The characteristics of the hot and cold water piped depend on many factors. At a large distance from the source to the consumer, the liquid inevitably cools. At low temperatures, this happens so quickly that a simple increase in heating fails to solve the problem. Insulation for expanded polystyrene pipes keeps the temperature of the coolant.
Expanded polystyrene and its types
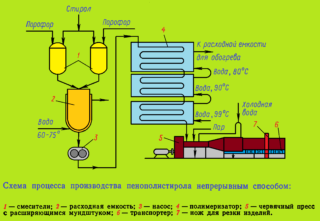
Styrofoam is a type of foam. The feedstock is polystyrene, but polydichlorostyrene, polymonochlorostyrene and other styrene copolymers can also be used. The manufacturing technology is simple: gas is dissolved in the polymer mass, which fills styrene granules. The mass is heated with steam. Under the influence of temperature, the granules increase many times until they fill the mold.
Most often, natural gas is dissolved in polystyrene. But if you want to get a fireproof option, the mass is filled with carbon dioxide. There is also vacuum polystyrene foam: in its production, air or gas is not needed.
Finished polystyrene foam consists of thin cellular granules. Micropores are contained inside them, voids are between them. The presence of numerous small cavities provides high thermal insulation properties of the material.
The characteristics of polystyrene foam are determined not only by the composition, but also by the manufacturing method.
No-stress
 The polymer granules are dried, then foamed at +80 ° C. Foaming agent is isopentane. The operations are repeated twice. Dry the material in the form, since even at a good density - up to 37 kg / cu. m, he is fragile. However, in its manufacture, almost 2 times less isopentane is required, which provides an affordable cost.
The polymer granules are dried, then foamed at +80 ° C. Foaming agent is isopentane. The operations are repeated twice. Dry the material in the form, since even at a good density - up to 37 kg / cu. m, he is fragile. However, in its manufacture, almost 2 times less isopentane is required, which provides an affordable cost.
Pressless polystyrene foam is more often used for warming building structures than pipes. The pores in it are open, it is sensitive to moisture.
Press
Prepared raw materials are laid in a mold and heated to + 120–145 C under a pressure of 8–12 MPa. In this case, the particles of the mixture sinter among themselves, and the blowing agent releases gas. After cooling, the preform is removed from the mold and heated in chambers for 90–120 minutes. When heated, the polymer softens somewhat and the gas released is evenly distributed throughout the volume.
Press material has higher noise and heat insulation qualities. It relates to electrical insulators and is used in the electrical and radio industries.
Extruded
Extruded polystyrene foam for pipelines is the best option. The structure of the material is fine-meshed, very uniform, the cells are closed, so the insulation is not afraid of water. It is much stronger than the previous options and is actively used in construction.
A foaming agnate is introduced into the polymer melt under a pressure of 10–20 MPa. The melt is rapidly cooled to + 130–140 C and extruded. They produce material in the form of plates and films and are used for thermal insulation of a wide variety of designs.
Specifications
Of great interest for pipe insulation is press and extruded polystyrene foam. Its pores are closed, which significantly reduces moisture absorption. Since it is necessary to insulate the external pipeline, unprotected from bad weather, this is an important property.
Non-pressurized is more often used for thermal insulation of walls, foundations, floors - structures, where its greater fragility and moisture absorption compared to the press version is less important.
The characteristics of the foam press, pressureless and extruded insulation for pipes are given in the table.
| Parameter | Expanded polystyrene | ||
| Pressureless (PSB) | Press (PS) | Extruded (EPS) | |
| Density, kg / m3 | 15–25 | 15–35 | 20–50 |
| Compressive strength, MPa | 0,18–0,19 | 0,20–0,30 | 0,25–0,50 |
| Thermal conductivity, W / (m · 0K) | 0,037–0,052 | 0,02–0,055 | 0,03–0,04 |
| Photoabsorption in 24 hours,% | 1,8–3 | No more than 2 | 0,2 |
| Vapor permeability, mg / (m · h · Pa) | 0,009–0,012 | 0,008–0,01 | 0,007–0,008 |
| Frost resistance, C | -65 | -70 | -70 |
Resistance to mold and mildew depends on the type of material. With high humidity and violation of the integrity of the pores, conditions arise for the multiplication of microorganisms. Special grades - PS1, PS4, PVC, have antiseptic properties.
Soundproofing properties have only closed cell expanded polystyrene. PSB insulation does not absorb noise.
