To heat the room, heating appliances of appropriate power are required. Calculation of the heat load for heating the building allows you to accurately determine what power the boiler will need, what size radiators need to be installed and which heating scheme will be most effective. When calculating, many factors are taken into account.
Heat load concepts
Space heating is a compensation for heat loss. Through walls, foundations, windows and doors, heat is gradually removed. The lower the outside temperature, the faster the heat transfer to the outside occurs. To maintain a comfortable temperature inside the building, heaters are installed. Their performance should be high enough to block heat loss.
Heat load is defined as the sum of the heat loss of a building equal to the required heating power. Having calculated how much and how the house loses heat, they will find out the power of the heating system. The total value is not enough. A room with 1 window loses less heat than a room with 2 windows and a balcony, so the indicator is calculated for each room separately.
In calculations, the height of the ceiling must be taken into account. If it does not exceed 3 m, calculate the size of the area. If the height is from 3 to 4 m, the flow rate is considered by volume.
Factors Affecting TH
Many factors affect heat loss:
- Foundation - the insulated version retains heat in the house, insulated passes up to 20%.
- Wall - porous concrete or wood concrete has a much lower throughput than a brick wall. Red clay brick retains heat better than silicate brick. The thickness of the partition is also important: the wall of brick with a thickness of 65 cm and foam concrete with a thickness of 25 cm has the same level of heat loss.
- Warming - thermal insulation significantly changes the picture. External insulation with polyurethane foam - a sheet with a thickness of 25 mm - is equal in effectiveness to the second brick wall with a thickness of 65 cm. Finishing with a cork inside - a sheet of 70 mm - replaces 25 cm of foam concrete. Experts knowingly argue that effective heating begins with proper insulation.
- Roof - pitched construction and insulated attic reduce losses. A flat roof made of reinforced concrete slabs allows up to 15% of heat.
- Glazing area - an indicator of thermal conductivity in glass is very large. No matter how airtight the frames are, heat passes through the glass. The more windows and the larger their area, the higher the heat load on the building.
- Ventilation - the level of heat loss depends on the performance of the device and the frequency of use. The recovery system allows you to slightly reduce losses.
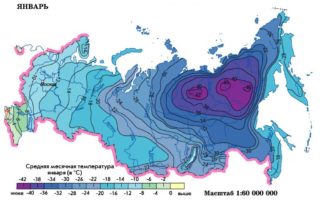
- The difference between the temperature on the street and inside the house - the greater it is, the higher the load.
- The distribution of heat inside the building - affects the performance for each room. The rooms inside the building cool less: when calculating a comfortable temperature, they consider the value of +20 C. The end rooms cool faster - the normal temperature here is +22 C. In the kitchen, it is enough to heat the air to +18 C, since there are many other sources of heat: stove , oven, fridge.
When calculating the heat load of an apartment building, material, thickness and insulation of partitions and ceilings are taken into account.
Characteristics of the object for calculation
The heat load on heating and the loss of heat at home are not the same thing. There is no need to heat a technical building as intensively as residential premises. Before proceeding with the calculations, establish the following:
- Purpose of the object - residential building, apartment, school, gym, shop. The heating requirements are different.
- Features of the architecture are the sizes of window and balcony openings, the installation of a roof, the presence of attics and basements, the number of storeys of a building, etc.
- The temperature standards - for living rooms and office they are different.
- The purpose of the room - the parameter is important for industrial buildings, since each workshop or even a site requires a different temperature regime.
- The design of external fences - external walls and roofs.
- Maintenance level - the presence of hot water supply reduces heat loss, intensively working ventilation increases.
- The number of people who are constantly in the house - for example, affects the indicators of temperature and humidity.
- The number of coolant intake points - the more there are, the greater the heat loss.
- Other features - for example, the presence of a swimming pool, sauna, greenhouse or the number of hours when people are in the building.
When calculating heat losses in a store or at a catering point, the amount of equipment that generates heat is taken into account - showcases, refrigerators, kitchen appliances.
Types of thermal loads
Thermal loads are of a different nature. There is some constant level of heat loss associated with the thickness of the wall, the roof structure. There are temporary ones - with a sharp drop in temperature, with intensive ventilation. The calculation of the entire heat load takes this into account.
Seasonal loads
So called heat loss associated with the weather. This includes:
- the difference between the temperature of the outside air and indoors;
- wind speed and direction;
- the amount of solar radiation - with high insolation of the building and a large number of sunny days, even in winter the house cools less;
- air humidity.
The seasonal load is distinguished by a variable annual schedule and a constant daily schedule. Seasonal heat load is heating, ventilation and air conditioning. The first 2 species are referred to winter ones.
The formulas use not short-term sharp changes in temperature and humidity - maximum, but averaged: values observed for the 5 coldest days of the 5 coldest winters in 50 years.
