The central heating system of residential premises provides for one common boiler room, from which the heated coolant is distributed through the pipes into the houses to consumers. The role of the coolant temperature controller is performed by the elevator unit of the heating system.
Device and principle of operation
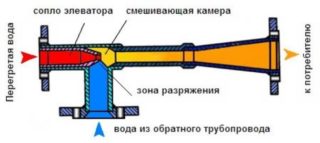
The elevator of the heat assembly - a solid cast iron casting - is a mechanical device that looks similar to an asymmetric tee. The only variable part is the nozzle diameter, which affects the degree of vacuum and determines the mode of suction of chilled water from the return. The value of the vacuum should not exceed 2 bar, for which the nozzle diameter, as the only regulator, is calculated with a high degree of accuracy.
Depending on the tasks to be solved, the elevator of the heat unit is manufactured in several standard sizes, which are assigned numbers from 0 to 7.
- The smallest elevator No. 0 is 256 mm long and weighs 6.43 kg.
- The length of the largest elevator No. 7 is 720 mm, weight - 34 kg.
Choose an elevator, focusing on the diameter of the heat pipe, so as not to lower the throughput of the system.
According to technical conditions, heating mains can operate in three modes:
- 150/70 ° C;
- 130/70 ° C;
- 95/70 ° C.
The first number indicates the temperature of the water in the direct pipe, and the second indicates the chilled liquid in the return pipe.
The end user can be located at a considerable distance from the boiler room - high temperature values in the direct pipeline are set to compensate for heat loss during transmission to a distance and dispersion in cold climatic conditions. At the same time, domestic heating equipment (batteries, pipes) cannot be operated at temperatures above 95 ° C according to their technical characteristics and sanitary standards.
There are several reasons for the restrictions:
- at higher temperatures, cast-iron batteries become brittle, and aluminum batteries are not able to maintain the pressure of the system and fail;
- modern metal-plastic and polypropylene pipes cannot work at temperatures above 95 ° C - they begin to deform, cracking is possible;
- overheated heaters can cause burns on contact.
Internal pressure in the heating main does not allow superheated water to turn into steam. When transferring due to losses, the temperature of the carrier decreases, but not significantly, the issue of obtaining a coolant at an operating temperature does not solve. To solve the problem, a heating elevator is used in which the superheated coolant from the boiler room is diluted with cooled liquid from the return pipe.
The equipment surrounding the elevator forms a mixing system and is called the “thermal elevator unit”.
The principle of operation of the device:
- Superheated coolant is fed to the inlet of the elevator unit, passing through the nozzle, it loses pressure.
- The decrease in pressure causes the chilled water to flow from the return to the discharge zone.
- In the mixing chamber (long part), the flows are mixed to the specified parameters.
- Through the diffuser (expanding part), the coolant of the working temperature enters the heating system.
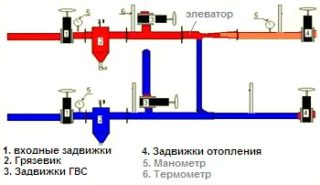
In the general scheme, the elevator unit is located on the incoming pipe of the highway. A dirt collector is installed in front of it, which serves as a trap for dirt and small debris contained in the coolant stream.
The task of the surrounding equipment - valves, pressure and temperature sensors - to ensure the safe operation of the device and implement the principles of control.
Design Features
In addition to the one-piece cast-iron version, there are other designs that allow you to mobilely change the diameter of the nozzle. Such models solve issues of quick adjustment of the temperature of the coolant, but they are structurally complex and have a high price.
For example:
- Elevator assembly with a cone-shaped movable needle. When moving it, the nozzle clearance value and the degree of dilution of the heat flux with return water cooled by water are regulated. The needle position can be adjusted manually or automatically.
- A device with a servo drive, mobile changing the nozzle clearance by a signal from temperature sensors.
Devices operating in automatic mode increase the mobility of the system and its capabilities in terms of fine-tuning. But because of the structural complexity and high cost, they have not yet found wide application.
Possible malfunctions
The elevator itself is a reliable device that works in a stable mode. Its only malfunction may be damage to the nozzle, since superheated water is a rather aggressive agent.
Malfunctions can be in the surrounding equipment:
- mud clogging;
- valve breakage;
- incorrect operation of the sensors.
Violations in the operation of the elevator and the equipment of the unit are manifested as fluctuations in the temperature of the coolant and are solved by revising the device, replacing the nozzle, cleaning the sump or repairing the valves.
To prevent malfunctions, regular (once a year) maintenance of the elevator unit is carried out - the dirt formed due to the poor quality of the coolant is cleaned and removed, the diameter of the nozzle is checked, and all joints are tight.
Advantages and disadvantages
The elevator unit as a heat flow regulator in the heating system is used for a long time, during which the strengths of the system and its shortcomings were identified.
The advantages of this temperature adjustment include:
- simplicity of design and reliability;
- functioning silently;
- Does not require power to work;
- poor response to the aggressive environment of superheated water;
- the ability to maintain constant characteristics of the coolant at the outlet;
- combines the functions of a pump and a mixer.
Weaknesses are expressed in several points:
- a pressure differential of the forward and reverse lines of 2 bar;
- only works in one mode;
- in case of violations on the heat main, the system does not work, which can lead to freezing;
- Each building requires a separate node.
The disadvantages of the elevator heating unit are insignificant and completely overlap with the advantages, which explains its widespread use.
Wiring diagrams
The heating unit is used in systems with various parameters, where special schemes for connecting the elevator unit are required for stable operation, requiring the use of additional equipment.
The scheme of the heating unit with a water flow controller
The main factor that allows you to control the heat flow temperature of the heating system is the water flow. The measurement of this indicator causes fluctuations in the coolant in the devices and makes the operation of the heating system unstable.
To eliminate such phenomena in the system, a regulator is mounted in front of the elevator unit, ensuring a constant flow of coolant.
Such a scheme is extremely important in houses with hot water supply, where there are periods of active water intake from the system (morning, evening, weekend, etc.).
The disadvantage is that when the temperature of the driving heat flow decreases, the circuit is not effective.
Scheme of the heating heating unit with nozzle regulating the elevator
The ability to mobilely adjust the nozzle throughput allows you to maintain constant performance at the outlet when temperature changes in the main pipeline.
Nozzle adjustment is effective only with full automation of the process with the use of additional equipment:
- thermal sensor;
- pressure gauge;
- servo drive, etc.
Such schemes do not find wide application because of the requirements for high pressure in the system, the increasing load on the nozzle and the high cost.
Diagram of the elevator unit with a control pump
This connection scheme is used in autonomous heating systems of private houses. It allows the node mechanism to function normally with insufficient pressure in the heating system (less than 2 bar between the inlet and return).
A jumper is installed between the direct heat conduit and the return to which the pump is installed, the use of a temperature regulator is mandatory.
The use of connection schemes with additional features is not always justified - they complicate the system, require electricity supply. The reliability of the system and its complexity are inversely related to each other. It should also take into account a significant increase in the cost of the heating unit and the cost of electricity.
Safety Precautions and Operation
A few general rules for ensuring the safe operation of the equipment of a heat point:
- staff must be qualified;
- Workers should be familiar with the rules for operating equipment.
The elevator assembly of the heating system does not require special attention - enough current inspections. After the scheduled inspection, it is advisable to seal the system in order to fix the settings and avoid unauthorized interference.