The supply system that mixes the air in the room is called the supply ventilation. Combined devices simultaneously heat the flows. In buildings, there is a difference between natural and forced air supply. The first type is carried out due to the pressure difference between the flows, and in the second case, fans and other units are installed.
The need for efficient ventilation
Supply and exhaust ventilation differs from air conditioning in that it uses external air from the street. Stale air has a negative effect on health and emotional state, so you need to take care of the fresh atmosphere. Waste masses are discharged by duct exhaust.
In a room where people are constantly located, the required air exchange is 30 m3 / h per person, and in the absence, conversion on standby is recommended. For an apartment with 4 residents, ventilation should change the air at the rate of 120 m3 / h, and in the absence of people - 40 m3 / h.
Window units made of metal-plastic with double-glazed windows supply air at the level of 2 - 5 m3 / h and do not even provide on-duty ventilation, despite the built-in devices for micro-ventilation, self-ventilation, and air conditioning. The emission of harmful substances, which saturates the microclimate from furniture, modern decoration, matters. In such conditions, an organized supply air ventilation unit is required.
Advantages and disadvantages
Ventilation in the apartment is organized compactly, special technologies help reduce noise. Modern installations meet the increased requirements for cleaning and filtering air masses. Enclosures and ducts are distinguished by their pleasant appearance and can be hidden from view behind a suspended ceiling or decorative elements of walls.
The positive aspects of using the supply and exhaust ventilation system:
- meeting the need for air exchange;
- branching scheme with the given characteristics of work in each room;
- the possibility of using heated exhaust streams to increase the temperature of the incoming air (recovery).
Ventilation in private homes supplies air to all functional areas. Management is carried out in an automated way and allows you to set the feed rate in different rooms, as well as adjust the degree of heating.
Supply ventilation has several disadvantages:
- it is difficult to mount in an operated building; there is not always a place;
- the use of noise isolation will take even more usable space;
- a forced feeder requires material costs.
The street air masses are cold in winter, so organization of heating is required. To clean the streams of dust and elementary particles, you need to install separate filters or a disinfection system.
Main goals
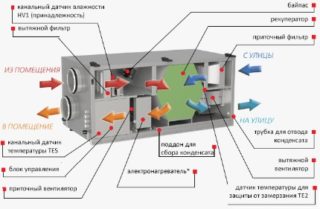
The air handling unit filters the air and delivers the cleaned volumes to the main for subsequent distribution in the rooms. In warm time, cooling of the streams is organized, and in winter - heating. The circuit includes a water, charcoal filter and electric heaters. The speed is given to the flows with the help of fans, the control is carried out by automation.Insulating material is used to protect against cold and noise. If the supply system is equipped with an air cooler, it is called a central air conditioner.
Ventsystem provides:
- the intake of the required volume of air from the outside;
- regular updating of the microclimate, and not just individual episodes;
- lack of sharp flows and drafts;
- reduction of dust, the number of insects, noise.
Supply ventilation does not solve such issues as maintaining the required humidity and temperature of the internal space.
Supply ventilation classification
The general ventilation system supplies air to all rooms of the building, this scheme is used in industrial volumes. Harmful substances in the production process are distributed throughout the space of the workshop, and there is no way to capture them at the local level. Air enters the work area (1.5 - 2.2 m above floor level). A local ventilation unit delivers air to specific areas or rooms.
By the presence or absence of ducts
In the channel scheme, air flows move through pipelines of a certain section. The risers and shafts in the walls are carried out during construction or during the reconstruction of the task. On them, air inflow and removal can be simultaneously carried out.
The hinged pipeline is located under the ceiling. It includes a central unit for processing air masses, for example, disinfection, filtration, heating or cooling. Placement of such a pipeline requires space, so channel systems are almost not installed in urban apartments with a wall height of 2.45 - 2.6 meters. Channel schemes are used in public places where there is a large crowd of people.
Channelless ventilation in the apartment involves the installation of a forced turbine in a wall enclosure or floor slab, while the flow is fed into one room.
By design
The supply ventilation chamber attracts consumers by combining with specialized equipment to change the properties and characteristics of the microclimate. During the injection of air, it can be heated and cleaned.
Functional diagram is performed in two designs:
- Monoblock. It includes one module, where the necessary devices are located for high-quality and uninterrupted operation of the ventilation installation. The place is usually an exterior wall or window unit frame. It does not differ in work efficiency, because due to the limited arrangement of fans the entire area of the apartment is not covered.
- An extensive network contains several injection units as part of a common highway using various types of hoods and pipes that supply fresh air to all rooms and office premises of an apartment or house.
The pressure in the system is created by an external module with a turbine, and the inlet is located in a residential area where clean air is needed. Installation of a ventilation unit is not permitted in the area of a bathroom, bathtub or kitchen.
