To ensure uninterrupted power supply to industrial and residential facilities, power cables are used. One of the important tasks is to minimize energy losses during its transportation. There are many diverse cable products. For the operation of electrical and electronic devices, copper wire is more often used.
Advantages and disadvantages of copper
Copper is widely used for making wires. The competitor is only fiber optics. According to some characteristics, it is second only to silver. The following advantages of copper wire products can be noted:
- high conductivity and heat resistance;
- relatively low resistance;
- strength at the same time as ductility and flexibility;
- corrosion resistance, lack of oxidation.
The disadvantage of copper products is the high price. Cable copper products also have more weight than aluminum. This fully pays off with a long service life.
Variety of products
The assortment of the modern cable industry includes wires, cables with metal conductors, cords, tapes and other products. The main types of electrical wiring are network, through which information is transmitted, and power for transmitting current. Depending on the purpose, there are the following varieties of wire products:
- Actually, wires;
- power cables;
- products for telephone lines;
- computer
- special purpose wires.
There is a certain marking for their systematization. Products are supplied in the form of segments of various lengths, which are wound on a spool or rolled into a bay.
Copper wire and cable design
At first glance, these products do not differ from each other. But a specialist in electrical engineering can easily determine the type of product. Usually the name is indicated in the specification. TU and GOST contain various characteristics relating to cable and wire. They are divided by the thickness of the shell, insulation and the number of cores.
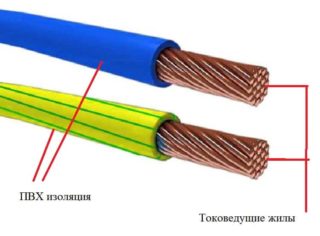
A wire consists of one or more wires twisted together, in light tubular insulation or without it. A cable, unlike a wire, has an outer sheath. Includes one or more insulated conductors. It can be used under water, in the ground and other difficult conditions.
Any conductor includes the following elements:
- conductive conductors;
- insulation with dielectric properties;
- a shield to protect the core from electromagnetic interference;
- outer shell;
- protective elements for use in harsh conditions.
Products are divided into single-core rigid, which are used for hidden wiring, as well as multi-core, soft and plastic. Each stranded conductor is insulated separately, then they are enclosed in a common sheath. Such products withstand repeated kinks during operation.
As an insulating material used PVC, rubber, polyethylene, paper, fluoroplastic. Also, the wire may be in silicone insulation or coated with enamel.
Parameter Overview
The main part of the cable structure is a metal core through which electric current flows. The main parameters are DC resistance, throughput and cross section.All cores are produced according to regulatory documents that define the standard for DC resistance of 1 km of cores at 20 ° C (GOST 22483-77).
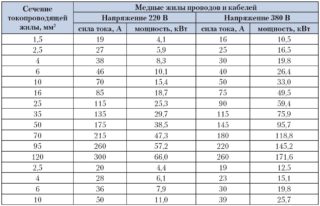
The permissible current for copper wires depends on the total power of the consumers and the voltage of the electrical circuit. It is calculated by the formula: I = P / V and is 10A per 1 mm2.
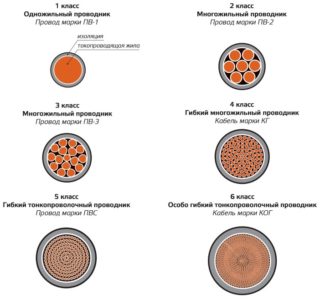
The wire grade is from 1 to 6, the higher the number, the greater the flexibility. For stationary stationary wiring, products of class 1–2 are used. For mobile mechanisms, a flexible wire with a class of 3 to 6 is suitable.
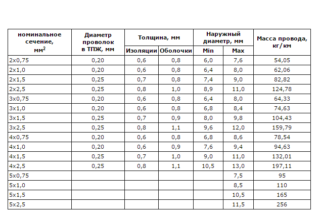
According to the PUE, the most rational cross-section of a copper wire in networks with household appliances is 1.5–2.5 mm2 for outlets, 0.75–1.5 mm2 is enough for lighting.