Advantages and disadvantages
The obvious advantage of the material is the ability to give it a different shape. If the insulation does not fit tightly into the structure, it makes no sense. Expanded polystyrene insulation is made of the required shape and desired volume.
Insulation pipe polystyrene foam has other advantages:
- very low thermal conductivity - any brand guarantees the preservation of heat, 12.5 cm of expanded polystyrene replaces 53 cm of glued timber;
- the foam does not rot, is not susceptible to fungi;
- the materials used for the pipe insulation are not afraid of rain, frost, since they practically do not absorb water;
- the shell is exploited in the temperature range from -70 to +65 C, the temperature destruction begins when heated more than +160 C;
- minimum weight facilitates installation;
- the service life varies from 40 to 60 years - it depends mainly on the action of sunlight.
The disadvantages of insulation for pipes are associated with the features of the polymer material:
- All types of polystyrene are somewhat afraid of sunlight. This affects the duration of use.
- The material is flame retardant, but remains combustible. Special fire-resistant brands also burn, but their ignition temperature is higher - +490 C.
- When burned, polystyrene emits harmful substances. The risk of poisoning is high.
- Expanded polystyrene is somewhat resistant to acids and alkalis. However, concentrated solutions, solvents, and even most paints destroy the structure of the material. It is forbidden to paint thermal insulation.
The disadvantages of PS or PSB limit the scope. More often, polystyrene foam is used to isolate the outer pipe.
Features of the manufacture of insulation for expanded polystyrene pipes
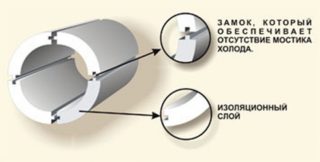
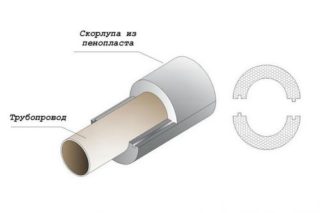
Polystyrene foam insulation for pipes is cut with a heated string from polymer plates. This is a prefabricated cylinder of 2 or 4 segments with different bending radius. A well cylinder is assembled from 8 segments. Spikes and grooves form at the edges of the halves. For additional fixation use glue or adhesive tape.
Features of a heater:
- A shell is used to insulate pipes with a surface temperature of up to +80 C. If an additional gasket is installed between the insulation and the pipe, it is allowed to insulate pipes with a surface temperature of up to +110 C.
- The polystyrene foam sheath for the outer pipe is treated with compounds to protect against ultraviolet radiation.
- The minimum diameter of the segment circle is 17 mm, the maximum is 1220 mm. Standard length is 1 m.
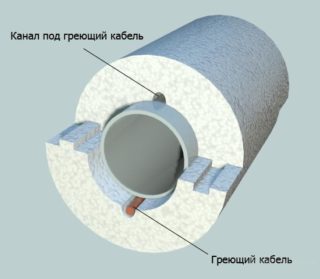
- It is possible to make custom-made shells for individual sizes. In some modifications, a groove is formed in the thickness of the material for the heating cable.
For thermal insulation of internal pipes, PSB is used. For external - extruded or extruded polystyrene foam.
Fields of application
Expanded polystyrene plates are used for warming a wide variety of objects:
- thermal insulation of internal and external water supply, heating, including main;
- insulation of the foundation, roof, walls;
- manufacturing of household and industrial refrigerators, refrigerators;
- protection against freezing - roads, sites, underground highways;
- packaging for fragile and valuable items;
- production of isothermal wagons and vans.
High-density options are the most durable and rigid thermal insulators. They are used as structural material.
Correct pipe insulation with polystyrene foam
Thermal insulation of pipes, especially of large diameter, is a difficult task. With a small volume of the pipeline, you can cope with it yourself. In other cases, you need to invite a team of specialists.
Technology:
- They dig a trench up to the level of soil freezing. This data can be found in the directory.
- At the bottom of the ditch 10–20 cm of sand is compacted.
- The pipes are treated with anticorrosion compounds and laid on the bottom of the trench so that a gap equal to the thickness of the shell remains between the pipe and the bottom.
- For the installation of the shell, 2 people are needed: one supports the lower segment, the second installs the upper one, fits tightly and fixes the shell with tape.
- Corner elements are cut with a knife directly in place and fixed in the same way.
- The shell is treated with a protective compound or covered with a film. Fall asleep in the trench.
Fixing to glue is considered less reliable and takes more time.