The stove and chimney are common components of the system. If the firebox is not folded correctly, it can smoke, heat up poorly, the same can be said about the pipe. One of the main conditions for the proper functioning of the channel for the removal of gases is the diameter of the chimney. A certain traction must be created in it, this can only be achieved by coordinating the power of the boiler and the smoker itself.
How the chimney is arranged

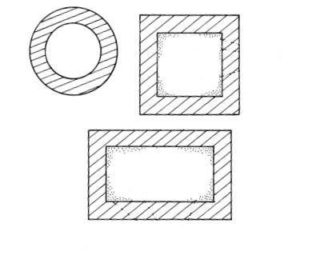
The device of the smoke exhaust channel consists of a pipe, which can be of circular cross section of different diameters or square, rectangular in shape. The system is connected to the boiler equipment through the outlet. In addition to the removal of gases, part of the oxygen enters the furnace through the smoke, which contributes to the combustion process.
The main parts of the chimney:
- Pipe channel. This is the main part of the design. As a rule, inside the device there should be smooth walls so that soot settles less on them and there is no additional resistance to air flow.
- Gate valve. This element is installed at the beginning of the stroke, with it you can partially or completely block the channel, achieving a certain traction force. The damper helps to keep heat indoors with a well-heated stove.
- A condensate collector is a necessary part of the chimney where moisture enters, which precipitates on the inner walls when cooling steam, which is always present in smoke. The location of this device in the general scheme is usually below the vertical riser.
- The inspection window is a small hole in the chimney that is covered by a door so that you can view the channel for the presence of soot, tar deposits and foreign objects in it and, if necessary, remove them.
The draft inside the gas exhaust system is due to the fact that the pressure at the top and bottom of the channel is different. The larger the chimney, the faster the smoke comes out of the stove.
If everything is correctly assembled, the combustion products cannot get inside the heated room.
What are pipes made of?
Four main building materials from which chimneys are made: galvanized steel, ceramics, stainless steel, clay-based brick.
Square chimneys built of brick in accordance with all standards of furnace work are highly fireproof and lack the ability to accumulate soot deposits on the walls. In addition, the material is quite heat-resistant and strong by mechanical standards. The only drawback of brick is its susceptibility to destruction due to the destructive effects of chemical reactions between water and sulfur oxide.
Steel chimneys are convenient in that they allow you to get a channel of any configuration. The disadvantage is the short service life, as the metal has the property to burn through and corrode. More resistant are stainless elements.
Pipes made of ceramic material calmly withstand elevated temperatures and the aggressive environment of settling condensate. The assembly of such a structure is difficult to carry out due to the large mass of elements where a frame of steel rods is used for strength.
- Chimney sandwich
- Asbestos-cement pipes
- Steel chimney
- Brick chimney
Varieties of systems
The type of load-bearing structure determines the category of a particular flue. For this indicator we can distinguish:
- Self-supporting structures.The basis here is a sandwich chimney. A feature of the latter is the ease of installation on the roofing, where the base of the pipe is supported and fixed in the interior of the building. Systems have many limitations on their application, from the temperature of combusting products to chemical instability.
- Near-façade structures are fixed directly to the supporting walls of the building, so there is no need for an additional foundation. The modules that make up the pipe are easy to replace, so this version of the chimney is considered the most economical.
- The smoke exhausts in the form of columns are brick buildings, at the base of which a powerful foundation is laid, usually these are circular or square arrays, vertically going up. There are metal columns, where several buildings are assembled in a single ensemble, the so-called multi-barrel system.
- Chimneys collected on the principle of trusses have found application in areas with unstable seismic conditions; they have additional supports.
- Mast structures consist of a support tower stretched on cables, where one or more pipes pass inside.
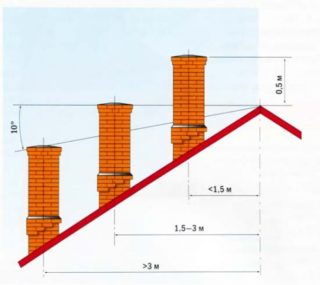
High-altitude dymars experience tremendous wind loads. To make such structures more stable, it is necessary to fix them at the mid and highest point or along the entire length with brackets if the pipe is near the load-bearing wall of the house.
Chimney Options
The main parameters of the chimney include its internal configuration, diameter or cross-sectional area and height. All these parameters are selected in a complex to create the necessary traction for a particular boiler equipment.
The oval cross-section has the property of twisting the combustion products in a spiral direction due to the uneven heating of the vertical walls, while they receive additional acceleration.
A rectangular cross-section works well, but on the condition that inside the surface is close to perfect in smoothness. Otherwise, roughness and irregularities lead to inhibition of the flow inside.
The diameter and height of the structure must correspond to the power of the heating installation, with which it is supposed to heat the house.
How to calculate the diameter of the chimney
Different heating appliances have their own draft requirements. The same calculation method cannot be used for a fireplace, stove and gas boiler, since the volume and design of the furnaces are different, the amount of combustion products and the rate of their formation are different. For the practical determination of the diameter of the pipe for all types of equipment, their own formulas and rules have been developed.
For a bath stove
Since the designed sauna stove has a furnace, it is easiest to calculate the diameter of the chimney for it, starting from the size of the furnace compartment. The regularity of experimentally derived is that when a fuel is burned a certain amount of gas is emitted, the volume of which will effectively go outside if a proportion of 10 to 1 is observed, where the first number of units characterize the furnace size and the second number is the cross-sectional area of a round pipe.
If we are talking about a smoke erected from a brick, it does not matter square or rectangular, its inner passage should be larger than the blower door or ash chamber. The excess should be somewhere in 1.5 times.
The minimum size of the square channel for a low-power furnace should be 140 mm / 140 mm. The length of the chimney for a wood-fired stove in a bathhouse can be arbitrary.
For gas boiler equipment
A gas boiler, like other heating plants, is characterized by power, expressed in kilowatts of thermal energy per unit area. The diameter or internal size of the pipe directly depends on this power.
The norm of the chimney for a gas boiler of a rectangular channel shape must comply with the rule that there are 5.5 cm² of passage per 1 kilowatt of unit power. The diameter of the round chimney should not be narrowed compared to the diameter of the outlet of the combustion chamber in a gas installation.
Calculation of the chimney for a wood-burning stove
First, the volume of combustion products entering the smoke channel is found by the formula
Where, B - the rate at which firewood burns (depends on the type of wood and is determined by the tables), V - the amount of air required for the combustion process, t - temperature of gases in the pipe;
Then carry out the calculation of the chimney, according to the formula:
Having determined the total area of the passage, based on the obtained diameter, it is easy to calculate the inner sides of a square or rectangular smoker.
The rule that the internal size cannot be less than the size of the blower door is also relevant here.
Connection of a collective smoke channel
The need to have one smoker for several households arises if there is a need to save money, space or there is no way to organize a different exhaust gas system. From a technical point of view, this is a perfectly acceptable option and such structures are effectively operated. In this case, two options must be considered:
- Connection to the device of the same type of heating device.
- Connection to the line of fundamentally different thermal installations, for example, a gas boiler and a brick fireplace.
In the first case, there is no difficulty in including the equipment in a common channel, since for such devices the smoke channel can be calculated for one traction index at which all units will work correctly.
In the second option, it will not be possible to coordinate the device, since the chimney for the fireplace should occupy 1/10 of the furnace area, which is too much for the boiler. The result is either excess or insufficient traction for one of the devices, which is fraught with negative consequences.
The best solution would be to use a two-channel system. Its essence is that the inner space of the pipe is divided into two channels, each of which is designed for its own heating equipment.