An accurate calculation of the cable cross-section is necessary when arranging a home electrical network. Incorrect calculations will lead to the purchase of a short or thin occasion, which will heat up. This can cause a fire and the accumulation of static current on the surfaces of household appliances.
What is the calculation of cable cross section for?
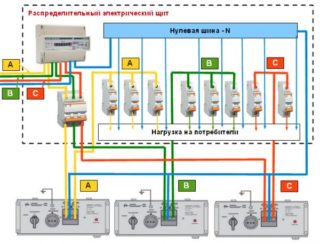
The apartment or home electrical network must be economical, safe and reliable. To prevent the effects of electricity on a person and the room itself, it is necessary to calculate the optimal conductor cross-section.
Lack of calculations has the risk of rupture, deformation of the wiring, which will cause a short circuit or electric shock. A small cross-sectional area will increase the voltage of the wires. This will cause them to overheat.
A large cross-sectional area is safer, but more money is spent. Careful calculations will help ensure uninterrupted network operation and financial savings.
What affects the heating of wires
In the process of using household appliances, the wiring is very often heated. Overheating occurs due to several factors:
- Wrong choice of conductor cross-sectional area. The thicker the cable has a core, the more current it transmits without overheating. You can find out the necessary parameters by marking the product or after measuring with a caliper.
- Inconsistency of materials of manufacture. A copper wire transmits voltage better, differs in small resistance. Veins made of aluminum with high resistance heat up more.
- Number of cores. The thick core single core conductor is characterized by high current transfer strength. Multicore modifications are flexible, but have a lower ultimate power transfer current.
- Installation specifics. With a tight installation in the pipe, the cables heat up more than with open wiring.
- Features of isolation. Inexpensive materials with poor-quality insulation are unstable to deformations and temperature effects.
The low electrical conductivity of aluminum wires provides a larger cross-section in comparison with copper.
How is power consumption calculated?
Based on the PUE in the apartment and the house, it is allowed to organize copper or aluminum wiring. Before laying it and purchasing consumables, it is advisable to calculate the optimal cable cross-section according to power consumption. The user will need:
- Make a list of all household appliances in the apartment.
- Affix its power against each unit (indicated on the label or in the instructions).
- Sum all numbers.
- Identify a rare, periodic, and permanent type of device.
- Add up the power constant and periodically turned on.
- Set the approximate load time and the voltage indicator.
- With a coefficient of 70% (0.7), calculate the thickness of the conductor.
The value of the power of household appliances can be seen in the table.
| Device type | Power, W |
| Electric kettle | 1000-2000 |
| Oven | 2500 |
| Electric stove | 2000-4500 |
| Refrigerator | 200-1000 |
| Dishwasher | 2000 |
| Washing machine | 2000-2500 |
| Boiler | 1100-2000 |
| A vacuum cleaner | 1500-2000 |
| TV | 70-200 |
| Iron | 2000 |
| Microwave | 800 |
| PC | 250-600 |
| Lighting | 500 |
| Mixer | 2500-4000 |
| Hair dryer | 400-1800 |
| Fan | 1000-2000 |
| Air conditioning | 1200-3000 |
The voltage value in a three-phase network is 380 V, in a single-phase network - 220 V.
Features of calculating the power of hidden wiring
When the project indicates the possibility of laying hidden wiring, the diameter and parameters of the cable section must be purchased with a margin. To the indicator obtained after calculation, 20-30% is added. Such calculations exclude conductor heating in confined spaces with minimal air access.
If several conductors are laid in closed channels, the thickness of each increases by 40%. Each product is placed in an individual corrugated pipe for additional protection against overheating.
How to calculate cable cross-section by power
To calculate the apartment wire according to the power indicators for a three-phase network, the formula I = P / (U * 1.73) is used, where
- P - power, W;
- U is the voltage, V;
- I - current, A.
In independent calculations, it is necessary to take into account the material of the cores, the maximum power consumption and the voltage in the network.
Maximum power consumption
For the exact value, you need to know how much energy each device will consume. Then the indicators are summed up and the average value is calculated. To get the full value, another 5% is added.
Conductor Material
The apartment chain is made up of two types of conductors:
- Aluminum - inexpensive materials for laying networks at a height. The metal does not oxidize, but for an even load distribution, it is worth stopping your choice on a wire with a large cross section.
- Copper - strong, resilient, with good electrical conductivity. Provide uniform current supply to each consumer. If the house has an old switchboard or transformer, the wires are connected with a third metal.
The PUE says that the standard load of the network through which electricity passes to residential and industrial buildings is 25 A. You can select the optimal section from the summary table.
