Today in modern construction there are branches in which studies are conducted to improve the construction technology, they also improve the quality during operation, the air exchange in the building is no exception. Problems in this area are relevant and are solved by selecting the multiplicity for the ventilation system. Full-scale tests are conducted and standards are written based on them. The most successful country in this matter is the United States. They developed the ASHRAE standard, using the experience of other countries, namely Germany, Denmark, Finland, and their scientific developments. In the post-Soviet space there is also a developed analogue of such a document. In 2002, ABOK developed the standards “air exchange standards for public and residential buildings”.
The construction of modern structures is carried out with the calculation of increased insulation and high tightness of windows. Therefore, optimal air exchange is very important in such cases to comply with sanitary standards and the corresponding microclimate. It is also important not to damage energy conservation, so that in winter the ventilation does not draw all the heat, and in the summer - cool air from the air conditioner.
To determine the calculation of air exchange in rooms, except for hospitals, a new method was created, which is described in ASHRAE 62–1–2004. It is determined by summing the indicators of the value of fresh outdoor air, which is supplied directly for breathing, given the area of the room, falling on one person. As a result, the value turned out to be significantly lower than the later edition of ASHRAE.
Air exchange rates in residential buildings
When carrying out the calculation, it is necessary to use the table data, provided that the saturation level of the malicious components is not higher than the MPC norms.
| Premises | Air exchange rate | Notes |
| Living sector | Multiplicity 0.35h-1, but not less than 30 m³ / h * people |
When calculating (m3/ h) according to the multiplicity of the volume of the room, the area of the room is taken into account |
| 3 m³ / m² * h of residential premises, with an apartment area of less than 20 m² / person. | Rooms with air enclosures require extra hoods | |
| Kitchen | 60 m³ / h for electric stove | Air supply to living rooms |
| 90 m³ / h for use with a 4-burner gas stove | ||
| Bathroom toilet | 25 m³ / h from each room | Same |
| 50 m³ / h with a combined bathroom | ||
| Laundry | Multiplicity 5 h-1 | Same |
| Dressing room, pantry | Multiplicity 1 h-1 | Same |
In cases of non-use of premises for housing, indicators are reduced in this way:
- in the area of residence at 0.2h-1;
- in the rest: kitchen, bathroom, toilet, pantry, wardrobe for 0.5h-1.
In this case, it is necessary to avoid the ingress of running air from these premises into residential buildings, if it is present there.
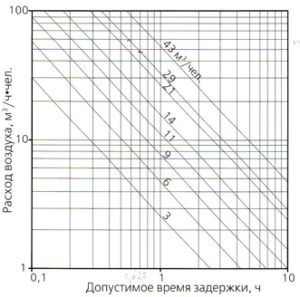
In cases where the air entering the room from the street passes a large distance to the hood, the air exchange rate also increases. There is still such a thing as delayed ventilation, which implies a lag in the ingress of oxygen from the outside before it begins to be used in the room. This time is determined using a special chart (see figure 1), taking into account the lowest rates of air exchange in the above table.
For example:
- air consumption 60 m³ / h * people;
- volume of housing 30 m³ / person;
- time delay 0.6 hours
Air exchange rates for office buildings
Norms in such buildings will be much higher, because ventilation should effectively cope with a large amount of carbon dioxide emitted by the office staff and the equipment located there, remove excess heat, while supplying clean air. In this case, there will not be enough natural ventilation, the use of such a system today cannot provide the required hygienic and air exchange standards.During construction, hermetically sealed doors and windows are used, and the panoramic glazing device completely limits the ingress of air from the outside, which leads to air stagnation and a deterioration in the microclimate of the housing and the general condition of the person. Therefore, it is necessary to design and install special ventilation.
The main requirements of such ventilation include:
- the ability to provide sufficient fresh clean air;
- filtration and disposal of used air;
- lack of exceeding noise standards;
- convenient management;
- low level of energy consumption;
- the ability to fit into the interior and have a small size.