How to determine the cross section of a stranded wire
The safety and reliability of the wiring in the house depends on the correct choice of wire. Overloads lead to overheating of the conductors, the insulation melts, which leads to a short circuit and fire.
The cross section is determined depending on the number of devices that will consume electricity. Therefore, it is necessary to calculate their total power used in the apartment. The result is multiplied by 0.75. There are tables where the ratio of the cross section to the current strength and power is indicated. The cross-section of a round cable can be determined by the formula:
S = π x r2, where π is 3.14; r2 is the radius squared. The radius of the conductors is measured using a caliper, the thinnest are measured with a micrometer.
If there are several wires in the core, their total cross section is calculated. It should correspond to the calculated one, some change is allowed in the direction of increase from the standard. The indicator cannot be underestimated, as equipment can be added or replaced during operation. Therefore, in the calculations it is necessary to apply a coefficient of 1.5.
Copper Wire Grades
Single-core mounting wire HB3 0.75 is mainly used for voltages up to 600 volts. Product 3 classes of flexibility with a tinned copper conductive core. PVC insulation. Designed for fixed inter-instrument mounting, connecting electrical and electronic devices.
PVA - multi-core flexible mounting copper wire with vinyl double insulation. It has a round cross section (0.5–25 sq. Mm) from 2 to 5 cores. It is used to connect mobile electrical equipment, but can be used for home wiring.
Flexible copper stranded wire PuGV (PVZ), rated voltage 450 volts, cross-sectional area 6 mm2, insulation - PVC compound. It has no outer shell. They are used for laying low-voltage power lines; placement in concrete and masonry, as well as under plaster, is possible.
The winding wire is designed for winding coils of oscillatory circuits, chokes, transformers, electromagnetic relays. Enamel, fiber or combination materials are used for insulation. The main parameter is not the cross section, but the diameter of the conductive core. In the manufacture, a special production technology is used for extremely thin conductors.
Copper cable brands
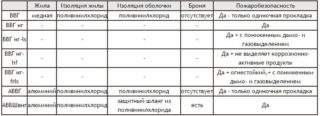
VVG - copper multi-wire flexible cable. One of the common types for electrical wiring both in the apartment and in the workplace. Used to connect any electrical equipment to the network. Consists of several copper cores and external insulation. Each of the conductors is twisted in one plane, protected by a sheath and has its own color. It has non-combustible modifications - round VVGng, and flat VVGp.
NYM is a cable with an insulating layer of non-combustible polyvinyl chloride. The number of cores is from 1 to 5, the cross section is from 1.5 to 16 mm2. Maximum strength and heat resistance is achieved due to coated rubber, which fills the space between the cores.
Flexible cable (KG) is used in conditions of direct voltage up to 660 V, or alternating current - 1000 V.Due to its flexibility, the product is used for portable equipment. For example, connecting the holder to the welding machine.
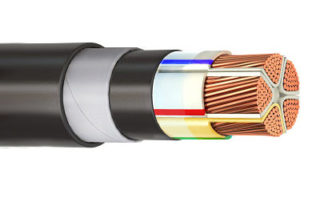
The high-voltage PvPg copper cable is designed for a network of 6 to 10 kV. It has one core with a cross section from 50 to 800 mm2. The core insulation and the outer sheath are made of cross-linked polyethylene with a protective screen. This makes it possible to lay the cable along the bottom of the reservoir, underground.
Applications for copper cable
It is widely used in industrial enterprises where there is a danger of fire or explosion. The installation of internal wiring of residential and industrial premises, public buildings is also carried out. Cabling and wiring products for use are distributed as follows:
- stationary laying underground;
- mobile connection;
- overhead power lines;
- in signaling and control networks with low currents;
- installation of household wiring;
- special conditions using heat-resistant and fire-resistant conductors.
To transfer energy to distribution substations, a power armored cable with protection from a lead and metal sheath is used. Control cables with protection against mechanical damage are used to connect mechanisms and devices both in the open air and in tunnels and channels.
Different brands of copper wires and cables are designed to perform certain tasks. When repairing or building, the choice of cable products must be approached responsibly. The reliability and safety of energy supply depend on this.