The main type of heating in the private sector remains natural gas. It is affordable, cheap and highly efficient. To supply blue fuel to the home, you need to choose the right pipes for gas. All the nuances are taken into account: gas pressure, distance from the highway, method of installation.
Varieties of gas pipelines
Gas pipeline - communication, including pipes for gas transmission, pumps, treatment plants, distribution points and much more. At its site, the consumer is faced with the simplest construction of a pipeline, valves and counting devices. Despite its simplicity, the principle of operation of the circuit is the same as that of the highway.
Gas pipelines are divided into 2 main categories:
- trunk - supply gas over very long distances;
- distribution - move blue fuel from the gas distribution station to the end user.
The latter are divided into lines with different pressures.
Low pressure lines
Gas is supplied under a pressure of not more than 0.005 MPa. Under such pressure, methane flows to the stove, boiler, boiler. Although the pressure is low, gas leaks pose a risk of accidents and explosions.
Steel, copper and polyethylene pipes for gas pipelines can easily withstand such a small pressure.
Medium pressure lines
Gas is transported under pressure from 0.005 to 0.3 MPa. Under such pressure it is allowed to supply fuel to industrial consumers within settlements. The line provides gas to reduction points, from which gas is redistributed to multi-unit residential buildings, public and administrative. It is allowed to lay a gas pipeline inside production facilities.
The connection to the private house of the medium pressure line is prohibited.
High pressure lines
This includes a gas pipeline of categories 1 and 2. In the first case, the pressure in the pipe reaches 0.6-1.2 MPa and higher, in the second - 0.3-0.6 MPa. Category 1 lines are being built to supply gas to turbine plants, to plants where high pressure gas is required.
A category 2 gas pipeline is used within the city to supply fuel to enterprises or distribution points.
The choice of pipes for the gas pipeline
Which pipes and why are used for internal gas pipelines, depends on many factors:
- Purpose - gas is supplied to the consumer with minimal pressure. When installing gas supply, you can take metal-plastic, steel and copper pipes.
- Ultraviolet action - steel and copper products can be installed anywhere inside and outside the house. Plastic ones are sensitive to the action of sunlight, they are located in shaded places.
- Laying method - a steel or copper gas pipeline is laid above the ground, underground, in walls, in open places. Plastic is allowed to be laid only underground outside the house and only in open places indoors.
- Durability - Copper lasts the longest. Steel gas pipes are subject to corrosion and need protection. Their service life is shorter.
- Complexity - plastic pipes are flexible, connected by soldering. Thus, contours of any complexity are constructed. Steel need to be welded and connected through fittings. This makes gas supply difficult.
The laying of gas pipes is carried out at the expense of the owner of the home, therefore, when choosing, cost must be taken into account. Consider the price of the pipeline, meter, valves, as well as the cost of installation.
Which pipes are better to use for gas
Domestic gas pipes are made of steel and copper. There are also bronze and brass, but extremely rare.
Both materials have the main quality for the gas pipeline: they do not pass gas at all. Evaluate options by the following characteristics:
- Copper does not corrode. The service life of the pipeline is 50-100 years. Steel is susceptible to corrosion and with the most careful care will not last more than 20 years.
- Copper is ductile. Tubes of small diameter can be bent. Steel need to be welded.
- The cost of the copper pipeline is much higher. Steel gas pipes have the lowest price.
Copper pipes are much more beautiful. They do not need periodic painting and often act as part of the interior of the kitchen.
Standards and restrictions for laying pipes
SNiP 42-01-2002 regulates the construction of gas pipeline structures serving the final consumer. The rules are binding, as they provide fire safety and sanitary standards.
In the apartment
The gas pipe is laid according to a pre-designed scheme. Its task is to supply fuel to gas equipment: stove, boiler, boiler. Usually all the equipment is placed in the kitchen. Installation rules in dwellings are very strict:
- installation in residential premises or ventilation ducts is strictly prohibited;
- crossing of window or doorways is not allowed;
- The gas pipeline can only be laid in rooms with a height of at least 2.2 m, well ventilated or equipped with ventilation;
- distance from the pipe to the floor - at least 2 m;
- if designs with flexible sleeves are used, their length should be less than 3 m;
- surfaces next to gas appliances are insulated or trimmed with panels insensitive to temperature;
- installation of the gas pipeline in the wall or behind decorative decoration is prohibited, it must be freely accessible.
When designing gas supply, a gas meter is provided.
In a private house
Inside the building are guided by the rules described above. When laying an external gas pipeline, the following recommendations are followed:
- The higher the pressure in the supply gas pipeline, the farther it fits from the house. The distance between the low pressure circuit and the foundation of the house is at least 2 m. If the medium pressure line runs alongside the building, the distance increases to 4 m.
- From the gas pipeline to the door or window opening should be at least 50 cm.
- From the pipe to the roof at least 20 cm.
- A plastic gas pipeline is laid underground. Steel allows both aboveground and underground installation.
The fewer turns and bends the gas circuit includes, the more reliable it is.
Options for laying gas pipes
There are several ways to lay a gas pipeline. The choice is made taking into account the characteristics of the site, pipeline material, gas pressure.
Underground
It is considered the safest, as it eliminates the mechanical impact and the influence of sunlight. This method is ideal for plastic piping. For steel is not the best, since the latter need periodic inspection and maintenance.
The method is costly. Pipes are laid to a depth below the level of freezing of the earth - at least 0.8 m. In cold regions, the depth of the trench increases to 1.2 m.
Aboveground
Less secure method. The pipeline is installed on metal risers of different heights. Such a method is resorted to with high relief and complexity of the site, with a large number of buildings, where it is difficult to fulfill all the requirements of SNiP. Only steel pipes for gas may be used.
Interior
Inside the building, the gas pipeline is installed in an open way.It is allowed to hide communications in pre-made strobes in the wall, however, they can be blocked only with easily removable panels. Free access to pipes is a prerequisite.
Gas protection zone
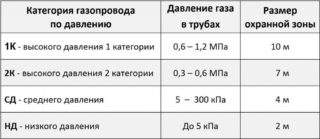 When laying communications, they observe one more condition - they organize a security zone. Its value depends on the methane pressure in the pipeline and its diameter:
When laying communications, they observe one more condition - they organize a security zone. Its value depends on the methane pressure in the pipeline and its diameter:
- For gas supply to a private house, pipes with a cross section of not more than 80 mm are used. The security zone is 2 m on each side if the pipes were laid above ground or above ground.
- For contours of polyethylene products, the security zone is 3 m from the axis of the pipeline.
- If communications are laid through a forest belt or plot with shrubs, the dimensions increase to 3 m.
- If the gas pipeline is mounted above the ground, the distance from the tree to it should equal the height of the tree.
In the security zone, you can’t fire, loosen the soil to a depth of more than 30 cm, store chemical compounds (acids, alkalis) and any household waste. Also, no structures are allowed within the zone.









