A special device resembling an air conditioner or a refrigerator is used to transform, transfer and convert heat energy. The heat pump is not used for heating - it only conveys more heat than it receives from the network. Using the device, it is possible to pump the energy of soil, air or water into heating communications.
Principle of Operation and Design
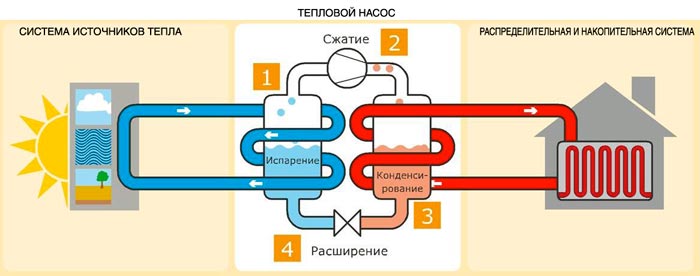
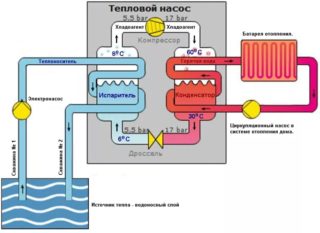
The heat pump consists of a freon circuit with a compressor, an expansion valve, heat exchangers (condenser, evaporator) and a copper pipe. The nodes are connected together using fittings and automatic parts.
The principle of operation of the unit is based on the selection of low-grade heat:
- water (from +2 to +7 degrees);
- air (from -25 to +35 degrees);
- soil (from -5 to +5 degrees).
In the process of taking heat resources, the initial medium is cooled, and the refrigerant of the internal circuit begins to boil and transforms into steam. The gas is compressed by the compressor and dramatically loses volume, while pumping up temperature and pressure. The action of pre-heated freon is to transfer heat resources to the heating main. Heat pumps operate in a closed manner, using only energy without direct heating of the coolant.
The unit allows you to get 3-5 kW of heat from 1 kW of used energy.
Varieties of heat pumps
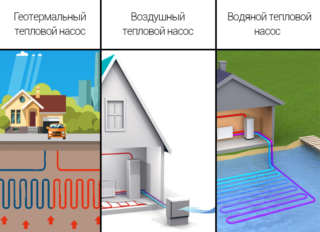 Heat pumps for heating a private house are classified according to several criteria. Depending on the type of energy transfer:
Heat pumps for heating a private house are classified according to several criteria. Depending on the type of energy transfer:
- Compression - consist of a compressor, condenser, evaporator and expander. The equipment operates on the principle of a compression cycle and expansion of the coolant with further heating.
- Absorption - operate on the basis of absorbent and freon. The absorption device is highly efficient and is a new generation pump.
According to the heat source, you can pick up the device:
- air - extracts heat from the atmosphere;
- geothermal - takes energy from water or soil;
- secondary - works with the secondary heat of water or air.
Secondary heat devices can take energy from sewage.
The heat pump apparatus also varies in the environment of the intake and transformation of energy, features and methods of operation.
Ground-water system
Devices allow you to get heat from the bowels of the earth year-round. According to the type of geothermal contour, the following modifications can be selected:
- Horizontal - a system in the form of pipes located below the freezing of the soil, at a depth of 1.5-2 m. The temperature regime during the year reaches + 3 ... + 15 degrees, so heat can be obtained at any time.
- Vertical - the collector looks like a well 50-200 m deep. Inside are special probes that take heat away from a constant temperature gradient.
When arranging the vertical contour, the geological composition of the soil must be taken into account. On the site where the horizontal contour is located, you cannot build houses or lay tiles.
Water-to-water system
To heat the room, you will need to use the energy of groundwater with a constant temperature of +7 and above degrees. The technology provides for the supply of water by a centrifugal pump to a special station. Thermal energy is transferred to antifreeze by the lower circuit of the device. This option is allowed in areas:
- without groundwater or with a minimum level of their occurrence;
- with wells in which the water mark does not drop;
- with minimal salt composition and pollution;
- equipped with a drainage well, capable of receiving from 2200 liters of effluent per hour.
The best option for water-to-water equipment is the area near a river or other body of water.
Water-to-air system
Heat pumps do not heat the air inside the rooms, but the coolant itself. It can be used for heating, preparing hot water. The system has several advantages:
- installed without drilling the external circuit;
- differs in reliability and durability;
- effective in autumn and spring.
The disadvantages of pumps include:
- lowering of COP when temperature reaches +1.2 degrees;
- the use of reverse for defrosting the outdoor unit.
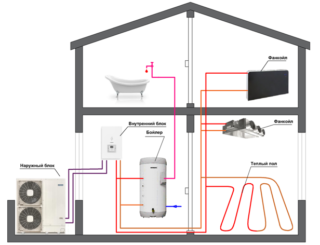
Stations are not the only means of generating heat. They function in conjunction with a heating boiler.
Air-to-air system
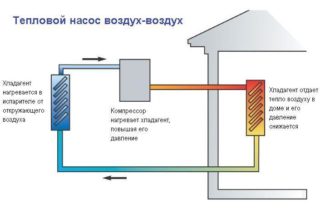 Air-to-air devices receive thermal energy from street air masses. Outwardly, they resemble air conditioners, but can work at low temperatures. Cold air is heated in the condenser. The benefits of VT include:
Air-to-air devices receive thermal energy from street air masses. Outwardly, they resemble air conditioners, but can work at low temperatures. Cold air is heated in the condenser. The benefits of VT include:
- a price comparable to the price of an air conditioner;
- quick installation;
- no risk of leakage of heat carriers.
