To make the house comfortable, it is important to correctly equip the water supply system. Providing round-the-clock water supply with good pressure is more difficult to achieve in high-rise buildings, since each apartment is equipped with autonomous plumbing fixtures.
Features of the water supply system of an apartment building
 Water supply is carried out thanks to engineering lines, water pressure regulators, metering and filtering devices, shut-off and control valves.
Water supply is carried out thanks to engineering lines, water pressure regulators, metering and filtering devices, shut-off and control valves.
The water supply system in the MKD is designed for apartment wiring. The more floors, apartments and sanitary equipment, the more difficult it is.
The main feature of water supply to high-rise apartments is that the liquid must go through several preliminary stages of purification from impurities and disinfection, for example, by chlorination. In private houses powered by a local source, such manipulations are usually not carried out. Only local filters are used.
Design work on the creation of a water supply system in a high-rise building is carried out in accordance with the standards of SP 30.13330.2012. The main points of the document on which engineers rely:
- water compliance in terms of composition and quality with sanitary standards;
- the temperature regime of the hot liquid at the points of tapping is at least 60 degrees;
- the absence of an increase in the hydraulic resistance of valves and pipes during operation;
- the presence of continuous water circulation with a significant distance between the coolant and the consumer.
It is acceptable to combine fire water supply with drinking water.
Components of a central water supply system
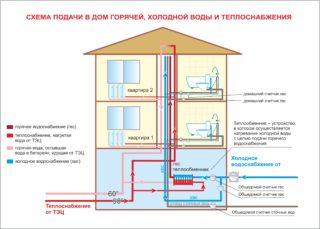 In buildings with many apartments, a centralized water supply system is usually used. It involves connecting to the common highway of most buildings in a city or village. It is notable for the complexity of the design, since it involves the provision of water to hundreds of residential premises with different locations.
In buildings with many apartments, a centralized water supply system is usually used. It involves connecting to the common highway of most buildings in a city or village. It is notable for the complexity of the design, since it involves the provision of water to hundreds of residential premises with different locations.
Cold water is drawn from the surface from natural reservoirs far from pollution sources or from artesian wells. A maximum of 3-story cottages can be fed from the wells.
The centralized supply includes not only water intake, but also the purification of the received moisture with a further direction to consumers. The system consists of the following elements:
- water intake designs for fluid intake;
- pumping stations directing water to the treatment sites;
- cleaning equipment;
- water pipes for transporting water flows to consumers;
- containers for storing moisture reserves.
The functionality of water supply largely depends on high-quality pipe layout and the creation of the necessary pressure in the pipeline. Household appliances and plumbing equipment for work need a pressure of three atmospheres. This indicator is considered a practical minimum of water pressure. In high-rise buildings, an increase in pressure in the internal highway of more than six atmospheres is allowed with the indispensable installation of gearboxes on apartment inputs.
Types of water supply schemes MKD
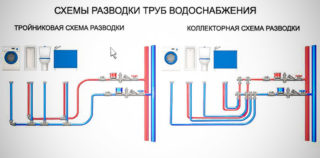 Water supply systems are divided into three varieties:
Water supply systems are divided into three varieties:
- consecutive;
- collector;
- combined.
A sequential scheme of cold or hot water supply for a house is considered traditional. The people called it tee because of the use for wiring of the same name fittings. The main feature is the parallel installation of hot and cold lines.Mounting such a system is simple, it is economical in terms of consumables, but it has significant flaws:
- it is difficult to get to individual sections of the highway;
- it is impossible to supply water to each plumbing fixture;
- It is difficult to detect and repair leaks, breakdowns.
A similar scheme is used only in houses where the apartments are small, with a minimum of plumbing, for example, in studios and dormitories.
In multi-storey new buildings with an expanded layout, involving a large number of sanitary appliances, a collector wiring diagram is being equipped. This option will allow you to use several household appliances at the same time without reducing the pressure at various points of connection.
The principle of water supply is that each consumer is connected in isolation with the collectors of hot and cold risers. The pipeline has few branches, which reduces the risk of leaks and increases throughput. It is easy to hide behind wall panels.
Simple collector water supply systems in multi-unit buildings are easy to maintain, but it is quite expensive to equip them. In addition to additional consumables, the installation of plumbing is not cheap. Installation here is much more complicated than with sequential distribution of water.
Most often, in multi-storey buildings, combined water supply schemes are used. They combine the advantages of the first two options. Installation of equipment is cheaper. Difficulties can arise here at the design stage - wiring planning requires engineering professionalism.
The nuances of supplying hot water to residents of high-rise buildings
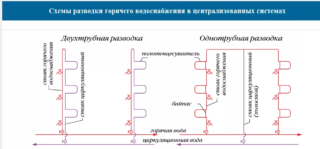 The water distribution in the high-rise building is dual-zone, water is supplied from the hot and cold riser. The hot water supply system in an apartment building is based on the use of looped inlets - top and bottom. They are necessary to maintain high temperatures in the highway. The fluid circulates in the pipeline due to the force of gravity and thermodynamics, even in the absence of water analysis. When the water in the riser is cooled, it flows back into the boiler, and then diverges through the pipes. There is a transfer due to the elevator unit.
The water distribution in the high-rise building is dual-zone, water is supplied from the hot and cold riser. The hot water supply system in an apartment building is based on the use of looped inlets - top and bottom. They are necessary to maintain high temperatures in the highway. The fluid circulates in the pipeline due to the force of gravity and thermodynamics, even in the absence of water analysis. When the water in the riser is cooled, it flows back into the boiler, and then diverges through the pipes. There is a transfer due to the elevator unit.
If the building has many floors, pumping equipment is used to improve the pressure in the pipes. It takes water from the return line. The return is fed to the heater.
The circulation option of hot water supply is more profitable, but some houses still use dead-end DHW systems, where water moves from the heating source through pipes without reverse heating. Usually these are cottages in a couple of floors or industrial workshops. Deadlock wiring is easier to install, but can not always ensure compliance with water temperature and microclimate standards in sanitary facilities.
Hot water mains require thermal insulation, with the exception of connections to individual plumbing fixtures. “Cold” pipes located in basement and wet rooms are also insulated to protect against condensation.
The supply of hot water in a multi-storey building can be carried out open and closed ways. The first type of heating network involves mixing liquid from a pipeline heated in a boiler. After that, water is sent to consumers. Closed heating systems involve surface heating of the liquid without contact of the coolant and the water stream. The latter option is more profitable in terms of maintaining high water temperature.
All buildings under construction or in the process of renovation are equipped with water meters. They are placed at the inlets of cold and hot water pipes - into the building and into each apartment. In the DHW circulation system, metering devices are installed on the supply and return lines.


