In general, ventilation is understood as a set of devices that in a room of one type or another carry out high-quality air exchange to achieve an optimal microclimate for a person.
Modern ventilation is able to provide constant support at a qualitative level of the main parameters of the air mixture in various premises.
Existing classification of ventilation systems
Nowadays, there are a large number of types of ventilation systems, which is due to the different purpose of the premises, the nature of the process that goes through there, the type of emissions that must be removed from the air mixture and the like.
Depending on this, the following types of ventilation systems are distinguished:
- the appearance of pressure, which leads to the movement of air flows - with a mechanical or natural type of motivation;
- depending on the destination - exhaust and supply;
- in the area of its operation - general exchange and local;
- depending on their design features - channelless and channel.
Consider all the above types of ventilation in more detail.
By pressure
As already noted, this classification implies the presence of two varieties: natural and mechanical. Let's get acquainted with their features.
Natural ventilation
The movement of air flows in the case of using this type of system is carried out:
- due to different levels of air temperature inside and outside the room;
- as a result of different air pressure at the lower and upper levels;
- due to the effects of wind pressure.
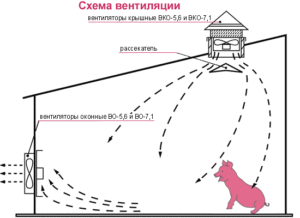
Aeration is often used in production shops where significant heat is generated, and the concentration of dust and other contaminants does not exceed 30% of the normal value. Its use will not give any result in cases where, under the conditions, the flow of external air causes the formation of condensate or fog, and also if it is necessary to pre-treat the supply air mixture.
In a room with excess heat, the air mixture will always be warmer than the one that is outside. As a result of this, heavy air from the outside when ingested will displace lighter warm air from there. Therefore, in a confined space there will be a natural movement of air, which was caused by an excess of heat, such as that caused by the influence of a fan.
Systems with a natural type, where the movement of air flows is carried out as a result of different pressure of the air column, imply that the height difference between the place of air release and the point of its intake was at least 3 meters. At the same time, it is recommended that the air ducts located horizontally do not exceed 3 meters in length, the flow velocity in them is no more than 1 meter per second.
When exposed to wind pressure, the air mixture moves as a result of increased pressure from the side of the room facing the wind, and reduced pressure from the opposite side or on the roof. If at the same time there are openings in the walls of the building, then on the first side the air flow will enter the room, and on the other hand, exit it. In this case, the flow velocity will depend on the magnitude of the pressure differences.
Such a ventilation system is very simple and does not imply the use of any equipment or electricity. But its dependence on wind speed and its direction, temperature and some other factors does not allow to effectively solve complex problems of airing rooms.
Mechanical ventilation
These types of systems imply the presence of special equipment - fans, heaters, engines, which allows you to move air currents over long distances. This requires the cost of electrical energy, although its functionality does not depend on the environment and its conditions.
The use of such systems allows for additional processing of air - its heating, cleaning, humidification and the like.
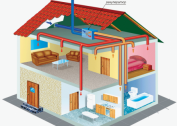
It should be noted that in reality mixed ventilation is most often used - its presence implies the use of elements of a mechanical and natural system.
Purpose: supply system
Supply ventilation systems are used to supply fresh air to the ventilated room instead of the vented one. When using it, the air mixture supplied to the room can be subjected to additional processing - heating or cooling, filtration, and humidification.
Exhaust system
The exhaust system, on the contrary, ensures the removal of heated or contaminated air mixture from the room.
Most often, both exhaust and supply systems are used at the same time, due to which the exhaust air mixture is constantly replaced with a fresh one.
But sometimes there is only one system. In this case, air enters the room from adjacent to it or from the outside through special openings in the walls or is removed from it outside or into adjacent rooms.
Features of local ventilation
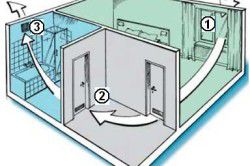
Unlike all of the above ventilation systems, which are of general exchange types, that is, those that ventilate the entire space of the room at once, the local ones ventilate only certain places.
Moreover, such systems can both supply air to the right places - the local ventilation system of the supply type, and removes the exhaust mixture from them - the exhaust system.
Local supply system
Among the supply systems used in specific places, there are:
- air showers;
- curtains;
- oases.
The first type is a concentrated air flow supplied at considerable speed to a specific point in the room, most often a workplace.
Curtains are used to create partitions from the air or to change the direction in which the air flow moves.
The last type is the sections fenced off from the entire room into which the low-temperature air flow is directed.
Often in production, a general exchange system is used at the same time - to remove pollution immediately from all over the space, and local, which provides maintenance of individual parts of the room.
Local ventilation
A similar system is used when the place where pollution occurs is completely localized. Moreover, there is almost always a need to prevent the movement of contaminants throughout the room.
The most effective in such cases are the suction - varieties of shelters, cabinets, side suction, umbrellas, covers for all kinds of appliances and the like.
Often their use is highly effective, since they quickly remove contaminants directly from workplaces, preventing their occurrence in the rest of the space.Since at the same time a high concentration of pollutants occurs, the operation of the system allows you to achieve an excellent sanitary effect, along with this it displays very little air mixture.
But local systems are not ways to solve all the requirements put forward for ventilation. So, not all pollution in the air is localized, more often they are dispersed throughout the available space. At the same time, the supply of the air mixture to separate parts or its withdrawal from them does not ensure the achievement of the required parameters of the air environment.
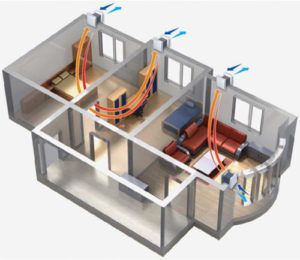
Supply and exhaust systems for the entire space
Ventilation of the general exchange variety is designed to work immediately with the entire space of the room. A similar type of device ensures that the inside of the room is clean air from the outside.
Exhaust type provides an effective conclusion of the used air together with any pollutants from the entire volume of the room. Its simplest example is a conventional exhaust fan, there are also many more complicated devices.
Systems with and without channels
Regardless of the above types of systems used, all of them are equipped with a sufficiently large number of ducts - duct type ventilation, and also may not have them at all - channelless systems. An example of the latter type is conventional fans built into the ceiling of a room or its wall. Also, natural ventilation can be attributed to this type, which does not include the use of any air ducts.
Ventilation components
As already noted, any ventilation that enters the room with fresh air flow is divided into varieties, depending on such characteristics:
- by appointment;
- places of service;
- the method of movement of the air flow;
- design features.
Regardless of the type of system used, almost all of them use a standard set of components:
- fans and ventilation installations and units - devices that provide air movement in any direction;
- thermal curtains are used to prevent the passage of the air mixture into a specific area or change its direction;
- noise absorbers - for the quiet operation of equipment;
- filters and air flow heaters - devices designed for cleaning and necessary air treatment;
- air ducts through which air flows;
- regulating and locking devices that serve to provide control over the operation of the entire system;
- air flow distributors controlling its movement.
Thus, there are many types of air purification systems, due to which it is possible to provide high-quality ventilation for any occasion and type of room.