Well drilling is a technically complex and responsible process. However, the formation of the source column is not a reason to immediately drink water from it. First you need to pump the hydraulic structure thoroughly. The speed of the procedure depends on the correct choice of the pump for pumping the well after drilling, as well as on the type of soil on the site.
Well pumping

Source pumping is the process of sampling the first volumes of water from a mine. Since the liquid, contrary to the expectations of the master, is completely unsuitable for use. More often it contains dirt and oil from the rig, impurities of rocks, sand, clay. If you do not pump the source in a timely and sensible manner, over time it will silt up. As a result, its performance will drop. And later the water will completely disappear.
The duration of the buildup takes from 1-2 hours to a day or more. It all depends on the type of soil, the depth of the structure. The well on the sand is washed faster. Work on clay layers or horizons on limestone requires a longer buildup. But after the hard work of the pumping equipment, all particles of dirt, inaccessible even to the filter, are washed out of the aquifer as close as possible to the mine.
The buildup, flushing of wells is carried out in such cases:
- primary drilling of a source;
- siltation of a hydraulic structure after winter;
- long idle well in the country.
It is especially difficult for owners of sources on clay beds. Here, during washing, a viscous solution forms, which oozes far and deep into the layers of the horizon. It is washed for a long time and is very difficult. As a rule, it is necessary to remove more than 500 m3 of water from a clay trunk in order to obtain a potable resource.
Pumping Methods
For high-quality cleaning of the source, several methods are used:
- Air purge. Under high pressure, an airlift enters the shaft using an airlift. The process requires special equipment with a powerful compressor. Purge is performed only for sources with a depth of not more than 30-40 m. The disadvantage of this method is that dirt with air masses randomly flies up. It is impossible to control their direction. With this technique, there is a high risk of pouring muddy liquid over the entire territory of the site. After all, it is not known how long the source will have to be pumped with gases. Only a specialist should do this purge.
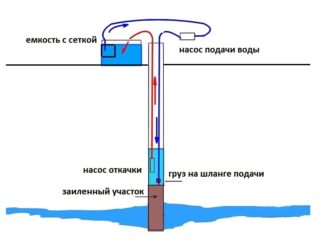
- Water wash. Liquid under high pressure is poured either directly into the shaft pipe (direct flushing), or into the annulus with its further outlet through the barrel of the casing.
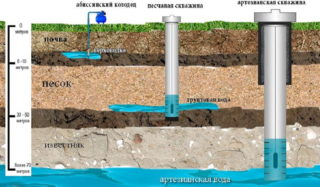
- Use of a bailer. This method is well suited for shallow sources (Abyssinian surface needle or sand). The principle of work is simple. With the help of an electric winch, the master lowers a heavy driving glass with a shutter in the lower part to the depth of the structure. When it falls, the sleeve grabs dirt, silt, well deposits. When the choke is lifted, water exits, the choke closes, sand, debris, rocks rise up. Here, the master empties the driving glass and then continues to work until the source is completely cleaned.
- Flushing and pumping wells with a powerful pump (motor pump). This is the easiest way by which you can “stir up” and launch a new hydraulic structure.
The duration of the procedure depends on the capacity of the discharge equipment including.
Flushing pump
To rock a well after winter or immediately after drilling, you need to choose the right pump model. Several requirements are presented to him at once:
- Type of equipment. Only submersible and centrifugal. The vibrating unit will not cope with such a volume of contaminated water, and will quickly fail (it will simply burn out or clog). In addition, vibrations will constantly balamute the water, which is undesirable when flushing. The submersible device can be lowered to the maximum necessary depth and dirt can be taken immediately from the points of its maximum accumulation.
- Inexpensive model. It makes no sense to buy an expensive pump for pumping the source. It is possible that the equipment will break down more than once during the performance of work. That is why you need to regularly raise the unit up for inspection, cleaning. So the device will work more reliable. But you need to be prepared for the fact that you have to change 1-2, or even more pumps.
- Powerful. Only high-performance models can handle dirty water. Low-power devices simply do not pull the task. The more productive the unit, the more intensively the source is pumped.
- Permissible dive level. If the source shaft is 40 m, and the pump can only be lowered to a maximum of 35 m, unfortunately, its help will be zero, and the energy consumption will be in vain.
The fact that the flushing was successful will be indicated by the crystal clear water supplied by the pump. Experts say that for a mine with a depth of 50 m or more, it may take 2 days to pump. Not every master can launch a new hydraulic structure in this way.
Work execution technology
The main thing when starting a well with a pump is to properly install it. Lower the equipment almost to the bottom. The distance from the bottom point of the well to the inlet of the unit should be 40-70 cm. If you raise the device higher, this will not give the expected effect. If you lower the pump to the bottom, it will pump only rocks (sand, clay) and will quickly fail. In addition, with a low installation of the unit, there is a high risk that it will simply become dirty in the silt masses. Raising it from there will be extremely difficult.
Mud admixture is diverted either to the nearest ravines or to country roads. The main thing is that it does not bother anyone. Yes, and it is undesirable to drain muddy slurry close to the well, since dirt can ooz into the shallow aquifers again.
The principle of flushing the well looks like this:
- Pumping equipment is lowered into the source shaft to the desired elevation.
- The equipment is plugged in and the dirty water is pumped out. You need to work continuously to get ahead of the water supply source.
- The unit is regularly lifted, washed and again lowered into the well.
- Work is performed until the appearance of completely clean water.
It is important to note that during the buildup, the bottom of the structure may sink. This means that the pump will have to be immersed deeper to completely remove all sludge from the lower point of the barrel.
Common mistakes
When performing source buildup, wizards often make these errors:
- Wrong depth of pumping equipment. To determine it accurately, it is advisable to measure the level of immersion along the cable. In this case, you need to know the length of the shaft of the mine. With a high position of the unit, all sludge remains in place, which leads to even greater problems with the source later.
- Dirty water discharge close to the source. If the slurry is disposed of in this way, there is a high probability of its circulation back to the aquifer.
- Use a safety cord for the pump instead of a strong cable. Unfortunately, the load on nylon is too high when working with sludge masses. The pump just gets dirty in them, and raising it with such a thin device is problematic, no matter how hard you try. Nylon can just break off. The pump will remain in the well, which will require complex repairs.
If the independent pumping of the source is delayed for 3 or more days, it makes sense to get expert advice.
How to deal with siltation
To ensure that the private source is not subjected to siltation, it is important to constantly operate the well. Continuous streams of water simply do not allow the smallest organic particles to settle at the bottom of the mine.
Additionally, you need to monitor the quality of coarse filters. If possible, they should be changed regularly. Otherwise, they simply clog sand, and then silt.
If, however, the source has silted over during the winter, it can be washed out in spring using a narrower casing (the diameter of the string must be smaller than the main shaft). It must be mounted in an existing barrel and under high pressure to supply water to the inner tube. That will erode the sludge and push it through the annulus. If the work is done correctly, the well will function again.
If the silted source is deep (an artesian well), it is often cheaper to drill a new one than to pump the old one. Especially if the building is older than 25 years. And even more so if the well tends to silt up regularly even with its continuous operation.