Any scheme of an energy-saving lamp for 220 V is a combination of electronic components, each of which performs its own, very specific function. Small deviations from the basic design do not fundamentally affect its general characteristics. Basically, these differences are manifested in the variety of types of socles, as well as in the power consumed by the product.
Types of energy-saving lamps
Known examples of energy-saving bulbs, which traditionally include LED, halogen and fluorescent models, are classified according to the following criteria:
- view of the cap;
- the glow temperature characteristic of each model;
- power consumption;
- bulb shape.
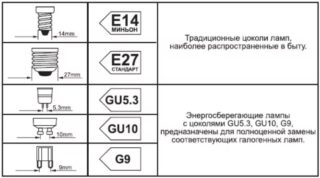
In view of the cap used to fix the bulbs in the lighting device, most of them are divided into threaded and pin products.
The most common in everyday life are threaded socles, which are screwed into standard cartridges of various diameters (as for incandescent lamps).
When describing the product, this element is indicated by the letter “E” followed by a number corresponding to the diameter in millimeters. The standard size of most manufactured lamps is E27, and products with a diameter of E14 are installed in lamps or sconces.
Threaded bases are most often used in lamps designed for street lighting (in DRL and sodium). The pin type products are suitable only for fixtures of a special design and high power. They have different modifications, differing in the number of pins (two or four), and their connectors are marked with the letter “G” with the corresponding numerical icon.
Depending on the glow temperature, measured according to Kelvin, each sample of an energy-saving lamp emits light of its “own” shade.
- Warm light with an indicator of 2700 K, outwardly resembling a yellow tint. It is very similar to the glow of ordinary incandescent lamps.
- Natural white with a temperature of 4200 K. These are the so-called "fluorescent lamps" having a neutral color.
- "Cold" glow, like a shade of white with a temperature value of 6400 K.
Cold light is close to the blue spectrum and resembles a slightly bluish color. Bulbs with such a glow are most often used in industrial premises and are designed for power from 65 watts or more.
Energy-saving products vary in the shape of the bulb: spiral, arcuate and tubular.
Work principles
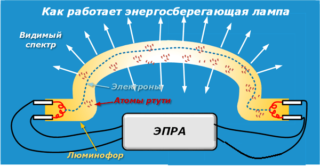 We will consider the principle of operation of energy-saving emitters using the example of CFL - a compact fluorescent illuminator, which is in great demand among the population. This type of lighting device consists of a hollow glass bulb, the interior of which is filled with mercury vapor. When a high voltage is applied to the contacts between its electrodes, an arc discharge is formed, leading to the formation of ultraviolet radiation, invisible to the human eye. To turn it into visible light, the inner walls of the flask are coated with a phosphor, which allows to obtain a bright glow.
We will consider the principle of operation of energy-saving emitters using the example of CFL - a compact fluorescent illuminator, which is in great demand among the population. This type of lighting device consists of a hollow glass bulb, the interior of which is filled with mercury vapor. When a high voltage is applied to the contacts between its electrodes, an arc discharge is formed, leading to the formation of ultraviolet radiation, invisible to the human eye. To turn it into visible light, the inner walls of the flask are coated with a phosphor, which allows to obtain a bright glow.
When comparing it with the same indicator for incandescent lamps of similar power, the light output in this case is noticeably higher. The disadvantage of such products is the inability to directly connect 220 volts to the power circuit. As a result, it is mandatory to use a special conversion device called electronic ballast.
LL device
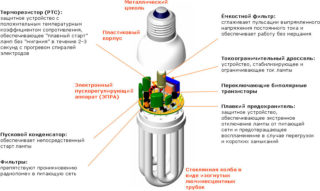
Under the external structural elements is the electronic circuit of the lamp - it is referred to as an electronic ballast or ballast. This node in its entirety is not in every model of the “housekeeper”. In the same place where the starting regulator is installed in a classic configuration, the economy lamp circuit consists of the following main modules and parts:
- starting capacitor, providing a powerful pulse necessary to start the circuit;
- a network filter that allows you to reduce the level of radio frequency interference to an acceptable level - get rid of the flickering effect;
- a capacitive filter that smooths the ripple of the current component;
- a current-limiting inductor necessary to protect against overloads;
- bipolar transistors and driver.
