Batteries are actively used as elements of the heating system, but not all varieties are suitable for installation in residential premises. For the choice, the radiator device, material and shape matter. The type is determined taking into account the state of the heat main, communications, the type of energy carrier in the pipes and the time of the last repair of the system. The impact of water hammer is taken into account, so a combination of factors makes it difficult to choose a radiator for an apartment or a house.
Features of the design of the radiator
The battery is a separate heating device, consisting of elements with internal channels for moving energy. Heat is removed by convection, radiation, and heat transfer.
Sectional views allow you to increase the heating area by adding elements. Panel installations cannot be changed in shape, which is taken into account when calculating and installing the system. The accompanying passport indicates the temperature criteria for the operation of the device, the parameters of the working pressure, heat transfer.
Sectional radiator
A sectional heating battery device consists of a metal pipe in the form of combined horizontal collectors through which water passes. The channels are connected using vertical tubes of small diameter, and the entire system is located in a housing made of cast iron, steel or aluminum. Separate sections are twisted on a thread.
Radiators are used to heat the room, so the device device affects the quality of heat exchange. The material of the heat exchanger and the case plays a role, therefore, bimetallic options are used, including 2 types of materials.
Radiators should be able to be cleaned periodically, as scale settling on the inner surface reduces heat transfer.
Types of radiators in the form of execution
The heating capacity of the batteries depends on the exchange area, so the design is important.
The choice of form is influenced by factors:
- ceiling height and room area;
- maximum pressure in the heating main;
- duration of operation (long-term or periodic);
- boiler power, pipe material, characteristics of other devices in the system;
- chemical composition and physical properties of the energy carrier.
Radiators are selected in the form of sections, panels, lamellar and tubular types. The climate in the region influences the required heating conditions, the presence of aggressive factors, the cost of batteries.
Sectional Radiators
In heat exchangers sections of the same type are connected, which inside have 2 - 4 channels for the movement of water. Prefabricated elements are made of aluminum, steel, cast iron of various shapes and lengths. Room heating is coordinated by the number and size of sections.
Prefabricated batteries transmit heat by convection and radiation, operate economically, they are equipped with manual and automatic temperature controllers, taps, valves. Products are inexpensive, the ability to choose the center distance makes them popular for different buildings.
The disadvantages include the danger of leaks during a sharp pressure jump, difficulties with cleaning the internal channels and external cleaning of the intersection space.
Tubular batteries
The sectional design of the radiator includes 1 to 6 vertical collectors, which are combined by the upper and lower pipes, the coolant circulates freely. Heat transfer depends on the diameter of the pipes and the dimensions of the heat exchanger (0.3 - 3.0 m). Installations withstand pressure up to 20 atm.
Tubular batteries withstand pressure drops and water shocks. Smooth internal contours resist the accumulation of dirt and deposits. Welded joints do not leak. Appearance fits into various interiors. Radiators are available in various sizes, differ in the shape of the case. The disadvantage is the high cost.
Panel Models
The panel radiator looks like two metal shields welded together. Inside the plates there are vertical channels for the circulation of energy, and ribs are mounted on the outside, which increase the surface of heat transfer. The panels are arranged in 2 or 3 rows, the material is steel.
Advantages of models:
- low inertia makes it possible to quickly respond to changes in external temperature;
- Due to the ease of massive mounting is not required;
- compact devices are placed in any part of the room;
- low price.
To heat the model, you need half as much water as for a sectional battery. The disadvantage is that the panel installations do not withstand high pressure in the mains; the cleaned energy carrier must be poured into the system without dirt and impurities. Poor joint painting leads to corrosion and leaks.
Lamellar
The principle of operation of the radiator is convection exchange. The heat exchanger is a core with fixed fins made of thin metal. The inner tubes are used to transfer water. This type of radiator is installed in industrial and public buildings, apartment buildings with a centralized highway.
The degree of heating is controlled by increasing the number of plates. Radiators effectively heat the room, but when the boiler is turned off, cooling quickly occurs. The coolant must be heated to a high temperature and pass under pressure.
Material classification
Radiators should serve for a long time and withstand various aggressive influences. In a multi-storey building, operating conditions are not entirely suitable, since the coolant does not differ in quality. The apartment does not have aluminum appliances, as the radiator is wearing out and will quickly fail.
Manufacturers take care of the damage to the insides and protect the surface with polymers, but such options are expensive and not always in demand. Bimetallic and steel plants are less damaged by corrosion. For central heating from a city branch, cast-iron batteries are suitable.
Cast iron
A heavy radiator consists of sections and is characterized by powerful heat transfer. The device transfers pollution of an energy carrier, but a calcareous deposit and a scum accumulate on interiors. The plants work for a long time, sometimes they are removed, disassembled and cleaned under pressure to return the original heat transfer.
Along with cleaning, intersectional gaskets change, which eventually fail. Cast iron batteries have an outdated design and are not installed in closed automatic heating systems. In apartments that are heated from a central branch, such batteries can withstand pressure changes and water hammer.
Aluminum
The aluminum radiator in the heating system efficiently gives off energy and has a large area due to the impressive number of fins. Devices that withstand pressure in the system of about 12 atm are produced, and the pressure during pressure testing is at the level of 18 atm.
Sectional options for an aluminum radiator for heating:
- solid constructions with cast sections;
- extruded type with elements connected mechanically;
- combined options.
The advantages of aluminum radiators include small dimensions, lightness, large area. The disadvantage is the destruction of metal in the aquatic environment, especially in the presence of stray currents in the main. The oxide film inside is broken by an aggressive energy carrier, gas is released during the reaction, which in a closed circuit leads to a rupture of the battery.
Bimetal

Bimetallic plants are of high quality. The purpose and arrangement of the radiator allows the device to operate under high pressure and in the face of the danger of water hammer.
Batteries are manufactured sectional or cast, there are two types:
- from aluminum and steel;
- from aluminum and copper.
In bimetallic devices, water contact with aluminum is not provided. With this design, thermal conductivity is improved, weight is reduced and strength is increased. Radiators of two metals withstand pressure up to 100 atm., No corrosion is observed.
Design and principle of operation
The principle of operation of the radiator is that the heated energy carrier moves through the pipe system and enters the batteries, transfers heat, then moves along the return branch to the heating source. The radiator heats the air in the room by radiation and convection. For different types of devices, the ratio of thermal radiation and convection is different.
Steel and cast iron radiators heat the room with radiation, and plate and panel heaters transmit energy by convection due to the large total area of the fins and strips. The warm stream tends upward, in return cold air is drawn in, which heats up.
DIY radiator connection
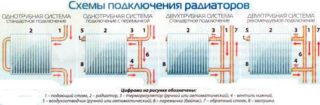
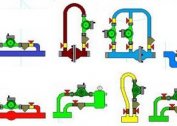
In the multi-apartment sector, batteries are mounted on one side of the room. The radiator is connected in several ways, depending on the pipe layout.
Use diagonal or cross connect. A submarine pipe is connected from one side of the battery in the upper section, and a discharge pipe is discharged from the other side at the bottom. Such a scheme is relevant for installations with a large number of sections of considerable length.
The lower connection provides for connecting the inlet and outlet of the radiator from the bottom to two nozzles on both sides of the heat exchanger. The scheme is characterized by low efficiency, but this option cannot be avoided if the heat supply system is arranged in the floor.