The effectiveness of the individual heating system in a private house can be significantly increased if properly used to use a fairly high (up to 3000C) the temperature of the flue gases that are released during the combustion of any type of fuel.
This is the purpose of recovery (from the Latin word recuperatio). This term refers to the preservation, return back of a portion of the thermal energy that has already been spent on the combustion of gas, coal, pellets, etc.
Recuperation is widely used in technology: in the metallurgical industry, in heating furnaces, in electric trunk transmission. It is equally useful to use it in everyday life. So, what is a recuperator - a unit that in practice increases the efficiency of heating equipment in a private house?
A little bit about the principle of heat recovery
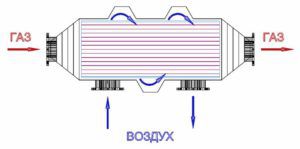
Clean air is needed for fuel combustion: its deficiency, and - especially in the cold season - low initial temperatures significantly increase the fuel consumption values required for its stable combustion. If you arrange so that the flow of incoming air and exhaust flue gases is separated by a wall of material with good thermal conductivity, then a significant part of the waste heat will give its thermal energy to the supplied air. The described process is air recovery, respectively, the device that implements it is called a recuperator.
Heat recovery is carried out in the following sequence. Cold clean air (with a decrease in the outside temperature, recovery occurs more intensively) is sucked in through the ventilation holes in the heating system of a private house and enters a heat exchanger, the housing of which can be made of any material that has good thermal conductivity. In the opposite direction (counter or cross), the flue gases discharged by the boiler or furnace smoke exhauster move along an adjacent duct. In the process of moving, in accordance with the rules of heat exchange, up to 80% of thermal energy is taken from the warm air by cold air, after which it is sent to the heating equipment of a private house. The flue gases that have given off their heat are emitted to the outside.
By the way, even after recovery, the temperature of the exhausted combustion products is quite high (up to 80 ... 1000C), in connection with which their reuse is possible, for example, for heating a bathhouse, garage and other utility rooms of a private household.
Recuperator in a private house - luxury or a necessity
Clean air recovery is a controlled thermophysical process. Its intensity can be increased due to the following factors:
- the use of materials that have an increased value of the heat transfer coefficient (for example, heat-resistant steel, cermets);
- increase in heat exchange surface area;
- lengthening the recuperator itself;
- improving the quality of manufacture and installation of the recuperator, in which air intake from one part of the recuperator to another would be excluded.
Strictly speaking, air recovery in the heating system is optional. But, taking into account the actual components of the heat balance of a private house, when up to 30% of the thermal energy leaves the house through the existing slots and leaks, and up to 15% of the heat is released into the smoke exhaust devices, the existing heat recovery unit for the apartment will allow its owners to save significantly on heating.Considering that the heating season in the conditions of our country lasts for half a year and then more, the financial benefits are obvious.
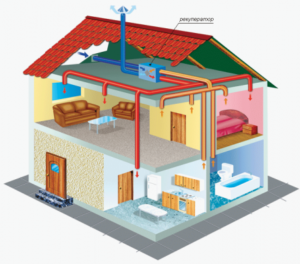
It is better if an air recuperator for ventilation of the apartment is provided even at the stage of construction of a private house, when the system of supply and exhaust ventilation is being developed.
Where to install a recuperator
Since the dimensions of the heat exchanger should not interfere with the functioning of the heating system, it is usually placed in the attic of the house. There the recuperator is an ordinary ceramic, steel or brick parallelepiped, equipped with an appropriate number of smoke and air pipes. The heated air then flows to the heating unit, and the exhaust through the deflector is thrown out.
A home recuperator not only increases the efficiency of heating equipment, but also allows you to adjust the relative humidity of clean air in all rooms. This is due to the fact that the recovery is always accompanied by heat exchange between the combustion gases and fresh air, and, therefore, moisture constantly forms on the walls of the heat exchanger. Through porous surfaces it is communicated to the supply air. Thus, with existing heating, indoor air humidity does not decrease, which favorably affects the climatic parameters and the health of residents, the condition of indoor plants, etc.
Industrial designs of recuperators are more compact, and therefore allow their installation in other technical rooms of the house / apartment.
Constructions of household recuperators
An air recuperator for an apartment and / or house is a structurally uncomplicated, but very responsible unit of the ventilation system, therefore a number of mandatory consumer requirements are presented to it:
- compactness;
- safety at work;
- heat resistance;
- ease of installation, routine maintenance and repair.
- stability of functioning.
Commercially available air recuperators for ventilation are divided into the following types:
- steel rotor type, in which heat transfer occurs due to the continuous rotation of the aluminum rotor located inside the housing. The rotation speed (and, consequently, the recovery rate) can be controlled by changing the speed of such rotation.
- steel plate type, with a heat exchanger in which replaceable cellulose cassettes are used: this provides control of indoor humidity indicators.
- made of refractory shaped bricks (or ceramics): with increased dimensions, they are characterized by high stability of the heat transfer process, therefore they are suitable for use in conditions of high flue gas temperatures.
- steel tubular: they are characterized by increased bulkiness, but they function well in the conditions of complex systems of supply and exhaust ventilation of two- and three-story private houses.
A recuperator - both for the ventilation system of a private house, and for heating the air - can be made with your own hands. The easiest way to make a plate heat exchanger, while aluminum is used as the material of the plates (at temperatures of flue gases up to 3000C) or steel grades 12XM or 15MX, whose heat resistance is 550 ... 6000C. For masonry brick recuperators use fireclay.
- Plate heat exchanger assembly
- Rotary heat exchanger assembly