For residents of apartment buildings, a standard for payment for heating services is established, which depends on the amount of thermal energy spent on maintaining a normal temperature in the house. This moment is prescribed in PP No. 306. Knowing what the heating is measured in, it is possible to predict the costs for a month, heating period or quarter.
What is Gcal
The concept of gigacalorie means a unit of thermal energy in heating. This energy within the premises is transmitted by convection from batteries to objects, and is radiated into the air. A calorie is the amount of energy needed to heat 1 g of water per degree at atmospheric pressure.
For the calculation of thermal energy, another unit is used - Gcal, equal to 1 billion calories. On average, heat consumption per 1 sq. Km. m. in Gcal in the Russian Federation is 0.9342 Gcal / month. If you translate the indicator into other quantities, 1 Gcal will be equal to:
- 1162.2 kW / h;
- heating 1 thousand tons of water to +1 degree.
Value approved in 1995.
Features Gcal for residential high-rise buildings
If the multi-apartment type of buildings is not equipped with a common house or individual meter, thermal energy is calculated by the area of the premises. When there is a metering device, horizontal or sequential route routing, residents independently determine the amount of thermal energy. To do this, use:
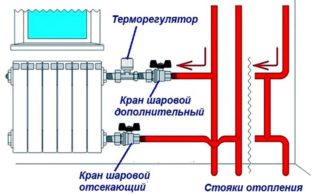
- Throttling radiators. With limited patency, the temperature decreases and energy costs are reduced.
- On the return is a general thermostat. The flow rate depends on the temperature in the apartment. With a small flow, the temperature is higher, with a large - less.
An individual meter is predominantly equipped with an apartment in a new building.
The specifics of Gcal for a private house
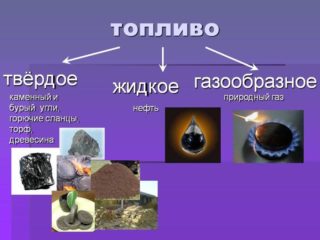
The material spent on heating is determined by the tariff for private buildings. According to average data, the cost of 1 Gcal is:
- gas - natural 3.3 thousand rubles, liquefied 520 rubles;
- solid fuel - coal 550 rubles., pellets 1.8 thousand rubles .;
- diesel engine - 3270 rubles;
- electricity - 4.3 thousand rubles.
The price of thermal energy depends on the region in which the private house is located.
General principles of computing
How thermal energy is calculated, PP No. 354 is established. Utilities are involved in the calculations, but they are also allowed to be produced by the residents themselves. You can determine the heat consumption after calculating the amount of thermal energy spent on heating for the year. This period allows you to get an average standard, since in summer the costs are less, and in the winter more. Payment according to the standard provides for equal costs for the heating period or calendar year.
The calculation scheme depends on several factors:
- equipping a house with a thermal energy meter;
- the ability to account for the heating of all rooms with individual appliances;
- The calendar payment time is winter or all year.
Calculating thermal energy for an apartment building is more difficult than for a private one. This is due to the presence of common places, residential and non-residential premises, ownership. Taking into account the dependence of heat energy on the dimensions of the room, it is worth following PP No. 354 and PP No. 306. They noted the distribution of the amount of heat used by the house in proportion to the area of the apartments. The total meter readings are divided by the proportion of the owners' housing.
Heat Calculation Methods
You can determine the cost of a gigacalorie of heat depending on the availability of a meter. In the Russian Federation, several schemes are used.
Payment without meters during the heating season
The calculation is based on what area of the apartment (living rooms + utility rooms) and is made according to the formula:
P = SхNхTwhere:
- P - amount payable;
- S - the size of the area of the apartment or house in m²;
- N - the heat spent for heating 1 square for 1 month in Gcal / m²;
- T - tariff value of 1 Gcal.
Example. An energy provider for a one-room apartment of 36 squares delivers heat at 1.7 thousand rubles / Gcal. The consumer norm is 0.025 Gcal / m². For 1 month heating services will be: 36x0.025x1700 = 1530 rubles.
Payment without a counter for the whole year
Without an accounting device, the calculation formula also changes P = Sx (NxK) xTwhere:
- N - rate of consumption of thermal energy per 1 m2;
- T - the cost of 1 Gcal;
- TO - coefficient of frequency of payment (the number of heating months is divided by the number of calendar). If the reason for the lack of an accounting device is not documented, K increases by 1.5 times.
