temperature.
It is because of these factors that it is desirable to install heating electric boilers in non-residential premises. The water system in this case will require less heating costs.
The best way to heat non-residential buildings and premises is that in which the heat supply system has an efficiency index of at least 85%.
Calculation procedure for heating non-residential premises and tariffs
Having chosen the optimal method of heating the air in the room, it is necessary to correctly calculate the parameters of the heat supply components. To do this, use a specific technique.
It consists in the following steps:
- Heat loss calculation. Based on the obtained figure, you can calculate the amount of heat for heating the room.
- Determining the system operation mode. In particular, the maximum degree of heating of the heat carrier and the level of its cooling. This applies only to the water system.
- Schedule system load. It depends on the temperature difference in the street and in the room.
This is just a general technique, which may vary depending on the selected heat supply system. Of great difficulty is the situation when the heating in the room is connected to the central system. In this case, it is necessary to precisely determine the tariffs for heating non-residential buildings and premises. Alas, each management company sets its prices, depending on consumption. You can find out the exact cost and terms of service using the online calculator.
When organizing autonomous heating of non-residential premises, one must be guided by current standards. In this case, additional conditions may be put forward, which depend on the purpose of the room.For example, the heat supply of a warehouse for household goods will differ from the same for food products.
The video shows an example of the organization of heating a warehouse using infrared heaters.