By the method of ventilation
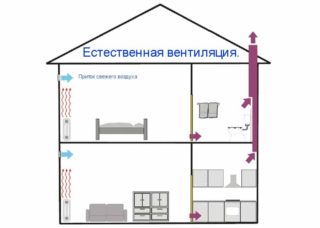
Most apartment buildings use natural ventilation. This involves the flow of air without coercion, the movement is due to the difference in the pressure of the external and internal air and temperature changes. Streams enter the apartment on their own through the cracks in the window and doorways. The spent masses are removed through the ventilation shaft, which has a branched structure.
The natural system belongs to the available species and does not require investments. The disadvantage is that regular malfunctions occur due to insufficient fresh air.Opening the openings partially solves the problem, but in winter a cold influx reduces the comfort of the room, and noise penetrates the windows.
The forced air purification system for the apartment provides a stable flow of oxygen, which is independent of the weather. Air is supplied by the fan blades, automation controls the flow rate, adapts it to the existing needs of air exchange. The system does not require human intervention, which makes it convenient.
Equipment Models
The ventilator is mounted in the outer wall and through the duct through the fan delivers fresh flow. The supply valve enhances the natural intake, its functioning is determined by the weather outside the window. In the summer, due to the small difference in temperature outside and inside, such a device shows little efficiency.
The breather combines ventilation and filtering of air masses. The compact device is placed in the wall and is able to ventilate a room with an area of up to 50 m2. The device has one or more filters that are regularly replaced with new ones. Its use is relevant in homes near gassed motorways or near industrial complexes.
Fans are axial or radial. The first view captures the flow of the blades and moves it along the central axis, with no radial distribution. Diametric turbines change the direction of the air; they are used at low resistances in the ventilation system.
Noise suppressors reduce the aerodynamic sound of streams; there are plate and tubular types in design. Their feature is the large curved area of the insulating surfaces, which are damped by vibration and noise. They are installed between the fan and the beginning of the pipeline.
Ways to optimize supply ventilation
Air purifiers are used to filter the supply air. The principle of their work, material and design are selected depending on the required microclimate characteristics. In ventilation systems, filters are divided according to the degree of purification; there are five in total. The smaller the particles are retained by the membrane, the higher the grade of purifier. Filters are characterized by dust capacity and aerodynamic counteraction.
Ventilation can work in contact with the heating system or replace it in some cases. The installations use electric or water heating elements. The first type is powered by electricity and converts energy into heat. Water elements are energy exchange chambers where a heated liquid transfers heat to the air.
Air recovery
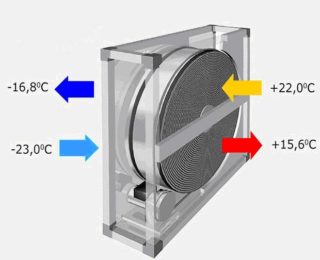
The technology is to reuse heat with recuperators. The procedure is performed in heat exchangers, where a heated removed stream transfers heat to the incoming cold mass. The process saves money for heating the inflows through the secondary use of the energy of the leaving masses, the creation of which has already been spent.
Heat exchangers come in two forms:
- Cross plate heat exchanger. In the unit, the supply and exhaust air do not mix, but pass through numerous channels with common walls. Efficiency reaches 70 - 85%.
- Rotary type recuperator. The exchange of energy occurs faster than in the previous form, while the flow and the removed flows are partially mixed. The efficiency is equal to the values of the cross plate device.
There is a recuperator with an intermediate exchange chamber. The inflow and the pulled mass are distributed in space, and the heat between the channels is transferred through the movement of liquid energy between the individual chambers. Efficiency is 50-60%, but such an application is justified if the exhaust air is heated and too dirty to mix.
Soil heat exchangers
To heat the feed stream in the supply ventilation, a thermal geothermal pump is used. This is a heating system that uses the heat of the earth's interior in the geothermal zones of the planet. Temperature differences help increase functionality and lower costs. Often geothermal pumps work in conjunction with solar heating.
Closed systems of geothermal heat are divided into types:
- Horizontal, when the collector is located at a shallow depth below the freezing mark of the soil, the pipes are set sinuously. The layout requires a large area.
- Vertical, if the pipeline is placed standing to a depth of 200 m. The option is used when the house is located in a small area or there is a danger of surface damage, for example, landslides.
- Water type. Pipes are located in bends or in an annular manner in the thickness of the reservoir below the freezing mark. A cheap method, but there are certain restrictions on the choice of a reservoir.
Open systems use for heat exchange the fluid passing in the heat pump system with an open cycle. This is re-circulation after passing through the highway when returning to the soil. The option is implemented in the presence of a large volume of clean water and official permission to use land water.