Table 1. The dependence of the cross section of a copper wire on power and current
| Wire cross section, mm2 | Voltage 220 V | Voltage 380 V | ||
| Current, A | power, kWt | Current, A | power, kWt | |
| 1,5 | 19 | 4,2 | 16 | 10,5 |
| 2,5 | 27 | 5,9 | 25 | 16,5 |
| 4 | 38 | 8,3 | 30 | 19,8 |
| 6 | 46 | 10,1 | 40 | 26,4 |
| 10 | 70 | 15,4 | 50 | 33 |
| 16 | 85 | 18,7 | 75 | 49,5 |
| 25 | 115 | 25,3 | 90 | 59,4 |
| 35 | 135 | 29,7 | 115 | 75,9 |
| 50 | 175 | 38,5 | 145 | 95,7 |
| 70 | 215 | 47,3 | 180 | 118,8 |
| 95 | 260 | 57,2 | 220 | 145,2 |
| 120 | 300 | 66 | 260 | 171,6 |
Table 2. The dependence of the cross section of aluminum wire on power and current
| Wire cross section, mm2 | Voltage 220 V | Voltage 380 V | ||
| Current, A | power, kWt | Current, A | power, kWt | |
| 2,5 | 20 | 4,4 | 19 | 12,5 |
| 4 | 28 | 6,1 | 23 | 15,1 |
| 6 | 36 | 7,9 | 30 | 19,8 |
| 10 | 50 | 11 | 39 | 25,7 |
| 16 | 60 | 13,2 | 55 | 36,3 |
| 25 | 85 | 18,7 | 70 | 46,2 |
| 35 | 100 | 22 | 85 | 70 |
| 50 | 135 | 29,7 | 110 | 72 |
| 70 | 165 | 36,3 | 140 | 92,4 |
| 95 | 200 | 44 | 170 | 112,2 |
| 120 | 230 | 50,6 | 200 | 132,2 |
How to correctly calculate other indicators
 When laying electrical communications, it is worthwhile to understand the dependence of the cross section on current strength, material length, voltage and load. These criteria need to be based on choice.
When laying electrical communications, it is worthwhile to understand the dependence of the cross section on current strength, material length, voltage and load. These criteria need to be based on choice.
Current
The magnitude of the current passing through the conductor at room temperature depends on the width, length, resistivity and temperature. In apartments and houses, copper wire is most often used, therefore, when selecting cross sections, they are guided by the PUE data.
| Section mm2 | Current, A by type of gasket | |||||
| Open | One pipe | |||||
| 2 single core | 3 single core | 4 single core | 1 twin | 1 three-core | ||
| 0,5 | 11 | – | – | – | – | – |
| 0,75 | 15 | – | – | – | – | – |
| 1 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 15 | 14 |
| 1,2 | 20 | 18 | 16 | 15 | 16 | 14,5 |
| 1,5 | 23 | 19 | 17 | 16 | 18 | 15 |
| 2 | 26 | 24 | 22 | 20 | 23 | 21 |
| 2,5 | 30 | 27 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 24 |
| 3 | 34 | 32 | 28 | 26 | 28 | 24 |
| 4 | 41 | 38 | 35 | 30 | 22 | 27 |
To install a specific device, it is worth clarifying its current strength and compare the indicator with the data in the table. If there is no value, they are guided by a large value. This prevents cable ignition at maximum load.
By lenght
In case of high current consumption, you should choose a short material. Excessive length will lead to a loss in the quality of power transmission - the voltage in individual sections will “jump”. The dependence of the cross section on the distance to the feeding point is prescribed in the normative table.
| Power, W | Current, A | 1.5 mm2 | 2.5 mm2 | 4 mm2 | 6 mm2 |
| 500 | 2,5 | 100 m | 165 m | 265 m | 395 m |
| 1000 | 4.6 m | 30 m | 84 m | 135 m | 200 m |
| 1500 | 6.8 m | 33 m | 57 m | 90 m | 130 m |
| 2000 | 9 m | 25 s | 43 m | 68 m | 100 m |
| 2500 | 11.5 m | 20 m | 34 m | 54 m | 80 m |
| 3000 | 13.5 m | 17 m | 29 m | 45 m | 66 m |
| 3500 | 16 m | 14 m | 24 m | 39 m | 56 m |
| 4000 | 18 m | – | 21 m | 34 m | 49 m |
| 4500 | 20 m | – | 19 m | 30 m | 44 m |
The value obtained during selection must be increased by 15 cm - the margin for switching by crimping, welding or soldering.
By load
For a three-phase network, a triple increase in the load moment is characteristic.A double jump in the load in the symmetrical voltage mode occurs because the current of the neutral conductor is zero. The exact data can be found in the table.
| Voltage difference,% | Cross-section load moment | |||
| 1,5 | 2,5 | 4 | 6 | |
| 1 | 108 | 180 | 288 | 432 |
| 2 | 216 | 360 | 576 | 864 |
| 3 | 324 | 540 | 864 | 1296 |
| 4 | 432 | 720 | 1152 | 1728 |
| 5 | 540 | 900 | 1440 | 2160 |
The calculation of the wire cross section for the load provides a simultaneity coefficient of 0.75 and can be carried out mathematically:
- A list of home appliances is being compiled.
- Based on the documentation or table, the rated power is indicated.
- The ability to operate equipment at a single load is being established.
