The Leningradka heating system is a popular, economical and uncomplicated way to heat small areas. This method has been known since the days of the USSR and is still used. Suitable for installation in buildings with one or two floors. You can make a one-pipe heating scheme yourself. To do this, you need to understand the principles of operation, basic technical characteristics and installation technology.
Operating principle
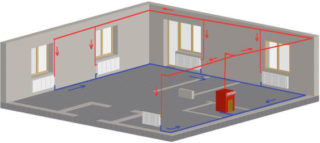
The classic Leningradka system is a set of heating devices that are connected by a single pipeline. A coolant circulates throughout the circuit, in the role of which is water or antifreeze. With the advent of new heating equipment, the system was improved, made it manageable and expanded functionality.
Depending on how the pipeline is located, the heating circuit is divided into two groups:
- horizontal
- vertical.
The location of the pipes can be upper and lower. In the first case, the heat transfer efficiency is higher, but the installation is more complicated. The lower installation of the system is easier to make, while it is necessary to put the pump.
Heat carrier can be circulated in the circuit in two ways - natural and forced using a pump. Also, systems are closed and open.
The recommended number of heating devices when installing the Leningradka system is 5. This value can be increased to 6-7, after having performed the corresponding calculations. Installing a larger number of radiators will not be effective, and its cost will be unreasonably high.
You can make heating in a private house "Leningradka" with your own hands. The assembly scheme, the choice of the type of circulation depend on the individual characteristics of the structure.
Advantages and disadvantages
The heating system "Leningradka" has its positive and negative sides. The pros include:
- Simplicity of wiring and installation. Significantly reduced installation work. You can install without the help of specialists.
- High efficiency.
- Profitability. Pipe consumption is 30% lower than other heating systems. In addition, the purchase of expensive equipment is not required.
- The introduction of control elements (bypasses, ball valves) made it possible to improve the circuit and adjust the temperature regime in different rooms.
- Adding new elements makes it easier to repair and replace without shutting down the entire heating system in the house.
- Universality. The system can be used in one- and two-story houses. The difference in the schemes will be small.
- Reliability. The heating system will function without interruption.
- With a lower location in a building with one floor, you can hide pipes in the thickness of the floor. It is important to observe measures of thermal insulation and tightness of the joints.
"Leningradka" has proven itself in one-story buildings with a small area.
The main disadvantages include the complexity of the calculations. The number of sections, pipe diameters depend on many parameters, including the individual characteristics of the house, so problems may arise with the correct determination of the parameters. Also, difficulties arise when balancing the system. For its implementation, additional equipment and repair work may be required. The system cannot be implemented in large apartment buildings due to its inefficiency.
It is important to consider that the horizontal "Leningradka" does not allow the connection of underfloor heating or towel dryers.
Features of each circuit
Horizontal and vertical heating systems have their own characteristics and are used in different types of buildings. You need to familiarize yourself with them before choosing the right one.
Horizontal layout
In small one-story houses, it is advisable to install exactly the horizontal layout of Leningradka. It is necessary to consider in advance that all heating devices should be on the same level.
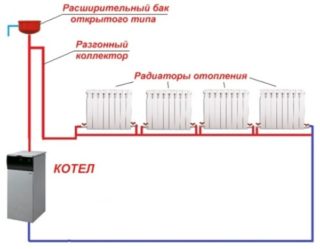
The simplest scheme consists of the following components:
- Heating boiler. It is connected to a water supply and sewage system. Can be used gas, wood or electric.
- Extended tank with pipe. Essential for an open system. Excess liquid that appears when boiling in the boiler flows from the nozzle.
- Pump. It is responsible for the circulation of the coolant along the circuit.
- Piping for hot water and the removal of a cooled heat carrier.
- Radiators with Maevsky cranes. Needed to release excess air.
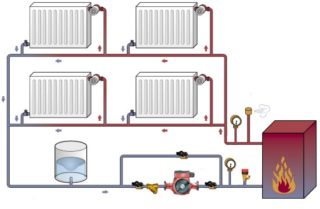
- Water filter. Allows you to collect small sharp particles that can damage the pipeline from the inside.
- Ball valves and bypasses. When you open one, the circuit is filled with water, the second is a secret one for draining the water.
All batteries can be connected from the bottom or diagonal connected. It is characterized by increased efficiency. The coolant enters from the top, and exits from the back side from the bottom.
Such a scheme has disadvantages. If repair is necessary, it will be necessary to completely turn off the entire heating system and drain the water. Also in the above diagram there is no way to adjust the heat transfer of the batteries.
The above problems can be solved by applying an improved scheme with ball valves placed in the pipeline and bypasses with needle valves in the lower pipe. These mechanisms make it possible to stop the flow of coolant into the radiator battery. If it is necessary to dismantle, it is not necessary to shut off the entire circuit, it is enough to shut off the taps. Through bypasses, water will circulate through the lower pipe. They also serve to control the amount of coolant in the radiator.
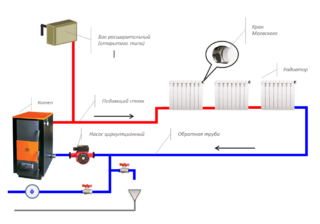
The closed horizontal system "Leningradka" with forced circulation works on a different principle. Here, hot water or antifreeze is supplied through a manifold pipe. She collects the cooled liquid and transfers it to the boiler for working out. With this arrangement, the entire system is under pressure due to a closed tank. In addition, there are elements of control and management:
- Fuse. It is selected according to the technical characteristics of the boiler - pressure.
