To combat the waterlogging of the site, its waterlogging, flooding of the foundation of a residential building and other buildings, storm sewers and a drainage system are intended. The effectiveness of these drainage systems depends on the correct choice of components for them, compliance with installation technology.
Purpose of drainage and storm sewage
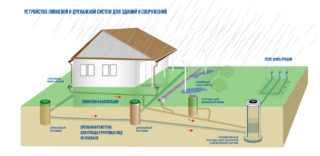 Each of these types of wastewater systems has a specific function:
Each of these types of wastewater systems has a specific function:
- Drainage sewerage (drainage) is a system designed to divert groundwater rising close to the surface, top water seeping through the soil stratum of atmospheric precipitation.
- Storm sewage (storm storm) - a system of drainage of precipitation collected by trays and pipes from the surface of the earth.
With proper installation, the combined operation of these systems protects the site as much as possible from flooding during snowmelt in the spring, heavy rains of the summer-autumn period, and winter thaws. Lay the drainage and stormwater during the construction of the house, after the construction of walls and roofs.
Device and principle of operation
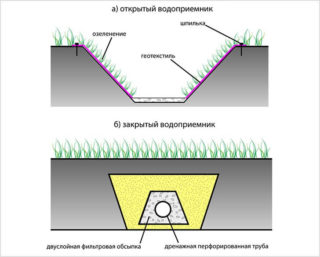 Depending on the location and design features, drainage and stormwater can be open or closed.
Depending on the location and design features, drainage and stormwater can be open or closed.
Open type drainage system
The drainage system consists of the following parts:
- a network of drainage ditches with a trapezoidal transverse profile, a depth of 1.5 m and a slope towards the catchment;
- an open catchment basin - a pond, a small lake, a kopanka - located at the lowest point of the site and collecting water from the drainage ditches.
Despite its low cost, this type of drainage is used very rarely. This is explained by the fact that with a large number of ditches, the land tenure area suitable for arranging lawns and planting trees is significantly reduced. An open drainage network is most often used when draining flooded areas before starting major excavation work on them (planning a trench digging for a foundation).
Closed-type drainage system
Modern closed drainage is located at a depth of 0.8-0.9 to 1.5-2.0 m. Its main components are:
- perforated polymeric drainage corrugated pipes with a diameter of 110 mm, wrapped in geotextiles and placed in the thickness of gravel;
- intermediate (rotary) inspection wells with a diameter of 315 mm;
- drainage drainage well.
The principle of operation of closed drainage consists in filtering soil water through a layer of gravel, geotextiles, collecting them into drainage pipes with further gravity transportation to the drainage well.
Open storm stormwater (linear)
 Surface storm sewage consists of the following elements:
Surface storm sewage consists of the following elements:
- polymer concrete or polymer trays with gratings, collecting water from concrete surfaces;
- doormitory located under the gutters and connected to the trays by underground pipes;
- sand traps - trays located at the end of linear surface elements with special containers designed to collect large debris and sand;
- underground PVC sewer pipes connecting the trays to the collector well;
- collector drainage well.
The stormwater allows you to collect and drain water not only from the gutter system, but also from the concrete surfaces of the blind area, garden paths.
Closed storm stormwater (spot collection)
Compared to open storm sewers, a closed system does not contain trays with gratings.The collection and disposal in it is due to sprinklers and underground pipes installed under the drains, which flow into the collector storm well.
Combinations of storm and drainage
For effective drainage of precipitation and groundwater, the two sewage systems must function separately. It is not allowed to discharge atmospheric precipitation into the drainage. During the period of active melting of snow and summer rains, the drainage pipe will not be able to let a large amount of rain and soil water through it and will cease to function. The only element that can combine stormwater and drainage is a common catchment well of large capacity.
Also, a placement of pipes in one common trench can be considered a kind of combination of these drainage systems.
Installation Steps
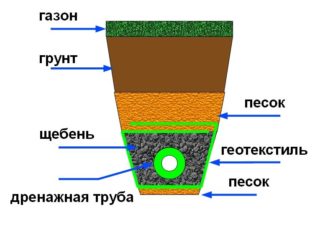 The most convenient and economical installation technology for storm and drainage in one trench consists of the following steps:
The most convenient and economical installation technology for storm and drainage in one trench consists of the following steps:
- digging a trench 60-70 cm deep, 40-50 cm wide along the perimeter of the foundation or blind area of the house and to the place where the collector well will be installed;
- digging a hole under a well with a depth of 1.5-2.0 m;
- installation of a well of 2-3 reinforced concrete rings;
- laying on the bottom of the trench of a sand pillow 5-10 cm thick;
- laying geotextiles on the bottom of the trench;
- backfill on the geotextile layer of gravel (fraction 20-40 mm) with a thickness of 10 cm;
- installation under drainpipes of rain-water catchers;
- laying in the trench of storm and drainage pipes with a slope of 3 cm / mp;
- connection with the help of tees and pipe sections of the rain-blower to the main drainage line of stormwater;
- installation of rotary inspection wells with mandatory rupture of their pipes;
- backfilling of pipes with a second layer of gravel 10-15 cm thick;
- backfilling of the trench with several layers of sand without tamping.
At the final stage, the stormwater drainage pipes and drainage pipes with holes of the corresponding diameter are discharged into the collector well located at the lowest point of the site.


