Drinking water should be safe for human health, have good taste and no smell. The requirements for it in the Russian Federation are strict, regulated by sanitary rules and norms, which indicate all indicators of water quality.
Checking the quality of drinking water
 Quality control of tap drinking water is assigned to business organizations that provide cold and hot water supply. Verification activities include systematic sampling of water from the water supply and laboratory analysis.
Quality control of tap drinking water is assigned to business organizations that provide cold and hot water supply. Verification activities include systematic sampling of water from the water supply and laboratory analysis.
The frequency of monthly surveys is determined depending on the total number of people served:
- up to 10 thousand people - twice;
- up to 20 thousand –10 times;
- up to 50 thousand - 30 times;
- up to 100 thousand - 100 times.
With an increase in the number of residents connected to one water supply network, the number of inspections increases by one for every five thousand people.
In private homes not connected to the central supply system, water is taken from wells and boreholes. The quality control should be carried out by the owners of the premises themselves in order to determine the amount of harmful impurities. It is possible to avoid health problems when conducting research twice a year - the composition of the water is constantly changing. Filtration systems reduce the risk of harmful elements entering the food and drink.
Main characteristics
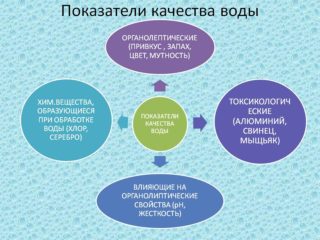
 Quantitative and qualitative components of water from natural sources depend on geographical and climatic conditions, the structure of aquifers. To find out how safe the liquid is, it is examined according to certain criteria.
Quantitative and qualitative components of water from natural sources depend on geographical and climatic conditions, the structure of aquifers. To find out how safe the liquid is, it is examined according to certain criteria.
The main indicators that are being tested: organoleptic, physico-chemical and bacteriological.
The first category involves the assessment of smell, color, taste, visual and weight determination of suspensions. In the latter case, the weight of the impurities remaining after filtering the sample is determined. Allowed value is 1.5 mg / l. The remaining parameters are calculated according to the results of more complex laboratory tests.
Hydrochemical testing
Includes testing for hardness, acid-base balance (pH), oxidizability and concentration of dissolved salts.
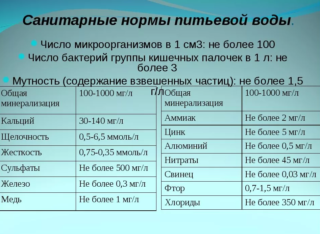
The main indicators of the quality of drinking water in this category and their values according to GOST:
- The pH of the hydrogen indicates the activity of hydroxide ions. If it is equal to seven, water is considered neutral, decreases - acidic, increases - alkaline. Normal levels range between six and nine.
- Hardness is determined by the concentration of calcium and magnesium ions in the water. Normally, it ranges from 7 to 10 mEq / L. Values of water hardness from deep underground sources from 50 meters - from 8 to 10 mEq / L, and with water intake closer to the surface - from 3 to 6 mEq / L.
- Oxidation indicates the concentration of organic compounds dissolved in water. Higher values indicate that the liquid is very contaminated with wastewater. Most often, oxidation is determined by the permanganate method. The indicator should not be higher than 5 mg / l.
- Mineralization reveals the concentration of dissolved salts. Measurement is carried out on a dry residue. The limit of salinity is 1000 mg / l. The optimal run-up of salt concentration is from 200 to 400 mg / l. The amount of calcium ions cannot fall below the value of 25 mg / l, magnesium ions - 10 mg / l.
The temperature indicator during the catchment should be in the range of 7 to 12 degrees. If it is higher, there will be no refreshing effect. Water colder than five degrees poses a health hazard due to the high chance of a cold.
Bacteriological research
The results of bacanalysis give out the concentration of pathogenic microflora. Studies determine the microbial number - the number of microorganisms that are in 1 ml of liquid. For tap water, this value should not be more than a hundred. Artesian springs are least contaminated with microorganisms. The microbial number there is no more than 30. The requirements for tap water according to SanPiN do not allow the presence of protozoa in it.
Pollution from fecal effluents is also determined by the concentration of E. coli in water. It is measured in counts and counts. In the first case, the amount of fluid in milliliters containing one E. coli bacterium is detected. For drinking water, the number of titers should be 300 or more. If the index is calculated in the opposite way. The number of Escherichia coli that are in 1 liter of drinking water is not more than three.
If toxic substances and radiation are suspected, toxicological and radiological studies will be required. The relevance of such analyzes is high if the sources of water intake are located near industrial enterprises.
The quality of the water packaged in bottles is determined by its class. It can be extracted from deep or surface sources, purified water, air-conditioning. In any case, its data should not go against the values of GOST, sanitary and hygienic standards.
Do-it-yourself water research
 For these purposes, devices are used that detect harmful cocking at home. But they are not cheap. In order not to splurge and at the same time be sure of safety, you can conduct tests with folk methods:
For these purposes, devices are used that detect harmful cocking at home. But they are not cheap. In order not to splurge and at the same time be sure of safety, you can conduct tests with folk methods:
- Determination of the presence of salts and impurities. One drop of water is applied to a clean glass and allowed to dry completely. If the glass surface remains without streaks, the water can be considered clean.
- Identification of opportunistic microorganisms, organics and chemistry. Fill a container with a volume of three liters, close the lid and put in a dark place for two to three days. The appearance of a greenish coating on the walls indicates the presence of microorganisms, the precipitate indicates an excess of organic matter, and the film on the surface indicates the presence of hazardous chemicals.
- Home drinking test. Prepare a weak potassium permanganate solution, approximately 100 ml, and pour into a glass of water. The liquid should lighten. If a yellowish tint appears, you should not drink such water.
Such tests will not be able to show all the pollution, for this large-scale studies are needed. If the tap liquid sharply smells of bleach or other chemicals, has acquired an unnatural shade and taste, oil stains on the surface or foreign impurities have appeared, a laboratory examination of tap water will be required. You can contact your local sanitary and epidemiological station.
Specialists will make a fence, conduct tests for toxicity and organoleptics, evaluate the fluid by chemical and microbiological indicators in accordance with generally accepted standards. Based on laboratory tests, they will recommend suitable filtration systems.
Water from the surface of the earth and from its bowels is used in the food, household, agricultural and industrial sectors. Quality indicators are regularly reviewed and measured. This is due to increasing year by year pollution of water sources. However, the requirements for drinking water remain unchanged. These are vital characteristics, since water directly affects people's health.


