Rainwater can destroy even the strongest walls. After all, as you know, water sharpens a stone. If storm drains or groundwater in excess will constantly fall into the soil near the foundation, a fungus will appear on the concrete, and then micro destruction. The building is threatened with regular dampness, cold and mold from the floor. For high-quality protection of the foundation from storm drains / groundwater, gutters are used to drain water on the ground. In the circles of professionals, they are called storm sewers or simply stormwater.
Definition and purpose of the drainage gutter
Gutters are used for high-quality drainage of rainwater from the ground. Livnevka is installed at all residential buildings, on motorways and carriageways, at all large-scale industrial facilities and public facilities: airports, train stations, underpasses, etc.
The stormwater has the following functions:
- Protects from flooding of the building and structure, removes water from thresholds and walls.
- Qualitatively removes rainwater from a given territory.
- Extends the life of the roadway and other hard surfaces.
- Maintains the soil in a relatively dry state during rain / snowfall. For these purposes, a special drainage system is still being laid, for which you need to pre-perforate the trays.
An improperly installed storm shower can provoke many problems from standard flooding of the foundation / basement to paralysis of traffic on the highway.
Gutter device
Storm sewage consists of separate drainage channels connected to each other in an extended collector. Structurally, each element is a U-shaped or U-shaped tray, which is laid bottom-down. The upper open part of the sewer element is covered from above with a special grill. The entire line is mounted on a slope. As a result, storm water flows into the collector through a grate / storm water inlet and moves in this form to the sewage system, local water bodies, etc. All large garbage in the form of a foliage of foliage, paper, bottles, branches remains on the surface of the storm water.
The gutter can fully perform the drainage function only if the collector slope and its diameter are correctly calculated for the volume of storm water.
All gutters are classified by load level.
- A15. Designed for minimum load. Such trays are mounted in the private sector, on bicycle and park paths.
- B125. Gutters withstanding a slightly higher load. They are usually mounted along a conventional roadway intended for passenger vehicles.
- C250. Such gutters are used in three elevated weather conditions. Most often shown for installation in a car wash.
- D400 Storm trays that can withstand heavy loads. Mounted on autobahns, roads and highways for international use, in the industrial zone.
- E600. One of the powerful storm trays. Designed for installation in industrial enterprises.
- F900 The most powerful gutters. Mounted at airports, airfields, military bases.
It is important to choose the right type of gutter so that the storm sewer works without failures.
Materials of manufacture
For the manufacture of drainage trays use the following materials:
- Plastic. Polymer troughs are resistant to aggressive effects and temperature changes. Have a good linear expansion. Plastic storm sewers can withstand loads of up to 60 tons of water per square meter.The only drawback of plastic trays is their poor adhesion to the concrete base.
- Metal. More often use clean or galvanized cast iron. The second option is preferable because it has anti-corrosion properties. The metal is resistant to transverse and longitudinal increased loads.
- Concrete trays. The best option for both private stormwater and industrial. Concrete gutters are durable and resistant to aggressive environments. However, the inner part of such a tray is prone to the formation of silty deposits, a fungus. In addition, each element has a quite impressive weight.
- Composite A mixture made of concrete with additives (plastic, sand, fiberglass) allows you to get durable and moderately light storm trays at the exit. They have performance characteristics that are better than plastic and slightly worse than reinforced concrete. The inner side of the composite gutters is smooth, unlike concrete.
Cast iron or plastic grates for drainage trays are used to protect the system from debris.
Stormwater sizes
For each type of storm shower, its own production dimensions are provided:
| Material | Length (m) | Width (m) | Height (m) | Section (m) |
| Plastic | 1m | 0.14-0.5 m | 0.06-0.79m | 0.1 m and more |
| Cast iron | 0.5 m | 0.2 m | 0.1 m and more | |
| Reinforced concrete | 0.5-4 m | 0.14-0.44 m | 0.15-0.88 m | From 0.1 m |
| Composite | 1m | 0.15-0.4 m | 0.1-0.5 m | 0.1-0.2 m |
Installation Rules
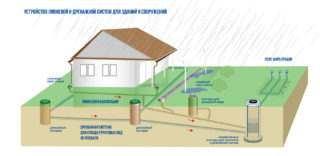 To properly mount a storm sewer, it is important to adhere to such rules:
To properly mount a storm sewer, it is important to adhere to such rules:
- The type of trays is selected in accordance with the estimated volume of effluents on the site. At the same time, another 25% must be added to the result.
- The material of manufacture must meet the expected load. For example, it makes no sense to spend money on the purchase of cast-iron gutters for home stormwater, or to mount plastic gutters on a freeway.
- Communication should be buried below the level of freezing of the soil (40-60 cm).
- Under the collector, it is necessary to lay a pillow from a layer of rubble and sand. The gutters are not laid on clean soil.
- When installing stormwater, a slope of 10 mm for each running meter of the collector must be made. This will provide sufficient strength of the free flow of effluents.
- It is mandatory to mount sand traps in the collector. They prevent clogging and siltation of the gutters.
- The upper grilles are securely fixed with screw locks. Otherwise, theft and then blockage of storm sewers are not ruled out.
When installing drainage gutters, it is necessary to take into account the degree of contamination of storm drains. Only with all the recommendations, the drainage system will work properly for more than a dozen years.




