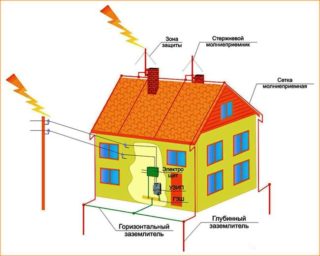
Grounding is an important technological process that protects a person from accidental electric shock during the operation of household appliances or electrical appliances. To replace the wiring, repair it or upgrade it, you first need to familiarize yourself with the grounding system that is used in a particular building structure. Upon completion of work, the safety of households, as well as the operation of equipment, will depend on this.
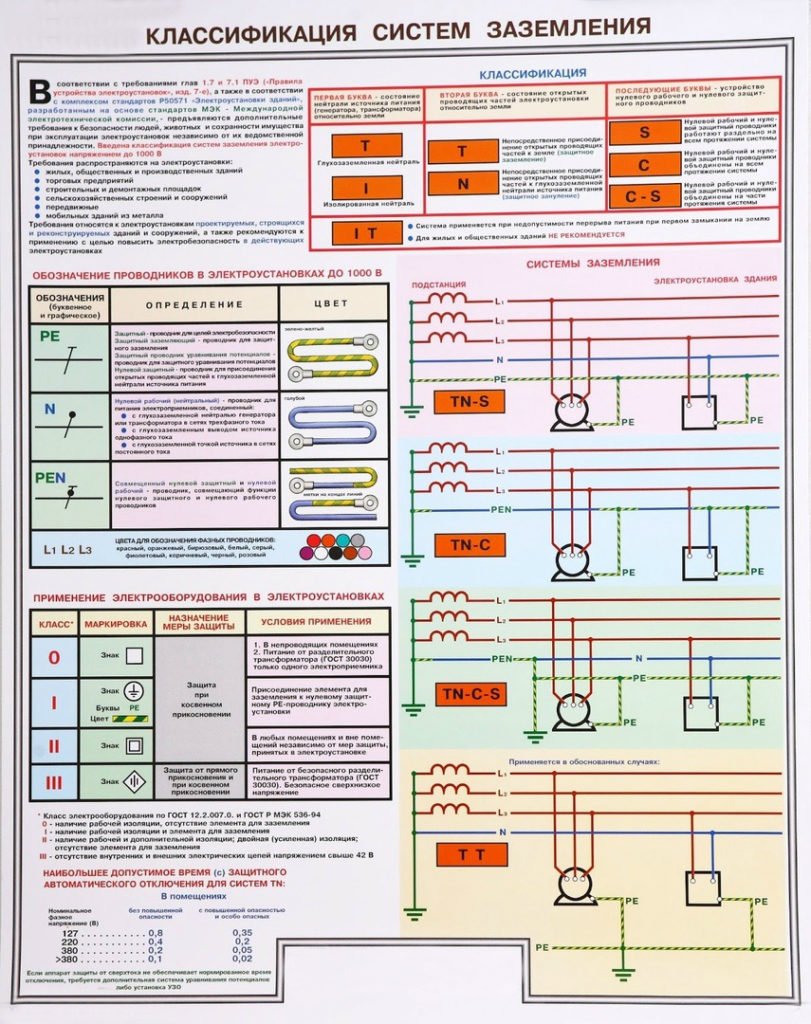
Classification of grounding systems
There are several types of grounding systems that were developed by the International Electrotechnical Commission and adopted by the State Standard of the Russian Federation. All of them are listed and described in detail in the "Electrical Installation Rules" (PUE).
- TN system and three subspecies;
- TT system;
- IT system.
Their main difference lies in the source of electricity used, as well as the methods of grounding electrical appliances. Classifications of grounding systems are indicated by letters according to a specific principle.
By the first letter, it is possible to determine how the power source is grounded:
- T - direct connection of the zero working conductor of the source of electricity (neutral) with the ground.
- I - in this case, the neutral of the electric power source is connected exclusively through the resistance.
The second letter in the abbreviation indicates grounding in the conductive open parts of the building:
- T - indicates a separate (local) grounding of the power source and electrical appliances.
- N - the power source is grounded, but consumers are grounded only through the PEN conductor.
The letter N defines a functional method, the essence of the implementation of which is the device of zero protective and zero working conductors:
- C - the functions of both conductors act thanks to a common conductor called - PEN.
- S - indicates that the working neutral conductor (N) and protective (PE) are separate.
Grounding systems are also divided into working and protective. The former is intended for the safe and efficient operation of all electrical appliances, the essence of the latter is to ensure complete safety during the operation of these appliances.
The voltage and current values can reach critical levels only for two reasons - improper use of equipment and lightning strikes.
Natural and artificial grounding
As a natural defense are used:
- Lead cable sheaths laid in trenches underground; rail tracks of non-electrified access roads, railways, etc.
- Reinforced concrete and metal structures of any building structures that are directly in contact with the ground.
- Underground water and sewer lines. Do not use metal pipes through which explosive and combustible substances pass.
As a rule, horizontal and vertical electrodes are used for artificial grounding conductors. The role of vertical can be played by a twig or a steel pipe, at least 3 meters long. The essence of the implementation is to immerse the upper ends in the ground and connect with a strip of steel using a welding machine. This technology forms a ground loop.
For the safe use of electrical appliances, natural grounding conductors must be used.Their application saves the family budget and time, since there is no need to build artificial grounding conductors. If the natural look satisfies all the requirements of the PUE for spreading resistance, artificial can not be built.
Comparison of artificial and natural contour
A natural circuit is two or more metal structures that come in contact with the soil for the safe use of household appliances. Natural grounding is also divided into the following varieties:
- Pipelines designed for various purposes located in the ground.