Example. The one-room apartment has an area of 36 m2, a tariff of 1700 rubles per Gcal and a consumer rate of 0.025 Gcal / m². Initially, it is required to calculate the frequency coefficient for 7 months of heat supply. K = 7: 12 = 0.583. Next, the numbers are substituted in the formula 36x (0.025x0.583) x1700 = 892 rubles.
Cost in the presence of a common house meter in the winter
This method allows you to calculate the price for central heating with a common meter. Since thermal energy is supplied for the entire building, it is oriented to the area for calculation. The formula applies P = VxS / StotalxTwhere:
- P - monthly cost of services;
- S - area of a separate residential premises;
- General - the size of the area of all heated apartments;
- V - General indications of the collective metering device for the month;
- T - tariff value of 1 Gcal.
Example. The owner’s housing area is 36 m2, the entire high-rise building is 5000 m2. Monthly heat consumption - 130 Gcal, the cost of 1 Gcal in the region - 1700 rubles. Payment for one month equals 130 x 36/5000 x 1700 = 1591 rubles.
Meters are in all apartments
Depending on the availability of a collective meter at the entrance and a personal device, a change in the readings is observed in each apartment, but this does not apply to heating tariffs. Payment is divided between all owners by area parameters as follows:
- They consider the difference in heat consumption on the common house and personal meters according to the formula Vdif. = V- ∑Vpom.
- The resulting figure is substituted in the formula P = (Vsom. + VpxS / Stotal) xT.
The meaning of the letters is decrypted as follows:
- P - amount payable;
- S - an indicator of the area of a separate apartment;
- General. - the total area of all apartments;
- V - collective heat consumption;
- Vpom - individual heat consumption;
- VR - the difference in the readings of individual and house appliances;
- T - tariff value of 1 Gcal.
Example. In a one-room apartment of 36 m2, an individual meter is installed, showing 0.6. 130 is knocked out on the house, a separate group of devices gave 118. The high-rise building's square is 5000 m2. Monthly heat costs - 130 Gcal, payment for 1 Gcal in the region - 1700 rubles. First, the difference in readings is calculated Vp = 130 - 118 = 12 Gcal, and then - a separate payment P = (0.6 + 12 x 36/5000) x 1700 = 1166.88 rubles.
Using a Boost Factor
Based on PP No. 603, a heating fee is charged 1.5 times more if the meter is not repaired for 2 months, stolen or damaged. A raising factor is also set if homeowners do not transmit the readings of the device or twice did not let specialists in checking the technical condition visit it. You can independently calculate the increasing coefficient by the formula P = Sx1.5 NxT.
The formula for calculating thermal energy (per 1 sq. Meter)
The exact formula for calculating thermal energy for heating is taken in the ratio of 100 watts per 1 square. In the process of computing, it takes the form:
Q = (S × 100) × a × b × c × d × e × f × g × h × i × j × k × l × m.
Latin letters denote correction factors:
- and - the number of walls in the room. For the inner room it is 0.8, for one external structure - 1, for two - 1.2, for three - 1.4.
- b - the location of the outer walls around the world. If the room faces north or east - 1.1, south or west - 1.
- c - the attitude of the room to the wind rose. The house is downwind - 1.2, downwind - 1, parallel to the wind - 1.1.
- d - climatic conditions of the region. It is specified in the table.
| Temperature, degrees | Coefficient |
| From -35 | 1,5 |
| -30 to -34 | 1,3 |
| -25 to -29 | 1,2 |
| -20 to -24 | 1,1 |
| -15 to -19 | 1 |
| -10 to -14 | 0,9 |
| To 10 | 0,7 |
- e - insulation of the wall surface. For structures without insulation - 1.27, with two bricks and minimal thermal insulation - 1, good insulation - 0.85.
- f - ceiling height. It is specified in the table.
| Height, m | Coefficient |
| Up to 2.7 | 1 |
| 2,8-3 | 1,05 |
| 3,1-3,5 | 1,1 |
| 3,6-4 | 1,15 |
- g - Features of floor insulation. For basements and socles - 1.4, with insulation on the ground - 1.2, in the presence of a heated room below - 1.
- h - Features of the upper room. If at the top there is a cold mountain - 1, an attic with insulation - 0.9, a heated room - 0.8.
