To preserve the decorative finish of the walls and increase the service life of the foundation and the blind area, it is necessary to ensure the removal of rain and melt water from the building. Private and municipal construction facilities need protection against excess moisture.
Varieties of gutters
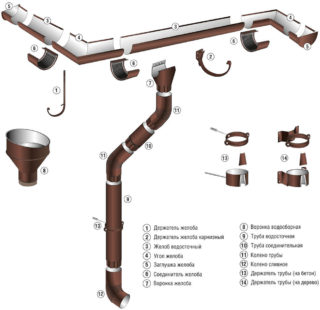 Distinguish between internal and external drains. Internal are used in buildings with a flat roof. All types of pitched roofs are equipped with an external gutter system. The area of the roof, the bearing capacity of the foundation, the purpose of the building and its number of floors affect the choice of the material of the ebb tide. The industry produces metal and plastic systems, which consist of the main elements:
Distinguish between internal and external drains. Internal are used in buildings with a flat roof. All types of pitched roofs are equipped with an external gutter system. The area of the roof, the bearing capacity of the foundation, the purpose of the building and its number of floors affect the choice of the material of the ebb tide. The industry produces metal and plastic systems, which consist of the main elements:
- Gutters are used to receive melt and rain water along the perimeter of the roof overhang.
- Connectors are designed for docking gutters horizontally.
- External and internal corner elements are necessary for the installation of the tide in the corners of the building.
- The funnel serves as a transitional element between the horizontal and vertical parts of the drainage system.
- Gutter plugs are used to prevent water draining along the edges.
- The brackets are a fastener for hanging the gutter system in the under-roof space and attaching the pipe to the building facade.
- The pipe is the vertical part of the drain. Designed for receiving water from the gutter and lowering the liquid.
- The drainage pipe, or elbow, serves to change the direction of the pipe. The part is used for contouring the protruding parts of the facade. There are knees with a corrugated or fixed bend angle. The most common angles are 45, 60 and 90 degrees.
- A drainpipe mark is a type of elbow designed to remove water from the base.
- Protective elements. The gutter net and funnel cap prevent leaves and other debris from entering the system, preventing clogging.
Installation is carried out by the same type of elements, a combination of pipes and fittings of different systems is impractical.
Metal constructions
The drainage system must meet the following requirements:
- mechanical strength;
- chemical resistance;
- light weight;
- low cost;
- ease of installation.
Metal outflows of drainpipes, regardless of the composition of the alloy, have a common drawback - a high noise level.
- Drains made of galvanized steel are not subject to corrosion, have a relatively light weight and low cost.
- Pural or galvanized polymer coated is gaining popularity due to the choice of coating color. Pural products have high chemical resistance. During transportation and installation, care must be taken, as polymer coating is quite fragile. Damage to the protective layer contributes to the formation of foci of rust.
- Aluminum castings of industrial production are varnished or resistant paint. They have sufficient resistance to negative environmental influences. Elements are riveted using sealant. You can save by collecting a drain from metal sheets, bending them at the installation site.
- Copper drains are beautiful, durable and expensive.
- Titanium-zinc gutters are considered the most durable, their service life exceeds 150 years. Due to the extremely high price, they were not used in mass construction.
When choosing metal products, it should be understood that when a product deforms as a result of snow or ice melting, its consumer qualities decrease.
Plastic constructions
PVC products are distinguished by high consumer qualities, combining:
- low cost;
- wide color gamut;
- light weight;
- ease of installation;
- chemical resistance.
Unlike metal, polyvinyl chloride pipes do not create noise during the drainage process. The mechanical strength of PVC casts is quite high, subject to the rules for installing the system. A wide range of connecting and fastening elements, the presence of pipes and drains of different diameters, make it possible to collect drainage systems of complex configuration.
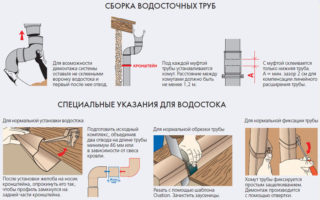
Installation of a drainage system
The calculation of the total length of the drainage system and its diameter is based on the area and slope of the roof. A specialist store consultant will help you choose the right size brackets and fittings. Unified structural elements speed up the assembly process.
Installation of a horizontal section
Before starting work, it is necessary to mark the horizontal section of the catchment. For the natural movement of water, it is necessary to withstand a slope in the range from 5 to 20 mm per linear meter. Depending on the roof construction, the brackets are attached to the rafter legs or to the wind board.
- Calculate the height difference based on the length of the roof slope.
- Fasten the first bracket so that there is at least 3 cm distance between the roof overhang and the upper part of the gutter. Failure to observe this rule will lead to the gutters breaking off during an avalanche.
- Mark the place of attachment of the last bracket at the design level, but do not fix it firmly, subsequently a height adjustment will be necessary.
- Pull the thread between the first and last bracket, mark the mounting points of the intermediate brackets.
- Lay the gutters, leaving 3-4 mm between them for linear expansion. Use the connectors provided by the manufacturer for joining.
- Fasten the plugs along the edges of the gutters.
It is not allowed to install the bracket under the connecting element.
The funnel of the drain pipe is located at a distance of 40-70 cm from the end of the gutter, so the last bracket must be raised 0.5-1 cm from the design height to ensure the movement of water to the funnel.
Gusset
 Arranging a gutter on a hip roof or on a roof of complex geometry requires the use of corner joints. For PVC castings, they are made according to the principle of linear connecting elements. The design of the corner joint allows you to use it to bypass the external and internal corners. When installing metal systems, the edges of the ebbs are cut at an angle, joined and secured by an external coupling.
Arranging a gutter on a hip roof or on a roof of complex geometry requires the use of corner joints. For PVC castings, they are made according to the principle of linear connecting elements. The design of the corner joint allows you to use it to bypass the external and internal corners. When installing metal systems, the edges of the ebbs are cut at an angle, joined and secured by an external coupling.
Vertical section
The vertical part of the drain is collected from pipes. To move from the horizontal to the vertical part of the system, it is necessary to use knees. The fewer bends, the less chance of clogging. Fixture of pipes to the wall is made using brackets. It is necessary to strictly maintain the vertical, checking the correct installation using the building level.
Gutter mark
Lastly, a gutter is installed. The height of the drain hole varies from 20 to 40 cm above the soil or blind area. The range of water discharge should be at least 50 cm from the wall of the building. It is possible to withdraw the mark into a storage tank, into a storm sewer, a filtration well, a drainage system, or into the nearest body of water.
Correct calculation and high-quality installation of the drainage system will extend the life of the building.




