Various options for a dead-end heating system involve the use of a two-pipe circuit laying circuit. If necessary, you can make the laying of a single-pipe system. To do this, you need to correctly calculate the diameter of the pipes and arrange the radiators, which will complicate the installation. The use of a one-pipe scheme makes home heating less efficient.
Types of Dead End Systems
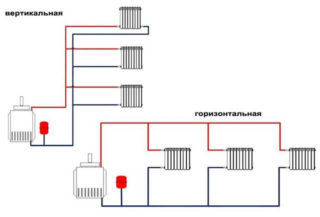
Depending on the features of the building, the dead-end heating system can be mounted horizontally or vertically.
Horizontal
This type of deadlock system involves the horizontal arrangement of radiators, combined by a supply line and a return to the general circuit. The entire highway consists of pipes of the same diameter, so the wiring is easy to install and more economical, especially for houses of a small area, where it successfully works with the natural circulation of the coolant. In houses with an area of 100 m2 or more, the use of horizontal wiring requires the organization of forced movement of the coolant through the system. Dead-end heating of the horizontal type allows installation of wiring to the floor, which successfully hides it from the eyes. In this case, it is better to choose reinforced polymer pipes and connect them with sliding sleeves.
Vertical
Dead-end vertical heating includes two or three horizontal circuits connected to a vertical riser. This wiring diagram is used in two or three-story houses to create pressure in the pipeline and accelerate the movement of the coolant. Each circuit is responsible for heating one floor of the house. This wiring scheme has limitations on the number of radiators that make up one branch. For efficient space heating, the number of appliances on the floor should not exceed 10 pieces. For a larger number of them, the installation of automatic pressure regulators will be required to balance the flow of heated coolant.
Dead-end heating with a vertical type wiring cannot be installed without using various fittings, which complicates the installation of the system.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of a dead-end heating system for a private house include:
- simple installation and operation;
- the universality of the system, since it is used for heating one-story and two-story buildings;
- the ability to replace the battery during system operation;
- vertical and horizontal types of heating are attractive in terms of cost, therefore they are popular among cottage owners.
The disadvantages of the dead-end system include the prolonged heating of radiators, the need for laying the length of the trunk and a large amount of installation work.
Work scheme of a dead-end heating system
In most cases, a dead-end heating circuit assumes that the coolant is supplied to and removed from the radiators along separate lines.
Work cycle:
- From the boiler, hot water is supplied to the expansion tank through the feed pipe.
- The heated coolant is directed along the outgoing pipe from the tank through pipes connected to the upper pipe of each radiator.
- Hot water, passing through the heater and giving it heat, flows through the lower pipe into the return pipe.
- The cooled coolant collected from all radiators is returned to the boiler via the return pipe.
After heating the water, the work cycle is repeated.
Installation Recommendations
When installing dead-end heating with your own hands, it is worth considering the recommendations of experienced masters.
- When calculating the throughput of the pipeline, the internal diameter of the pipes is taken. The right choice will reduce the number of fittings needed to connect the elements of the pipeline. The fewer the connections, the better the heating function.
- When distributing vertical dead-end heating, it is necessary to install shut-off and control valves on each branch. This will reduce the flow of coolant to the upper floors when no one lives there.
- Laying horizontal pipelines is performed with a slope. If natural circulation of the coolant is assumed, a slope of 5 mm per meter of pipe is made. If it is planned to organize forced water movement, the pipeline is mounted with a slope of no more than 2 mm per meter.
- When choosing temperature sensors, it is necessary to take into account the proposed method of circulation of the coolant. Since a thermal sensor of a certain design is suitable for each of the methods. Gravity flow instruments have more bandwidth.
- When installing the pipeline, you need to remember that the last radiator, unlike other devices in the circuit, is connected by a pipe of a smaller diameter.
If you follow all the recommendations, you can avoid mistakes and speed up the work.
Features of a dead-end heating device
Installation of the heating system is carried out taking into account the following features:
- Installing a large number of radiators slows down their heating. This problem is solved by dividing them into several branches. One such branch should have no more than five to six batteries.
- The trunk is mounted with a slope to the riser. Reverse slopes, as well as U-shaped rounds are not allowed.
- To compensate for the temperature difference between floors, pipelines are mounted from pipes of different sections.
- According to the scheme, the last battery is mounted above the rest.
- With a large length of the heating system, it is better to install several circulation pumps of lower power. Installing a power reserve pump will only increase power consumption.
If you know in advance about the above features, you will not have to spend time on remaking inefficient heating.
Hydraulics and balancing
If the heated area of the building does not exceed 200 square meters, the flow rate of the coolant is distributed naturally. In the hydraulic calculation for a two-pipe dead end heating system, pressure losses in each branch are calculated.
Balancing is necessary to connect the branches to each other in such a way that the pressure loss is the same in all branches. Installation of branches of balancing cranes branches simplifies the process. This avoids situations where the coolant, moving along the path of least resistance, will circulate only along the branch with low pressure.