- i - design features of window openings. In the presence of double glazing - 1.27, single-chamber double-glazed windows - 1, two-chamber or three-chamber glass with argon gas - 0.85.
- j - general parameters of the glazing area. It is calculated by the formula x = ∑Sok / Sp, where ∑Sok is a common indicator for all windows, Sп is the quadrature of the room.
- k - the presence and type of entrance opening. A room without a door -1, with one leaf on the street or loggia - 1.3, with two wings on the street or loggia - 1.7.
- l - Battery connection diagram. Indicated in the table
| Sidebar | Features | Coefficient |
| Diagonal | Feed at the top, return at the bottom | 1 |
| Single sided | Feed at the top, return at the bottom | 1,03 |
| Double sided | Return and feed below | 1,13 |
| Diagonal | Feed below, return above | 1,25 |
| Single sided | Feed below, return above | 1,28 |
| One sided | Flow and return bottom | 1,28 |
- m - the specifics of the installation of radiators. It is specified in the table.
| Type of connection | Coefficient |
| Open on the wall | 0,9 |
| Top hidden by a shelf or window sill | 1 |
| Closed on top of a niche | 1,07 |
| It is covered with a niche / window sill on top and an overlay from the end | 1,12 |
| With decorative body | 1,2 |
Before using the formula, make a diagram with data on all the coefficients.
Accounting devices for houses and apartments
A special device allows you to accurately calculate the tariffs for water supply, electricity, gas and heat. Users are allowed to install a heat meter to record heat energy consumption. The device measures in Gcal / h, kW / h and kJ / h. To date, popular.
Wing counters
The counter has the form of a mechanism with a perpendicular arrangement of the axis of rotation. The model is characterized by low sensitivity, which allows accurate measurement of heat costs. Regulators are suitable for rooms with good thermal insulation, temperature indicators of +26 degrees. The vane apparatus, with the functions of temperature correction to +22 degrees, considers a minimum of Gcal.
Benefits:
- inexpensive cost;
- battery powered;
- ease of use;
- accuracy of measurements.
Minuses:
- risk of damage due to water hammer;
- quick wear of the mechanism;
- increase in pressure in the system;
- when the impeller is jammed, the water flow is not allowed.
Vane-type devices are suitable for taking readings if a small volume of water is used.
Instruments with jump recorders
The pulse apparatus performs remote reading from 2-16 channels, therefore it is suitable for a private or apartment building.Accounting and data transfer is made to the LCD monitor, via a plug-in interface, to a laptop or computer using a network cable, via a GSM network.
The script by which you want to measure the readings is set by the user. Ultrasonic devices can be connected to a water and gas supply system, are part of the automatic energy metering system, or combined with a smart home system.
Benefits:
- many options for common house and private measurements;
- the ability to integrate into multiple accounting systems;
- strength due to the lack of movable nodes;
- beautiful appearance and compactness;
- protection against dust and moisture - the counter can be put in the kitchen or on the street;
- strong case;
- self-diagnosis features;
- extensive communication;
- execution with a removable computing unit or without it;
- the period between inspections is 6 years, between replacements - 10 years.
Minuses:
- high price;
- communication capabilities depend on the specifics of the output;
- the cost of acquiring flowmeters, pressure sensors, remote control modules for basic equipment.
For outdoor use, models with differential recorders with a moisture protection level of IP 68 are suitable.
The results of all calculations
With the correct use of the calculation formula, you can find out the amount of consumed Gcal of thermal energy. Information will help to plan the budget, to clarify the total amount payable. Based on the above formulas, we can conclude about the cost of gigacalories on the structure of up to 200 squares. This value is 3 Gcal per month. Given the duration of the heating season in most regions of the Russian Federation at 6 months, it is easy to determine the approximate heat consumption. You will need to multiply 3 Gcal by 6 months. The result is 18 Gcal.
The cost of gigacalories is easier to calculate for a private house by the indicators of an individual meter. The settlement process for apartments is complicated by the presence of a house and personal meter. However, such a procedure is implemented independently without visits to special organizations.
To calculate the thermal energy, special mathematical formulas are used. The most accurate data is substituted into them, and energy providers are informed about the independent calculation. When calculating, you can use online calculators or contact specialists who will perform all operations, focusing on the indicators of your premises and the type of meter.