Properly organized floor insulation in the apartment on the ground floor of the city house allows you to maintain a comfortable temperature in the home and guarantees a minimum of heat loss. It is allowed to insulate genitalia both at the stage of building construction and during its operation. The right choice of heat-insulating material will help to save energy spent on heating a house and reduce heat loss by at least 20 percent.
Ways of floor insulation
On the ground floors of apartment buildings, floor insulation is necessary to protect against cold air and moist fumes spreading from the basement. Particular attention is paid to this problem in residential buildings of the old buildings, in which the final coating during construction is laid directly on reinforced concrete floors.
Thermal insulation is required when homeowners intend to install a floor heating system that allows you to keep warm air within the living space. There are several methods of floor insulation in an apartment on the 1st floor, widely used in its repair.
- Arrangement of screed over previously laid heat insulator.
- The so-called "insulation on the lags."
- Covering with heat-insulating material fixed on the outside (from the basement side, for example).
Regardless of the method chosen and the type of material used, before you insulate the floors in the apartment on the 1st floor with your own hands, you will need to thoroughly prepare. First you need to examine the rough base and, if necessary, repair the cracks on it, and then remove the remaining clots of the solution.
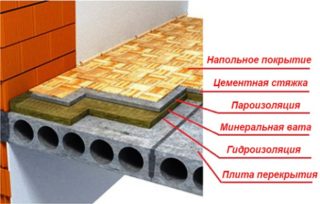
Concrete screed on top of the heat insulator
The special attention is paid to the choice of insulation for a concrete coating, since the success of the whole complex of ongoing work depends on its quality. The following materials are traditionally chosen as a heat-insulating base for screed:
- Bulk substances like expanded clay.
- Roll flooring.
- Insulators manufactured in the form of plates.
The first of these options relates to traditional approaches, since expanded clay was created in order to serve as a base for screed. The granules are simply scattered on a rough base with a layer 20 cm thick, and then poured with liquid concrete. However, this material is more suitable for private houses, as well as attic and attic structures. In urban apartments, preference is given to roll-type heat insulators, laid on a well-aligned base and fixed to it by means of a special adhesive composition.
When using materials with a self-adhesive base, remove the protective layer and lay the roll on the insulated base. In the upper part of the coating, the joints are glued with a special adhesive tape, and in the case of using a substrate with a reflector, an aluminum tape is selected for these purposes.
Typically, foamed polyethylene serves as a substrate for a laminate, a fine floor covering is laid directly on it.
Insulation of the floor with these methods requires the choice of material with a maximum density and with a minimum hygroscopicity index. For these purposes, various brands of "Penoplex" are suitable. Due to their light weight, insulation boards do not have a critical load on the base.
Lag insulation
This method is most often used when warming is performed by the method of "dry" sheet screed (under linoleum, for example).Its advantages include the absence of crude components, which require additional time to dry. At the same time, the load on the insulation is significantly reduced due to the use of self-supporting sheet materials (chipboard, OSB, plywood or GVL). The optimal from the point of view of costs is considered to be the choice of a low-cost and affordable mineral wool as insulation that has a density sufficient for this method of installation. In this situation, it is also allowed to use expanded polystyrene plates, but only subject to the availability of a reserve in height.
When it is required to artificially raise the floor level on the first floor, they often resort to backfilling with expanded clay. When using mineral wool, the thickness of the insulation layer depends on the type of structure (private house, cottage or city apartment).
Outdoor way
The so-called "lower" insulation is not used so often. At the same time, situations when this approach is the only possible are not uncommon. It is resorted to in the following non-standard cases:
- in housing there is an uninsulated basement or similar premises;
- the house is built on screw piles, high above the surface of a shaky soil;
- the level of soil freezing recorded by geological exploration in this region is not very deep.
In a private house, the outdoor method of insulation is widely used in the garage attached to it. The advantages include maintaining the height of the room by taking the insulation layer out and reducing the likelihood of moisture entering the elements of wooden structures.
Types of materials used
 To insulate the floors in a country house or on the ground floor in a city apartment, it is necessary to select a heat insulator of sufficient thickness and density. The most common options are mineral wool and expanded polystyrene (PPS), as well as classic expanded clay. The first is traditionally produced in the form of mats or rolls, and PPP - in plates of various thicknesses.
To insulate the floors in a country house or on the ground floor in a city apartment, it is necessary to select a heat insulator of sufficient thickness and density. The most common options are mineral wool and expanded polystyrene (PPS), as well as classic expanded clay. The first is traditionally produced in the form of mats or rolls, and PPP - in plates of various thicknesses.
Much less often, liquid sprayed coatings prepared on the basis of polyurethane foam and penoizol are used for the stated purposes.
The most unreliable in terms of thermal protection is ordinary polystyrene foam (polystyrene), which also has the lowest density index. This explains the fact that for thermal insulation on concrete, preference is most often given to extruded PPP.
When choosing a heater for the floor on the ground floor, a number of factors are usually taken into account. If it is supposed to equip a cement screed on top of the heat insulator, high-density protective materials that can withstand significant mechanical loads will be required to work. An exception to this rule is the case when plywood or other sheet materials are used as a substrate for the screed - in this situation, heaters with a lower density are acceptable. With a close location of wet soil, moisture-resistant materials are chosen: EPSP or mineral wool.
In a private house, especially if there are rodents in the basement, preference is given to polystyrene or expanded clay. The latter option is permissible only with high ceilings.
Possible errors when warming floors
The main mistakes most often made by amateurs when warming floors:
- Non-compliance with the gaps between the plates, taking into account the possibility of their compression.
- Incorrect assessment of the condition of the floors and an error in choosing the thickness of the insulator.
- Lack of waterproofing and protective treatment of wooden floor elements.
- The use of impermeable membranes to protect against moisture (they do not allow the floor to "breathe").
- Violation of the composition and sequence of the arrangement of layers of insulation materials.
One wrong step can “nullify” all previous efforts to insulate floors. Therefore, it is so important to take into account the views of experts and try to avoid these shortcomings.
Different options for floor insulation on the first floor with your own hands
When insulating floors in the basement of buildings, it is important to learn to distinguish and consider the following options:
- works are carried out in a typical panel house;
- insulation is subject to the first floor of an apartment building;
- a heat-insulating coating is arranged in a brick house;
- floors are insulated in a classic wooden building.
In the first case, especially in end or corner apartments, preference is given to the lagging method of insulation. Mineral wool mats with a thickness of 50 mm are usually used as thermal insulation. In this case, it is mandatory to use vapor barrier - an ordinary plastic film.
On top of such a pie, a fine floor covering is laid. On the basement floors of apartment buildings it is allowed to use the same method, in brick or frame wooden buildings a slightly different approach will be required.
Ground floor in brick building
The traditional approach to carrying out insulation work in brick houses is the use of expanded clay filling on the base of the soil or on the surface of the floor slab. A concrete screed is made on top of the bulk insulation. This method is best suited for buildings of significant size.
For warming according to the second option, it will be necessary to equip a special frame, in which PPS plates are then laid. The advantage of this approach is minimal labor costs. The contractor will only need to knead the screed, pour it over the previously filled or laid insulation and align it beautifully.
Wooden building
The insulation of the floor in a wooden house is also based on the use of a frame, the function of which in this case is performed by a timber crate. Its parameters are selected so that the insulation design can be made two-layer.
In order to better protect the floor from cold air flows from the shaft or basement, the heat insulator is mounted on the outside.
The effectiveness of thermal protection, subject to the observance of known technologies, depends on the correct choice of the method of floor insulation on the 1st floor.