- Air vent. Removes excess air masses from the system.
- Pressure gauge. Allows you to adjust and measure the pressure in the circuit. The optimal value is 1.5 atmospheres, the indicator may vary depending on the model. All data is registered in the documentation for the system.
When using a horizontal system, it is possible to control and adjust parameters through automation.
Vertical layout
In two-story houses with a small area, vertical Leningradka systems are installed. They also come in open and closed with two types of circulation. Heating with a circulation pump works according to a similar algorithm.
The vertical scheme with natural circulation of a closed form works as follows:
- The pipeline is mounted at the top of the wall at a certain slope.
- The heat carrier is transferred from the boiler to the tank.
- From it, the floor moves pressure into the pipes and radiators.
The boiler must be mounted below the radiator installation level, then the efficiency will be higher.
Natural and forced circulation
There are two systems for moving the coolant in the circuit - gravity and using a pump. They have a different principle of action, positive and negative traits.
To organize the natural movement of water in the circuit, complex work needs to be done to calculate the angle of inclination, pipe diameter, and the length of the water supply. The system should work smoothly and efficiently in a one-story house. In buildings with a large number of floors, the scheme will be ineffective.
A system with natural circulation looks less aesthetically pleasing, since the dimensions of the pipes for its implementation are larger than when operating from a pump. In a room with a gravity flow diagram, there must be a basement in which the boiler will be installed. The tank is placed in a well-insulated attic.
Disadvantages of natural circulation:
- When installed in two-story houses, the batteries at the top heat better than on the lower floors. To partially eliminate the problem, cranes and bypasses are installed. Also on the ground floor, radiators with an increased number of sections are installed.
- The rise in price of the system. Associated with an increase in the amount of consumable.
- Instability of work. Quality depends on water pressure and other factors that do not affect when using a circulation pump.
- The complexity of the calculations. A minimal deviation from the norm can ruin the functionality of the entire system.
The gravity-flow system is not suitable for installation in attic-type houses. This is due to the inability to evenly position the pipe in the absence of a full roof.
The system with the pump is reliable and stable. Installation of such a scheme is simpler, since accurate calculations of the angle of inclination of the pipeline are not required.
Mounting Features
Arrangement of a single-pipe system "Leningradka" requires care in the calculations and execution. For its implementation, it is necessary to pre-calculate the size of the pipes, the number of sections in the radiator, prepare the premises and do a number of other works.
The system consists of the following required elements:
- boiler;
- pipeline;
- heating battery sections;
- expansion barrel;
- tees.
If the Leningradka heating system with forced circulation is organized, another pump will be required. To improve the capabilities, ball valves (2 pieces per battery) and bypasses with a needle valve are used.
The main line can be mounted in the plane of the wall or on its surface. When inside the walls, floor or ceiling, it is important to make high-quality thermal insulation. Otherwise, heat losses will increase and the temperature in the radiators will be lower. This is due to microcracks that are formed in the process of wall breaking.
The installation location of the expansion tank and the boiler is preselected. The tank should be placed above the level of radiators - for example, in the attic. The boiler is usually mounted in the basement.
Material selection

The amount of heat in the radiator depends on the material of the pipes. Polypropylene or metal products are commonly used.
Heating in a private house from polypropylene pipes "Leningradka" is easy to do with your own hands. It is important to consider that such pipes are not suitable for installation in houses located in the northern regions. This is due to the properties of the material. Polypropylene melts when it reaches + 95 ° C, which increases the risk of pipe rupture at the maximum heat transfer of the system.
Metal products are mounted more difficult, since the welding of components is required, but their quality and reliability are at a high level. They are ways to withstand high temperatures. Differ in durability.
The diameter of the pipe depends on the number of heaters. If 4-5 radiators are installed in the house, pipes with a diameter of 25 mm and a bypass of 20 mm are needed. With a battery number of 6-8, a 32 mm line and a 25 mm bypass are selected. In the case of creating a gravity flow system, pipes with a diameter of 40 mm or more are bought. The size also depends on the number of batteries in the circuit.
When choosing the number of sections of radiators, you need to consider how much heat will be received by this or that heating device. Maximum efficiency will be noted in the first battery. In it, the temperature of the water drops by at least 20 ° C. Already colder water gets into the second radiator, because of which the efficiency decreases. To compensate for heat loss, the number of radiator sections should be increased. The first one takes into account 100% of the total capacity, the next ones take 110%, 120% and more.
Connection of elements and pipes to each other
Bypasses are built into the assembled trunk. They are manufactured separately with bends, the distance between which is calculated with an error of 2 mm. Backlash for trimming 1-2 mm is allowed. As this distance increases, the system may leak. To determine the exact dimensions, angle valves are turned in the radiator, the distance between the centers of the couplings is measured.
You need to weld or attach tees to the bends. One hole must be diverted for bypass. The second is selected by the distance between the central axes of the bends.
Welding parts
Metal pipes are joined by welding. For this, the master must have special equipment and skills to work with him. Otherwise, installation should be entrusted to professionals.
When welding, it is important to ensure that no internal influx forms. This will lead to a decrease in the amount of coolant that enters the radiator. With the formation of sagging work should be redone.
After welding the entire parts, the radiators are placed on the wall using angle valves and couplings. Bypasses with taps are laid in the strobes. Their length is measured, excess is cut off.
Final work
Before starting the heating system, excess air must be removed. To do this, open the cranes of Majewski. It is important to conduct a visual inspection of all compounds.
After that, testing the assembled circuit and performing balancing is performed. The temperature should be balanced in all radiators using a needle valve.