The conference rooms require the installation of additional supply devices, and the hood must be installed in the toilets, corridors and in the halls for copying. In offices, a mechanical hood is mounted in cases where the area of each cabinet exceeds 35 square meters. m
As practice shows, with the incorrect distribution of a large flow of air in offices with low ceilings, a feeling of draft is created, and in this case, people demand to turn off the ventilation.
Organization of air exchange in a private house
A healthy microclimate and well-being depend largely on the proper organization of the supply and exhaust system in the house. During the design process, ventilation is often forgotten or given little attention, thinking that one hood in the toilet will be enough for this. And often the air exchange is organized incorrectly, which leads to many problems and poses a threat to human health.
In the case when there is insufficient output of polluted air, the room will have a high level of humidity, the possibility of infection of the walls with fungus, fogging of windows and a feeling of dampness. And when there is a bad influx, there is a lack of oxygen, a lot of dust and increased humidity or dryness, it depends on the season outside the window.
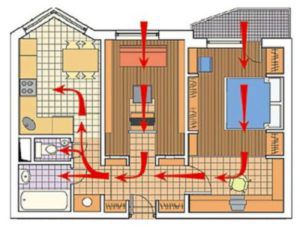
Properly arranged ventilation and air exchange in the house looks like this as shown in the figure.
The incoming air into the dwelling must first pass through the window leaf or open window sashes, the supply valve is on the outside of the dwelling wall, then, passing through the room, it penetrates under the door leaf or through special ventilation openings and enters the bathrooms and kitchen. It exits through the exhaust system for longer.
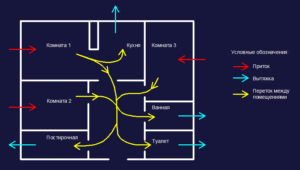
There is a different way of organizing the exchange of air in the use of ventilation systems: mechanical or natural, but in all cases, air flows from residential areas, and goes into technical areas: a bathroom, kitchen and others. When using any system, it is necessary to arrange ventilation ducts in the inner part of the main wall, this will allow avoiding the so-called overturning of the air flow, which means its reverse movement, as shown in Figure 2. Through these channels, the exhaust air is taken out.
What is air exchange for?
Air exchange is the flow rate of the supplied external air m3 / h, which enters the building using a ventilation system (Figure 3). Environmental pollution in living rooms comes from the sources located in them - it can be furniture, various fabrics, human consumption and vital products, household products. This also happens through gas generation from exposure to carbon dioxide exhalation by humans and other vital processes of the body, different technical fumes that may be present in the kitchen from gas burning on the stove and many other factors. Therefore, air exchange is so necessary.
In order to maintain normal air performance in homes, carbon dioxide CO2 saturation should be monitored by adjusting the ventilation system for concentration.But there is a second way, the more common one is the method of controlling air exchange. It is much cheaper and in many cases more efficient. There is a simplified way to evaluate it using table 2.
| Class by
GOST |
Air quality specifications | The flow rate of incoming air per 1 person, m3/ (hour * people) |
| IDA1 | High | > 54 (value at face value 72) |
| IDA2 | The average | 36-54 (value at face value 45) |
| IDA3 | Acceptable | 22-36 (value at face value 29) |
| IDA4 | Low | <22 (nominal value 18) |
But when designing a mechanical ventilation system in a house or apartment, you need to make a calculation.
How to check if ventilation works?
First, it is checked whether the hood is working, for this it is necessary to bring a sheet of paper or the flame from the lighter directly to the ventilation grill located in the bathroom or in the kitchen. The flame or sheet should bend towards the hood, if so, then it works, and if this does not happen, the channel may be blocked, for example, clogged with leaves or for some other reason. Therefore, the main task is to eliminate the cause and provide traction in the channel.
In cases where the draft is unstable from the neighbors, the air flow can go to you, while bringing odors to your apartment, this is a sign of reverse thrust. To eliminate it, it is necessary to mount special blinds, which will be closed when the reverse draft appears.
Conclusion
When building your own home, you must pay the necessary attention to ventilation in the house or apartment. And to invest the necessary amount in the creation of a correct and modern air exchange hood, which will make it possible to get the most comfortable microclimate and eliminate the threat of various diseases to your health in case of improper installation.