At present, a significant place in the list of monthly payments to the state treasury is made by heating fees. And it’s no wonder that everyone, at least a little versed in the pricing policy of DUK’s and ZhEK’s, wants to minimize costs in the heating season. In addition, it is important to note that recently the growth in the amount paid for electricity consumption is already becoming a trend. That is why frugal owners are trying to monitor the development of technologies in the field of heating appliances and systems, the use of which, according to the developers, minimizes costs without loss of heating quality. In this regard, the so-called vacuum radiators have been especially popular recently. Let's look at the question of what this new product is and is it so profitable and necessary, as it seems at first glance?
What is a vacuum radiator
 Being a novelty in the market of heating systems, this development has already managed to gain great popularity. What is the reason for such a good, it would seem, start? In appearance, these products are not much different from already bored sectional radiators. Carbon steel vacuum radiators are made.
Being a novelty in the market of heating systems, this development has already managed to gain great popularity. What is the reason for such a good, it would seem, start? In appearance, these products are not much different from already bored sectional radiators. Carbon steel vacuum radiators are made.
However, the cardinal difference is present precisely in the internal structure and the principle of functioning of these heating devices. Water, which is a coolant in the heating system, circulates exclusively through the horizontal pipe located below. Instead of ordinary water, the sections themselves contain a special lithium bromide liquid, the boiling point of which in an airless medium is approximately 35 degrees Celsius. Water comes into contact with lithium bromide liquid only through the surface of the sections.
Principle of operation
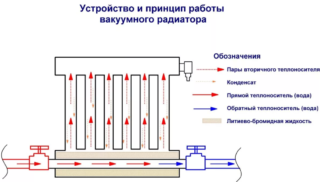 Step by step, the principle of operation of vacuum heating radiators is as follows:
Step by step, the principle of operation of vacuum heating radiators is as follows:
- coolant (water) enters the horizontal compartment of the pipe located below;
- heat is transferred to the secondary coolant (lithium bromide liquid);
- the secondary coolant goes into a gaseous state (evaporates);
- evaporation heats the radiator body, and then emits into the environment;
- the condensate remaining after the above process is lowered into the lower compartment, after which the process is repeated.
It is also worth noting that the smaller the volume of the heated fluid, the easier it is to heat it. That is why in one section at a time there is only 50 ml of coolant. And if we take into account the low temperature threshold of boiling of the secondary coolant, then a logical conclusion can be made: energy for heating in this way requires significantly less. It is the reduced costs of energy consumption that are the main advantage of heating systems of this type. Also, with particularly careful testing, it is possible to observe exactly uniform heating, which in fact confirms the operability of a fundamentally new circuit, on the basis of which vacuum radiators are designed.
In addition, radiators of this type work perfectly in tandem with other heat sources, such as boilers of various types and even solar collectors, and fit perfectly into any heating scheme, both centralized and autonomous.
Advantages and disadvantages
 By installing vacuum radiators in your home, you absolutely get:
By installing vacuum radiators in your home, you absolutely get:
- 80% less coolant volume in the radiator;
- accordingly, a significant reduction in power costs;
- complete elimination of the risk of corrosion of the inner surface of the radiator;
- no risk of clogging;
- minimization of costs associated with the installation of a radiator;
- increasing the speed of heating the air indoors;
- unpretentiousness in leaving;
- high wear resistance (average service life is 20 years);
- safety during use (vacuum radiators are fastened with two threaded joints, this type of fastening almost completely eliminates the risk of depressurization of the system).
If the radiator is still out of order, then due to its design features and the small volume of the coolant, the possibility of a flood is excluded.
The only noticeable disadvantage of vacuum radiators as a high-tech product is their high price compared to other types of radiators.
findings
Vacuum radiators are a great alternative to outdated aluminum. Moreover, this novelty of the market for heating appliances is characterized by a radically new principle of operation, which significantly reduces the price of electricity, eliminates the risk of blockages and corrosion, and also makes radiator maintenance easier. It is worth noting that maximum performance can be achieved by installing a vacuum radiator in an autonomous system with a boiler operating at low power, or by combining it with heat meters in a centralized system.