Constant heat
The year-round includes hot water supply and technological devices. The latter is important for industrial enterprises: digesters, industrial refrigerators, steaming chambers emit a huge amount of heat.
In residential buildings, the load on hot water becomes comparable to the heating load. This value varies little during the year, but varies greatly depending on the time of day and day of the week. In summer, FGP consumption decreases by 30%, since the water temperature in a cold water supply is 12 degrees higher than in winter. In the cold season, hot water consumption is growing, especially on weekends.
Dry heat
Comfort mode is determined by air temperature and humidity. These parameters are calculated based on the concepts of dry and latent heat. Dry is a value measured by a special dry thermometer. It is affected by:
- glazing and doorways;
- sun and heat loads for winter heating;
- partitions between rooms with different temperatures, floors above empty space, ceilings in the attics;
- cracks, crevices, gaps in the walls and doors;
- air ducts outside heated areas and ventilation;
- equipment;
- people.
Floors on a concrete foundation, underground walls are not taken into account in the calculations.
Latent heat
This parameter determines the air humidity. The source is:
- equipment - heats the air, reduces humidity;
- people are a source of moisture;
- air flows through cracks and crevices in the walls.
Typically, ventilation does not affect the dryness of the room, but there are exceptions.
Methods for calculating the heat load for heating a building
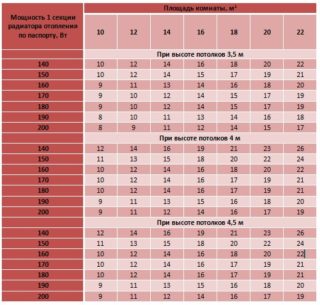
In order to calculate the necessary heat load, data on temperature and humidity standards are taken from GOST and SNiP. There is also information about the heat transfer coefficients of different materials and structures. When calculating the passport data of radiators, a heating boiler, and other equipment, be sure to take into account
The calculations include:
- heat flow of the radiator - the maximum value;
- maximum consumption for 1 hour when the heating system;
- heat costs per season.
An approximate value is given by the ratio of the calculated data with the area of the house or rooms. However, this approach does not take into account the structural features of the building.
Calculation of heat loss using aggregated indicators
The method is used when the exact characteristics of the building cannot be established. To calculate the thermal load, use the formula.
Qot = α * qo * V * (tv-tn.r); Where:
- q ° - specific thermal indicator of the structure according to the project or the standard table. For buildings for various purposes - residential apartment building, garage, laboratory - it is different.
- and - correction factor, different for different climatic zones.
- Vн - external volume of the building, m³.
- Tvn and Tnro - temperature inside the house and outside.
The method allows you to calculate indicators for the entire building and for each zone or room. However, the formula does not include data on the thermal conductivity of the materials of which the house is built, and the indicators for wood, foam concrete and stone are very different.
Determination of heat transfer of heating and ventilation equipment
To obtain a more reliable result, use the calculation for walls and windows and additionally calculate the thermal load of the ventilation. Calculations are carried out in several stages:
- calculate the area of walls and glazing;
- calculate the heat transfer resistance using the reference data;
- calculate the coefficient according to the type of insulation - the data is also in the construction directory, you can specify in the product passport;
- calculate the level of heat loss through the windows;
- The calculated values are multiplied by the sum of the temperatures (inside and outside the building) and the total heat consumption is obtained.
Calculation of thermal ventilation load is performed according to the formula Qv = c * m * (Tv-Tn)where:
- Qv - heat consumption by ventilation;
- with - heat capacity of air;
- m - air mass: on average, normal ventilation requires an air volume equal to three times the quadrature of the room; mass is obtained by multiplying the value by air density;
- Tv-tn - the difference between external and internal temperature.
The overall indicator is obtained by summing the estimated heat loss of the building and losses through ventilation.
Calculation of values taking into account various elements of building envelopes
If for calculations we use theoretical data - indicators for heat loss of each material - the result is still not entirely accurate. In the calculations it is impossible to take into account the number and size of cracks and gaps, the work of lighting and so on.
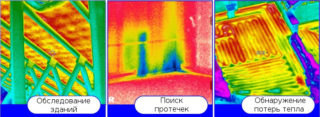
The most accurate result is provided by thermal imaging inspection of the building. The procedure is performed in the dark, with the lights off. It is recommended to remove carpets and furniture for a while so as not to distort the readings.
The examination is performed in 3 stages:
- with the help of a thermal imager, they study the room from the inside, carefully examine the corners and joints;
- measure losses from the outside - this is how all the features of materials and architecture are taken into account;
- The device data is transferred to a computer, the result is calculated.
Based on the results of the survey, recommendations are made: on insulation, reconstruction, and the choice of heating appliances.
Modern boilers are equipped with power regulators. These are devices that maintain performance at a set level, but prevent jumps and dips during operation. There are limits on the use of energy resources: if the set value is exceeded, the charge for gas or electricity increases. PTH limits fuel consumption.