In rooms of large area, filled with many heat sources, the installation of air conditioners is irrational. Achieve comfortable conditions with less energy costs allows the use of fan coil units. These are heat exchangers consisting of a fan and a radiator, inside of which water circulates. Before buying equipment, its capacity is calculated. Depending on the degree of consumer preparedness, the calculations are carried out in an academic or simple approximate way.
How to choose the power of fan coil correctly
The chiller-fan coil system is one of the variants of climatic equipment for creating a comfortable microclimate in office, commercial, industrial and domestic premises. The equipment is designed for two modes: cooling in the warm season and heating in the cold season. For multi-zone air conditioning systems, a combined option is recommended: the heat and humidity load is on fan coils, and ventilation provides clean air.
The main elements of the system: chiller - a machine for generating cold; and fan coil units - air conditioning units or fan coil units, which are heat exchangers. The coolant is water or an ethylene glycol mixture. The hydraulic unit circulates the fluid in the pipeline. The purpose of fan coils is to bring the room temperature to the specified parameters.
The principle of operation of the device: a fan blows air through a heat exchanger. A cold coil lowers the flow temperature. Chilled air returns to the room. The process is accompanied by the loss of condensate drained into the drain.
Fan coil selection
Closer air conditioning is selected at full cooling capacity. The cost of cooling exceeds the power spent on heating, so the calculation is carried out at maximum rates. Calculations require taking into account many parameters that affect the amount of heat and moisture released in the room:
- The receipt of apparent heat in the room:
- a) the location of the room and windows relative to the cardinal points;
- b) the number of people (with average physical activity an adult generates 130-150 watts of heat);
- c) material, thickness and quality of thermal insulation of walls and ceilings;
- d) lighting power;
- e) the heat generated during the operation of household appliances, computers.
- Climatic conditions characteristic of the region in terms of temperature and humidity.
- Coolant temperature in the chiller-fan coil system.
- The presence of ventilation, the magnitude of the influx of fresh air.
- Functional purpose of the room.
Methods for calculating fancoils
Having determined the total heat load in the room, they begin to calculate the power of the fan coil. Three calculation methods are used. They are distinguished by the complexity of execution and the accuracy of the results.
Academic
The most accurate version of the calculations, taking into account all possible parameters. The academic method involves a long and complicated calculation process, it will take a beginner 8-10 hours to choose a fan coil for a room with an area of 25-30 square meters. m. The calculations are similar to studies conducted for heat exchange processes in an air conditioning system. For work you will need:
- thermal conductivity coefficients of fencing materials;
- indicators of heat transfer of structural materials to the environment;
- moisture content and enthalpy (components of the id diagram).
 When calculating air humidity and its processing, the id diagram is used.It contains several parameters:
When calculating air humidity and its processing, the id diagram is used.It contains several parameters:
- relative humidity;
- temperature;
- moisture content (amount of steam in 1 kg of air);
- enthalpy (amount of heat in 1 kg of air).
By connecting the lines all the available indicators get a diagram of the air condition. It is used by specialists to calculate air heating and fan coil.
Clarified
Technical specialists involved in the design of air conditioning systems carry out calculations based on the average values of the reference values. The method is less accurate than academic, but gives a fairly reliable result. The calculation is based on the influence of humidity on the power of fan coils. Manufacturers in the specifications indicate two performance: explicit and complete. These parameters require explanation:
- The apparent performance of the device - takes into account all the influx of heat in the room without adjusting for humidity.
- The full performance of a fan coil is power in the cold, which is used to compensate for apparent and latent heat. The second parameter is the heat of condensation of the vapor in the liquid. It is calculated by id chart or special tables.
With low humidity, latent heat is up to 20%. Adding this number to explicit performance, get the full. With an increase in humidity, the proportion of latent heat increases to 50-60%.
Approximate or approximate
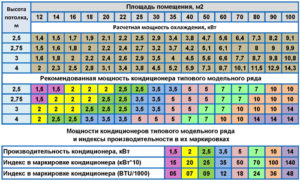 The simplest calculation option offered by employees at points of sale of air conditioning systems using fan coil units that do not have professional selection skills. Calculations occur quickly with a minimum set of parameters used. The generalized estimates in the premises for various purposes provide the following data:
The simplest calculation option offered by employees at points of sale of air conditioning systems using fan coil units that do not have professional selection skills. Calculations occur quickly with a minimum set of parameters used. The generalized estimates in the premises for various purposes provide the following data:
- for offices with office equipment and computers, an air conditioning closer with a power of 150 watts for every 1 square meter will be required. m;
- a living room with a ceiling height of 2.7-3 m needs a fan coil with a cold productivity of 100 watts per 1 sq. km. m square.
For example: the area of a room in an apartment is 20 square meters. m - Q = 100 X 20 = 2000 W or 2 kW.
Final power is determined without taking into account latent heat. In regions with a dry climate, the error is up to 20%, and with high humidity (80-90%) the error is within 50%.
Possible difficulties
Some manufacturers of climate control equipment indicate the cooling power of the fan coil not in conventional kW, but in BTU. British Thermal Unit means British Thermal Unit. The ratio of units is 1 kW = 3412 BTU / h.
Power devices for ease of customer orientation are indicated rounded. For example: 7000 BTU / h = 2100 W.
Features of calculation of fan coil
Manufacturers' data on the production of cold by an air conditioning closer are tied to standard temperature indicators:
- dry thermometer 27 °;
- wet thermometer 19 °;
- water at the entrance to the fan coil 7 °.
Variable factors include fan speed, the characteristics indicate high. There is still medium and low. Among the factors, the change of which affects the performance of the fan coil:
- inlet water temperature;
- air consumption (fan speed);
- the amount of water passing through the fan coil;
- air temperature indoors.
Self-calculation of the electric power of fan coil units for an office or production workshop can cause serious difficulties. Such work is trusted by specialists. With a refined calculation, an online calculator on sites related to climate technology helps. For domestic use of the device, an approximate calculation is suitable.