Among the disadvantages of the systems:
- the ability to operate only at temperatures up to -20 degrees;
- the need to install a special unit inside each room;
- lack of conditions for hot water.
Thermal equipment "air-to-air" can be used to additionally heat a cottage or a country house.
System Selection Criteria
Before buying a heat pump, you need to consider:
- The cost of arranging the system. To connect the VT in Moscow, you will need to lay a horizontal outline. A pit is excavated (10 thousand rubles / shift for renting an excavator), then preparation for work (5 thousand rubles) is made. A well costs 1000 rubles / mp, taking into account the installation and tying of the probe. In order for the system to work properly, you need 350 m of circuit or 350 thousand rubles.
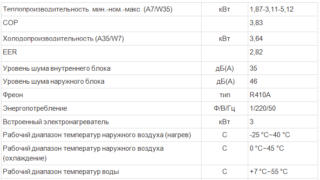
- Energy consumption. A 9 kW VT consumes 2.7 kWh of electricity, which is cheaper than a similar electric boiler.
- Payback. Alternative heating, taking into account installation costs and electricity consumption, will pay off after 3 years.
- Climatic conditions of the region of residence. VTs are ineffective in areas with frosty winters. They will not be able to pick up the right amount of heat from the soil, air or water.
- Device power. The owner of a one-story house of 10x10 squares should make calculations based on: the maximum negative temperature (-20 degrees); temperature differences in the street and in the room (20 - -20 = 40); heat loss of walls (brick - 13.5 kW). About 50% should be added to the last minimum power indicator.
- The capacity of the storage tank. With 3 starts of the pump, 30 liters of water are needed, with 5 starts - 20 liters.
When selecting equipment, the condition of the house and the features of the area where it is located are taken into account.
Advantages and disadvantages
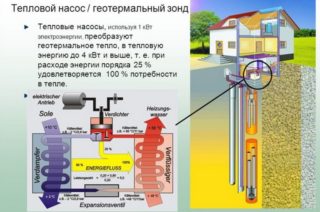 Heating communications with a heat pump have several advantages:
Heating communications with a heat pump have several advantages:
- energy saving: at a flow rate of 1 kW / h, 4 kW / h of heat is obtained;
- reduction in system repair costs;
- universality - suitable for installation in regions without gas pipelines, power lines, as will work from air, soil or water;
- full automation of the system - in case of prolonged absence, the owner can set a constant temperature regime of +10 degrees;
- environmental safety - does not produce oxides, acids and benzoic compounds;
- no emergency situations - the coolant and system components do not heat up to critical temperatures;
- the ability to operate at temperatures up to -15 degrees;
- reversibility - installations cool the house in the summer, removing heat from rooms and directing it to a reserve environment;
- long-term use: without major repairs, the pump is used for 25-50 years, the compressor spare part fails once every 15-20 years.
The disadvantages of using heat pumps include:
- financial costs for organizing a geothermal system;
- long (5-10 years) payback of the system;
- the need for additional heating in cold regions.
In underfloor heating systems it is allowed to use fan coil units that transfer heat or cold to air from water. If you have old housing, you will need a redevelopment of heating.
Popular heat pump manufacturers
Heat pumps are mainly manufactured by companies from Asia. The first to launch European products were Daikin, Mitsubishi Electric and Hitach. The equipment is also produced by manufacturers from South Korea (LG and Samsung), China (Midea and Gree).
The European brands Dimplex, Nibe, Alpha-Inno Tec, AJ Tech, CIAT, Technibel, Atlantic, Airwell, Buderus also have ATW modifications.
DIY heat pump
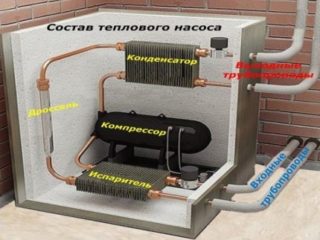 Making a heat pump yourself is only possible for heating a small house.
Making a heat pump yourself is only possible for heating a small house.
- Purchase an old refrigerator and disassemble it by removing the automation.
- Make a condenser from a 100 L steel tank, cut in half. A copper coil with walls 1 mm thick is placed in the tank.
- To make a coil by wrapping a copper tube on a gas or oxygen cylinder with the same distance between the turns.
- Lock the coils by threading the wire through the holes in the aluminum corners.
- Weld tank parts.
- Make an evaporator from a 60-80 liter plastic container. It installs a coil and thread for drain and feed pipes.
- Install the equipment in the room and bring 2 air ducts cut into the front sash to it.
- Solder copper pipes, pump freon.
- Make a start-up and connect the structure to heating.
Air will be supplied through the upper channel to the freezer, cool and be fed into the housing. After warming up with a heat exchanger on the rear wall, the air masses will enter the room.
As a result of the work, a system with a closed loop is obtained. Refrigerant circulates in it, taking and transporting energy from the evaporator to the condenser. The received thermal energy has a small power, therefore, it is necessary to additionally connect a warm floor or radiators of low inertia type.
The outlet water temperature will be no more than 50-60 degrees.
Scheme
To save on the independent manufacture of the device and its installation will help the bivalent scheme of the heating system. It involves calculating the power of the VT based on the minimum temperature. During the year, the installation will not work at full capacity.
Nanos in this case is a passive unit, to which a gas or solid fuel boiler is connected. The bypass is connected to the latter.
Thermal modification of pumps is an effective, but expensive equipment. With a long payback period, they will be the only alternative in areas without gas supply.