- Reinforcement of building structures, which is immersed in soil layers.
These types of protective circuit must be connected to the object with at least two elements. As a rule, they are installed in different parts of the structure.
As a natural defense, it is forbidden to use:
- heating systems and sewer;
- pipes, the surface of which is coated with an anti-corrosion compound;
- metal structures intended for transportation of combustible and toxic substances.
Artificial contours are special constructions made of metal. For work, they are immersed in soil layers. The most common examples of artificial protective circuits:
- Metal canvases laid in the ground. They may be characterized by different shapes and sizes.
- Rods, corners, pipes and steel beams placed in the ground.
Each element of the artificial circuit must necessarily have corrosion-resistant electrical conductors made of zinc or copper.
Types of Artificial Grounding
The main regulatory document in Russia, which allows the use of different grounding systems - PUE paragraph 1.7. It was developed taking into account the methods of grounding systems, their classification and principles. The document is approved by a special protocol of the International Electrotechnical Commission.
The abbreviated names of existing systems are combinations of the first letters of French words.
- T - grounding.
- N - neutral connection.
- I - isolation.
- C - connection of the working and protective neutral conductors in one wire.
- S - separate use of protective and working neutral conductors.
To understand what the differences and implementation methods are, you need to familiarize yourself with each variety in more detail.
Grounding Device TN
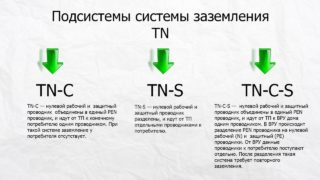 The most common type of grounding systems. Its essence is to combine zeros with the earth along the entire length. This type has another alternative name - the supply of a grounded neutral.
The most common type of grounding systems. Its essence is to combine zeros with the earth along the entire length. This type has another alternative name - the supply of a grounded neutral.
To implement the method, it is required to drive a group of pins into the ground technologically in an upright position so that the depth is not less than 2.5 meters. All pins must be connected to each other using a cable and strips in a single circuit of a residential building.
TN-C system
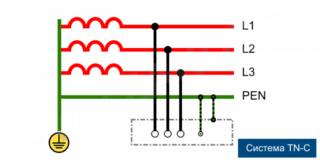 A fairly outdated system, which is still used in old housing stocks. The essence of protection is that zero N also plays the role of a protective conductor PE; two functions are combined in one conductor. The advantage of this method lies in the simplicity of implementation and low-cost manufacturing, designed for electrical appliances with a capacity of not more than 1000 V.
A fairly outdated system, which is still used in old housing stocks. The essence of protection is that zero N also plays the role of a protective conductor PE; two functions are combined in one conductor. The advantage of this method lies in the simplicity of implementation and low-cost manufacturing, designed for electrical appliances with a capacity of not more than 1000 V.
Today this type carries a potential danger, since it does not have a single separate conductor. If a neutral wire breaks during an emergency or an emergency, the entire electrical potential is concentrated on the devices, and this already carries a danger to human health and life, there is a possibility of a fire.
TN-S system
New buildings under construction use a new grounding system. The essence of its implementation is the presence of a separate phase wire, neutral and protective conductor.Conductors PE and N are separate components of the power supply system.
Of the accepted and approved methods of grounding the electrical network, the TN-S system is considered the safest and most reliable. Of the shortcomings should be highlighted high cost.
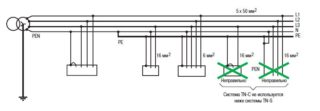
Grounding System TN-C-S
This grounding system incorporated the best qualities of its predecessors and partially eliminated their shortcomings. The method is relatively simple to implement, another advantage of the type - it can be implemented during the reconstruction and modernization of obsolete buildings. The point is to organize the TN-C system, here the neutral wire is divided into two conductors N and PE, then the TN-S method begins to be implemented.
However, the problem of the protective circuit of the TN-C system is still not resolved. If the bus breaks, all electric potential is concentrated on household appliances. You can deal with this drawback with the help of auxiliary structures, for example, a voltage relay, which is able to automatically conduct an emergency disconnection of devices from the network.
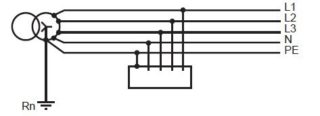
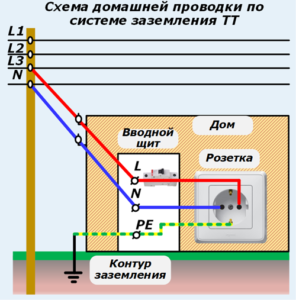
TT earthing
Functional grounding is used in those conditions when it is simply impossible to organize a grounding circuit of type TN. The essence of the implementation is two separate grounding devices. Most often used when laying overhead power lines. It is also used in the emergency state of zero conductors.
A feature of protecting a person from electric shock is the mandatory installation and use of a residual current device with a differential current of not more than 30 mA.
IT grounding circuit
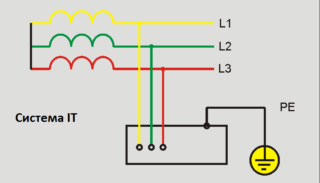 The system is used exclusively in mining, for example, mines or quarries. The features of using electrical equipment at such enterprises are such that it is simply impossible to provide a high-quality protective circuit there.
The system is used exclusively in mining, for example, mines or quarries. The features of using electrical equipment at such enterprises are such that it is simply impossible to provide a high-quality protective circuit there.
Only the neutral of the transformer is grounded with the help of measuring instruments that perform the functions of protection against electric leakage. If the devices pick up excessive power consumption, the devices will shut down abnormally.
The main purpose of grounding is to make the use of electrical appliances safe, and also to extend their operational life. Do not neglect the design and construction of grounding, this is an unjustified risk.