Estimated normative and actual indicators of specific thermal characteristics are the main markers used by specialists in the field of heat engineering. The numbers have practical value for consumers of their own and multi-storey buildings. The delta between the calculated and actual indicators is the coefficient of energy efficiency of the room, which reflects the cost-effectiveness of thermal communications.
The concept of specific thermal characteristics of a building
The specific thermal characteristic of the building is an important technical parameter, which is contained in the passport. Calculation is required when designing and building a building. The knowledge of the markers is necessary for the consumer of thermal energy, since they affect the rate indicator. The specific characteristic implies the presence of the value of the largest heat flux required for heating the room. When calculating the indicator, the difference between the street and the indoor indicator is measured 1 degree. The parameter is an indicator of the energy efficiency of the room. The average coefficient is recorded in the regulatory documentation. Marker changes reflect the energy efficiency of the system. Calculation of parameters is carried out according to the established rules of SNiP.
Method for calculating specific thermal characteristics
The specific heating characteristic may be of a calculated normative or actual nature. The first method involves the use of formulas and tables. Actual figures are subject to calculation, but the exact results are determined by thermal imaging inspection of the building.
Settlement and normative
The calculated data is calculated using the formula
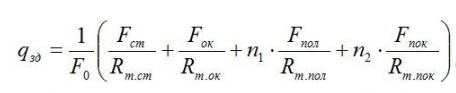
Where:
- qhealthy (W / (m3oC)) - an indicator of the heat lost by one cubic meter of a building with a temperature difference of 1 degree;
- F0 (m2) - marker of the heated area;
- Fst, FOK, Ffloor, Fpok (m2) - an indicator of the area of walls, windows and coatings;
- Rtst, Rcurrent, Rfloor, Rso on - surface heat transfer resistance marker;
- N- coefficient, which depends on the position of the room relative to the street.
 This is not the only way to calculate. Characteristics can be calculated using local building codes, as well as through certain indicators of a building with self-regulation.
This is not the only way to calculate. Characteristics can be calculated using local building codes, as well as through certain indicators of a building with self-regulation.
When calculating the actual parameters are involved:
- Q - fuel consumption marker;
- Z is the coefficient of the duration of the heating season;
- Tint - an indicator of the average temperature in the room;
- Text - marker of average street temperature;
- Q - coefficient of specific thermal characteristics of the room.
Most often resort to this calculation, since it is simpler. However, there is a significant minus that affects the accuracy of the final result: the temperature difference in the buildings is taken into account. To obtain the most informative data, they resort to calculations that determine the heat consumption by the heat loss index in various buildings and data from project documentation.
Actual
Self-regulatory organizations use their own methods.
They contain:
- layout data;
- components of architecture;
- year of construction of the building.
- outdoor temperature markers during the heating season.
In addition, the specific indicator of the heating characteristic is determined taking into account the heat loss in the pipes passing through the cold rooms, as well as the flow rate for condensate and ventilation.The coefficients are contained in the tables of SNiP.
Energy Efficiency Class Definition
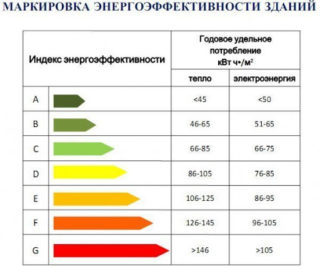 The specific heating characteristic of a building is the main marker of the energy efficiency class of any building. It is determined without fail in residential buildings with many apartments.
The specific heating characteristic of a building is the main marker of the energy efficiency class of any building. It is determined without fail in residential buildings with many apartments.
The marker is determined based on the following data:
- Change in actual and settlement-regulatory markers. The former are obtained by a practical method, as well as using a thermal imaging survey.
- Characteristic of the climate of the area.
- Regulatory data on heating, ventilation costs.
- Type of construction.
- Technical data of building materials.
Each energy efficiency class has a specific resource consumption per year. The indicator is contained in the passport of the house.
Basic methods for improving energy efficiency
Optimization of indicators implies a reduction in the tariff for heating due to improved thermal insulation.
The main methods include:
- Increasing the level of heat resistance of a building under construction. Facing works of walls are carried out, floors are finished with heat-insulating materials. The energy saving indicator rises to 40%.
- Elimination of cold bridges in the building under construction. Energy conservation increases by 3%.
- Glazing of loggias and balconies. The method optimizes heat storage by 10-12%.
- Installation of innovative models of windows with profiles containing several cameras.
- Installation of a ventilation system.
Residents can increase the degree of thermal insulation. Among the main methods should be noted:
- installation of aluminum radiators;
- installation of thermostats;
- installation of heat meters;
- installation of screens that reflect heat fluxes;
- the use of plastic pipes in the heating system;
- installation of an individual heating system.
Improving energy efficiency can reduce the cost of ventilation. Recommended use:
- window micro-ventilation;
- a system with heated air that comes from the outside;
- regulation of air supply;
- protection against drafts;
- ventilation systems with engines of different powers.
To improve the energy efficiency of an apartment building, high costs are required. Sometimes the problem remains unresolved. Reducing heat loss in a private home is simple. It is achieved in various ways. With an integrated approach to the problem, a positive result is achieved. Heating costs depend on the features of the system.
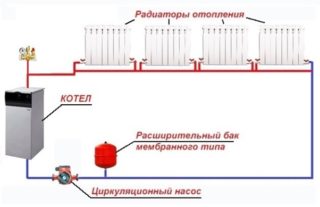
Private sector homes are occasionally connected to central utilities. For the most part, they have an individual boiler room. The installation of a modern system, which is characterized by a high level of efficiency, helps to reduce heat costs. The best choice is a gas boiler. Equipping the boiler with additional equipment is also shown. For example, the installation of a temperature controller can save fuel consumption by 25%. The installation of additional sensors helps to increase gas consumption savings.
The functionality of most autonomous systems is based on forced circulation of the coolant. For this purpose, a pump is mounted in the network. Equipment must be reliable and of high quality. But such models use a large amount of energy. In homes with forced circulation, 30% of the cost goes to operating a circulation pump. On the market are brands of class A units that are energy efficient.
Heat preservation is provided by a temperature regulator. The operation of the sensor is simple. The air temperature is read inside the heated room. As a result, the pump is in the off and on mode, depending on the temperature in the apartment or house.The response limit and temperature mode are set by the user. Residents use an autonomous heating system and get a good microclimate, as well as saving fuel consumption. The main priority of heat-shielding thermostats is to turn off the heater and circulation pump. The equipment remains operational.
There are other methods to increase energy efficiency:
- insulation of walls and floors through innovative heat-insulating materials;
- installation of plastic windows;
- protection of premises from drafts.
All methods make it possible to increase the actual indicators of thermal protection of the building relative to the estimated normative indicators. The enlarged marker reflects the degree of comfort and economy.