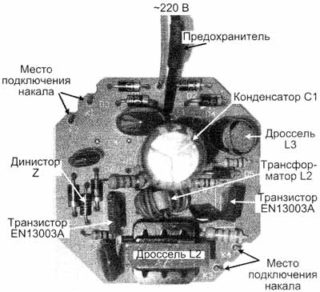
The bulb circuit contains a fuse that protects it from failure during sudden power surges, and a number of additional elements.
Component ballast circuits and features of its work
The electronic ballast includes a shaper, a transistor switch, and also an output transformer with resonant triggering elements. The order of operation of this block:
- The current pulse generated in the master module enters the base of the transistor and leads to its opening.
- Immediately after this, a capacitor charges, the speed of which is determined by additional circuit elements.
- From the output of the transistor switch, the pulses arrive at a small transformer.
- From its secondary winding through a resonant circuit with a capacitor, a reduced pulse voltage is supplied to the lamp contacts.
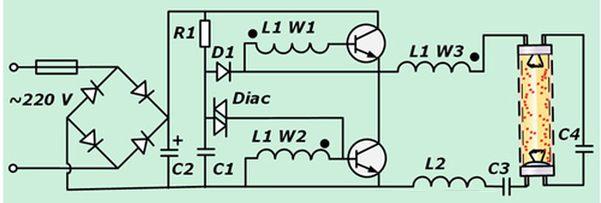
The glow formed in the tube is characterized by its inherent resonant frequency, depending on the capacitance of the capacitor connected in parallel. At the initial moment of ignition, the pulse size reaches up to 600 volts, which forces the use of special measures of protection against overvoltages. This can be done through the use of a shunt capacitor in the circuit, which allows immediately “breaking up” the resonance immediately after the breakdown and putting the lamp into working condition with constant glow. Its interruption is possible only after the operation of the switch installed in the lighting device itself.
Recovery procedure and need for repair
If a malfunction occurs in the energy-saving light bulb, it should be disassembled into its component parts. To do this, you will have to do the following operations:
- Disconnect the two prefabricated halves and then remove the flask.
- By means of an ohmmeter charged with a fresh battery, “ring” both filament spirals for the absence of a break in them.
- When it is detected, you can try to use at least one of them.
- To do this, it is necessary to bridge the burned branch with a resistor of 22 Ohms and a power of about 1-2 watts.
During this operation, you will need to dismantle the shunt spiral diode, if it is in the circuit.
All these actions are valid for energy-saving lamps at 20 W, no more.
If spirals burn out in lighting products with a power of more than 30 watts, it is very likely that the key transistor will fail. To restore the functionality of the circuit, replace them with new parts. In a single case, repairing a product worth a penny does not make sense - it is much easier to buy a new ballast.
The danger of LL and recommendations for use
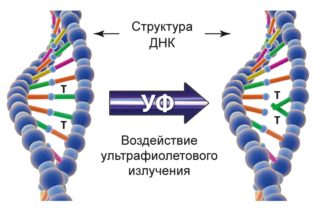 The presence of an ultraviolet component in the radiation of an energy-saving lamp is dangerous to human health. This negatively affects the condition of most vital organs:
The presence of an ultraviolet component in the radiation of an energy-saving lamp is dangerous to human health. This negatively affects the condition of most vital organs:
- exposure to UV radiation is harmful to the skin and leads to its early aging;
- possible disorders such as allergies, eczema and psoriasis;
- often, ultraviolet light causes attacks of epilepsy, migraine, and also worsens the general condition of the body.
The strength of the hazardous radiation depends on the location of the LL and the distance to the irradiated object. In this regard, they are not recommended for use in lamps mounted on a table or hung on walls. This is all the more important if we take into account the danger of radiation exposure on human vision.
An example of a practically safe emitter is a LBO O8M 36 N lamp with an electrical circuit of which can be found in any reference book. With the timely adoption of protective measures of an organizational nature, the operation of energy-saving emitters, as a rule, does not cause special difficulties.