- The correction factor for the time of use per day is calculated as a percentage of 24 hours for each of the devices.
- The rated power of the equipment is multiplied by the correction factor.
- All data is summarized.
- The value in the table is found and another 15% is added to it.
As manufacturers indicate averages, another 5% is added.
Voltage
If you plan to lay the cable over a long distance, the risks of voltage drop are taken into account. The indicator is influenced by:
- wire lengths - with increasing voltage drops;
- cross-sectional area - with increasing decrease in voltage drop;
- conductivity - standard size 1 mm2 / 1 m.
The voltage drop is equal to the current times the resistance. The indicator is calculated as follows:
- The current is calculated by the formula I = P / (U * cosφ). Cosf value for household power supply is 1.
- Based on the PUE tables, the current cross-section of the wire is set.
- The total resistance of the conductor is calculated. The formula Rо = ρ * l / S is used, where ρ is the resistivity of the material, l is the length of the conductor, S is the cross-sectional area. The total value of the resistance when passing current to the consumer and vice versa increases by 2.
- The voltage drop is found by the formula ΔU = I * R.
- The percent voltage drop ΔU / U is calculated.
If the result is more than 5%, a cable with a large cross section is selected.
By current density
Copper materials with a cross-section of 1 mm2 have an average current density of 6-10 A. Currents of this magnitude flow without overheating or burning of insulation. According to the PUE, an additional 40% must be added to protect the shells.
A limit of 6 A ensures the operation of the wiring without reference to time. An upper limit of 10 A indicates the permissible short-term load. With an increase in current strength up to 12 A, its density also increases, which leads to burning of the insulation.
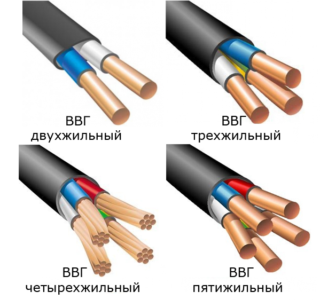
By wire marking
Apartment wiring is mounted using VVG-ng and VVG cables. The first is not subject to fire, designed for indoor, land and outdoor work. The material is available with 2-4 cores, with a cross section of each from 1.5 to 35 mm2.
Experts believe that for point lighting, a cable with a cross section of 0.5 mm² is enough, for a chandelier - 1.5 mm², for socket devices - 2.5 mm².
How to choose a conductor cross section
To choose the correct cross-section of the conductor, it is worth considering the length of the communications, the method of their arrangement, the features of the machines.
By type of wiring
By location, the wiring is hidden and open. In apartments, the second option is more often installed with the laying of a copper cable in the gate. To select its section, they are guided by the data of the table.
| Power, W | Current strength, A | Copper conductor | |
| Section area, mm2 | Diameter mm | ||
| 100 | 0,43 | 0,09 | 0,33 |
| 200 | 0,87 | 0,17 | 0,47 |
| 300 | 1,3 | 0,26 | 0,58 |
| 400 | 1,74 | 0,35 | 0,67 |
| 500 | 2,17 | 0,43 | 0,74 |
| 750 | 3,26 | 0,65 | 0,91 |
| 1000 | 4,35 | 0,87 | 1,05 |
| 1500 | 6,52 | 1,3 | 1,29 |
| 2000 | 8,7 | 1,74 | 1,49 |
| 2500 | 10,87 | 2,17 | 1,66 |
| 3000 | 13,04 | 2,61 | 1,82 |
| 3500 | 15,22 | 3,04 | 1,97 |
| 4000 | 17,39 | 3,48 | 2,1 |
| 4500 | 19,57 | 3,91 | 2,23 |
Settlement via the Internet
In order not to waste time counting manually, you can calculate the cable section parameters online. In the fields of the calculator you will need to enter:
- type of current - alternating or constant;
- material of conductors - copper or aluminum;
- load power - the sum of the power of all devices thrown on 1 wire;
- rated voltage of a network;
- for alternating current - power supply system, single-phase or three-phase system, power factor 1 for the apartment;
- cable management technology - open or hidden;
- the number of load wires - 2, 3.4 with separate insulation or 2-3 in total; for a DC system, all wires are considered, for an alternating one with a single phase - zero and a phase, for an alternating one with three phases - only a phase;
- cable length in meters;
- percentage of allowable voltage drop.
The obtained value is indicative, it will need to be coordinated with professionals and regulatory requirements.
No calculators or tables
For the accuracy of the choice of the cross section, it is worth using the theoretical and actual calculations in a complex way. Buyer needs:
- look at the cable insert about the cross section;
- measure the diameter of the core with a caliper or micrometer;
- calculate the cross-sectional area using the formula S = (z · π · d 2) / 4 (3), where S is the cross-sectional area; z is the number of cores (for a single-core wire z = 1); d is the diameter.
The correct selection of the conductor cross-section will ensure the reliability and quality of the laying of power lines in the apartment. These tables and formulas in practice help to control the work of electricians and verify their calculation results with their own.