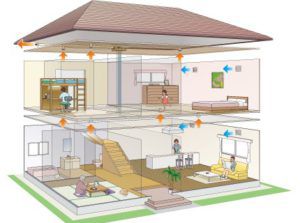
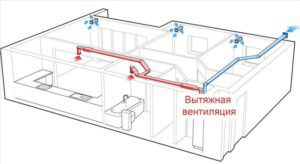
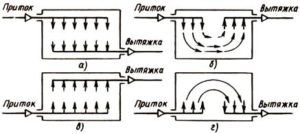
The correct process of air circulation is ensured by a normal ventilation system in the room, one of the criteria for determining which is the rate of air exchange.
The process of ventilation in the premises is due to the fact that polluted air is excluded from the work area, thanks to the natural exhaust ventilation system of the channel type.
Air exchange rate
The nature of the air exchange in the room directly depends on the type of construction:
- industrial purpose;
- "Change house";
- commercial premises.
For each type of room, a regulated indicator of the frequency of air exchange is presented.
The calculation of air exchange takes into account the type and characteristics of the equipment used in the room:
- Production type of fans;
- Household ventilation system;
- Holistic exhaust ventilation system;
- The use of recovery, recycling or PVA;
- Specialized air conditioning.
Multiplicity norms
When arranging a ventilation system, it will be necessary to calculate the amount of air in the working area for an hour, for this, several basic methods for determining the norm are distinguished. Determining the frequency of air exchange, the most reliable and relevant method is based on the choice of a norm indicator, based on the type and purpose of the building.
According to the table of calculated data, the ratio is found by the formula:
L = Vpom * KR (m3 / h),
in which L– data of a complete air exchange process; Vpom - calculated volume of the building, m3; KR - rate indicator (tabular).
Standards for the purpose of buildings are determined based on data from specialized design documentation of buildings and structures, which indicate the rate of air exchange:
- SNiP 2.08.01-89;
- SNiP 2.08.02-89;
- SNiP 2.09.04-87;
- SNiP 2.04.05-91.
Table 1. Air data and indicators of the multiplicity of the air exchange process in residential buildings (calculated) (SNiP 2.08.01-89 *)
| Purpose of construction | T Information | Multiplicity indicator | |
| Hood (m3/ h) | |||
| Flat | 18 (20) | 3 | |
| Dwelling with “t” less - 31 ° С | 20 (22) | 3 | |
| Kitchen: with electrical appliances with appliances, on gas |
18 | 60 75 90 |
|
| Bathroom (separate) | 25 | 25 | |
| Dressing room (separate) | 18 | 25 | |
| San. node + shower | 25 | 50 | |
| Shower compartment (connected) | 25 | 5 | |
| Lavatory (connected) | 16 | 25 (per 1 urinal) | |
| Wardrobe area | 18 | 1,5 | |
| Corridor in an apartment block | 18 | – | |
| Flight of stairs | 16 | – | |
| Premises for cultural events | 18 | 1 | |
| Washing and cleaning room | 15 | 7 | |
| Departments for the organization and storage of linen, personal items, sports equipment and household goods | 12 | 0,5 | |
| Medical isolation ward | 20 | 1 | |
| Repair boxes for elevators | 5 | 0,5 | |
| Garbage collection unit in prefabricated apartment buildings and dormitories | 5 | 1 |
For residential buildings and structures located in the corner, this value of the multiplicity should be taken in the calculations - 2 degrees higher, regulated in the table of norms.
In the machine lift compartment, the “t” air exchange should not exceed 40 degrees in the summer.
For older people and citizens with disabilities, a different than normal air exchange rate is provided.
Advanced air exchange calculations
To verify performance, an in-depth calculation of air exchange is proposed. The data for 1 hour are used in the specific calculation equation, the "V" of the room provided for 1 subject (normal) is taken as the basis:
L = L1 * NL (m3 / h),
where "L1" is the estimated volume (normal) for one subject, m3 / h * people; “NL” - the total number of entities located in the building at the same time.
Norms assume the regulated value of air, in m3 / hour:
- "20" - with minimal activity;
- "45" - with small physical exertion;
- “60” - with increased activity.
Also, the calculated data allows us to determine and select the most optimal climatic equipment, taking into account the data on the nature of ventilation and air conditioning:
- specific calculation for one unit of equipment;
- determination of the calculated indicator per unit area.
Features of the calculation of air exchange in the room
Before arranging the ventilation system in the room, it is necessary to determine how the air exchange process will take place. So, in most cases, provides for the direct release of air through the wall to the outside. This is due to an axial fan or a system of branched ducts, using a special ventilation pipe or centrifugal scroll.
Based on the obtained values, equipment is selected in the room.
Also of great importance is the ratio of the overall dimensions of the entire system to its specific amount of passed material, and air loss per meter of the system.
Pressure related to losses in the ventilation system is directly related to the air exchange flow in the room pipe system. This characteristic plays a large role, which must be taken into account when calculating the indicator and choosing climate technology.
With an air exchange system of 1000 m3 \ h, the most optimal size “D” will be an air duct system of 200 - 250 mm.
As a result, using a large diameter duct, a rather low resistance index and minimal values of equipment performance losses are formed.