To protect the house from heat loss, foam or polystyrene foam is used. Both materials are produced by foaming polystyrene, but the foam passes additional processing by extrusion. The properties of insulation differ, they have different thermal conductivity, moisture permeability, strength and are used on different surfaces.
Production of foam and polystyrene foam
The second name of the foam is extruded polystyrene foam. Polyfoam goes through the technological process of remelting and pressing in aggregates. The foam mass is placed in the extruder and processed by pressure and temperature. Melting converts the feed into foam with small air cells.
The technology for the production of expanded polystyrene consists in foaming the granules of raw materials in a container under steam pressure. The enlarged granules are dried and sintered into the total mass in special forms under pressure. The resulting blocks are aged from 15 to 30 days for natural drying from moisture, then cut into plates.
The production of materials goes through technological cycles and at the output heaters with differences in basic characteristics are obtained.
General properties
Common is the raw material that is used in the production of materials. Well-known polymers (plastics) are used.
Feed Category:
- polyurethane heterochain polymers;
- polyvinyl chloride;
- polystyrene;
- carbamides are formaldehydes.
Both materials have a common drawback - impermeability to steam and air. Expanded polystyrene and foam foam equally disadvantageously work as insulation from noise. They protect against shock on the floor or wall, but they do not remove the general hum.
Penoplex treated with impregnation and expanded polystyrene belong to the middle category of danger in case of fire, emit chemicals equally and die out over time. Animals do not use heaters for food; in the thickness of isolation, an environment is not created for the development of bacteria and fungi. Rodents destroy materials if they restrict passage to food.
Expanded polystyrene and polystyrene are lightweight and do not burden the load-bearing structures, are easily cut and simply stick to the surface. Materials are mounted without the use of personal protective equipment.
Feature Differences
The structure of the foam is represented by small cells (less than 1 mm), which have isolated shells. The air in them does not come into contact with the total mass. Expanded polystyrene consists of large and small balls, which are connected to each other by sintering when heated, between them there are conditional voids.
Production
Penoplex at the outlet goes through the stage of foaming and extrusion pressing. The production technology was developed in the USA more than 50 years ago. The material is obtained by combining polystyrene particles under the influence of temperature and high pressure. In the process, a foaming component is added as a mixture of CO2 (carbon dioxide) and light freons.
The melt is forced through a molding apparatus (extruder). The mass is affected by forces that form the internal structure of the material in the form of small cells. In slabs, residual freon is replaced by air. The sheets with a homogeneous structure are obtained.
To produce polystyrene foam, polystyrene particles are placed in a hopper, where high temperature and pressure turn them into spherical granules. Foaming is repeated several times to increase the size of the balls.The dried elements are fed to the molding, where in the unit under the steam the granules are glued together in a block.
Steam treatment leads to the appearance of excess moisture in the mass of material, so the blocks are dried in natural conditions. Large products are cut to the specified sizes vertically and horizontally on the sawmills.
Thermal conductivity
The thermal conductivity parameter affects the thickness of the material. Penoplex is characterized by a better indicator than expanded polystyrene. The first material has a denser structure, which determines the ability to protect the building from internal heat loss.
Characteristics of materials:
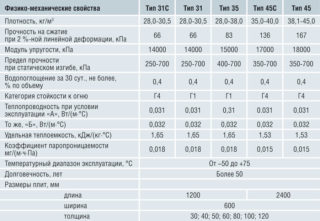
- Penoplex has a heat transfer coefficient of 0.028 - 0.039 W / m.K. The density of the insulator is from 26 to 45 kg / m3. Temperature range -50 - + 75 ° С.
- Expanded polystyrene has a thermal conductivity of 0.336 - 0.40 W / m.K in dry form. The density of the insulation is from 11 to 35 kg / m3, depending on the modification. It works at temperatures from -40 to + 70 ° C.
If the internal partitions and walls are insulated in a warm climate, polystyrene foam is used, since there is no need for strong thermal insulation. In conditions of frosty climate and high humidity, penoplex is used.
Moisture permeability and vapor permeability
The vapor permeability index shows the amount of air passing through a panel of a selected thickness over a given time at one pressure outside and inside. Moisture permeability indicates the ability of the insulation to absorb and retain water within the mass.
The difference in the indicators of materials:
- penoplex has a vapor permeability of 0.18 - 0.2 mg / m.p. Pa, absorbs 0.2% of the volume in 24 hours in water;
- expanded polystyrene is characterized by vapor permeability of 0.16 - 0.21 mg / m.ch. Pa, per day absorbs up to 1% of the liquid of the total weight.
Increased water absorption degrades the quality of the insulator, while the conductivity of the heat increases, and the strength decreases. Moisture-saturated materials are destroyed during freezing because water at low temperatures expands and breaks the structure.
Strength
Strength index characterizes the property of the insulation to deform under the action of force. The strength of expanded polystyrene is lower due to the fact that the structure contains small particles and it crumbles.
The difference in technical characteristics:
- the compressive strength of the foam - 0.26 - 0.46 N / mm², bending - 0.37 - 0.95 MPa;
- compressive strength of expanded polystyrene - 0.045 - 0.117 MPa, bending - 0.06 - 0.3 MPa.
A special type of foam with a high tensile strength and high density (about 45 kg / m3) is used to isolate airfield strips, roads and railroad tracks. The strength of the foam allows you to use it in the insulation of floors, on which you can walk.
Terms of service
The cause of the destruction of the material is the influence of the environment, for example, increased humidity, sunlight. The insulation decomposes under the influence of harmful fumes from the finishing layers or in direct contact with aggressive components.
- Penoplex isolates from the cold for 50 to 80 years.
- Expanded polystyrene remains in working condition for 30 to 50 years.
Materials based on foamed polyurethane do not rot.
Price
Penoplex and expanded polystyrene are available in different types and sizes. The difference is in the thickness and dimensions of the panels.
The cost of individual groups of goods:
- penoplex Comfort 12.94 m2, 18 sheets, size 1200 x 600 x 20 mm - price 1 089 - 1 352 rub. for packaging;
- penoplex Comfort 50 for a roof, size 1200 x 600 x 50 mm - price 153 rubles. per sheet;
- penoplex Comfort 100 for a roof, size 1200 x 600 x 100 mm - price 362 rubles. per sheet;
- polystyrene PPS-30 (PSB-S 35T) (density 30.0 kg / m3), size 1000 x 2000 x 40 mm; 1200 x 2000 x 40mm - 5250 rubles. per cubic meter.
A cubic meter of polystyrene foam costs almost 1.5 times less than a foam, therefore the first option is more often chosen, if operating conditions allow.
Material Applications
Penoplex is used for indoor or outdoor insulation work. The dense material ensures the strength of the layer and is easily put into the mounting position with glue, mastic or construction hardware.The surface of the insulator is finished with plaster, plastic, siding to protect against environmental conditions. The material is used for insulation of foundations, roofs, facades, floors, because it has low water absorption.
Polyfoam is used in conditions of low humidity, for example, for insulation of internal and external walls, partitions, and ceilings. An additional layer of waterproofing is required when warming the foundations in order to preserve the thermal insulation properties of expanded polystyrene.
The choice between polystyrene foam and polystyrene depends on the operating conditions of the material. The best option is acquired by the owner after consulting a specialist. There are designs that require high strength material and high protective characteristics. In other conditions, polystyrene may be useful as a more affordable form of insulator.