Air conditioning - a technological device for cooling the room. For the device to work properly, it is required to install it correctly and operate according to the instructions. It is important to understand where the air conditioner takes air from: from the room or from the street, and what conditions are needed to install the supply equipment.
The principle of operation of climate systems
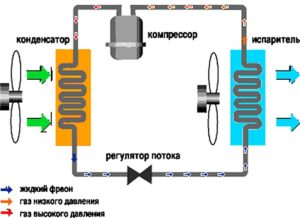 The chain of processes leading the system for cooling air when the device is turned on:
The chain of processes leading the system for cooling air when the device is turned on:
- Freon under the influence of high pressure enters the compressor, is compressed, heated, sent to the condenser.
- In the outdoor unit of the air heat exchanger, the refrigerant changes the state of aggregation from gaseous to liquid. The process is accompanied by heat generation and a decrease in the pressure of the fluid flow in the capillary tube.
- In the heat exchanger of the indoor unit, freon becomes gaseous, emitting cold and absorbing heat from the room.
Thus, the climatic device in the production of cold uses the indoor unit, and the external plays the role of a capacitor. If the split system is configured to supply heat, the blocks change roles - the air conditioner stops supplying cold air. Heat is transferred from the outdoor unit to the room using the same refrigerant.
When installing household climate control equipment, there is no structural design for laying air ducts to supply clean atmospheric air from the street. The communications that lead to the external elements of the system serve only to remove heat. Cooling devices start a closed circuit of processes that move the refrigerant. In one place it evaporates, absorbing heat, and in another it condenses, releasing it.
Air conditioners, which take air from the street to cool, occupy less than 35% of the climate technology market. This is due to their cost and installation complexity.
Types of air conditioners
In domestic conditions, devices are used that are conventionally divided into three large groups:
Mobile (portable) air conditioning is a good alternative to permanently installed climate control equipment. The device can be moved, moved from room to room or transported to another place without installation. Weight from 20 kg. In addition to ventilation and cooling, it can reduce the humidity level in the room. The mobile air conditioner processes the air in the room: one of the built-in fans draws in air mass through a system of openings, and then passes the stream to the evaporator of the refrigeration circuit. During operation, the fan removes the heated air masses through the air duct to the street and throws out the cooled stream into the room through the slotted hole system. The case of the portable device is equipped with a condensate drain pan, which is poured manually.
Window air conditioning is a cooling device, organized by a single body. It is installed in a window opening, a window leaf or a wall, the width of which is no more than 30 cm. The device is attractive due to its simple installation, operation and cost 30-40% lower than other representatives of the product group. A window monoblock takes part of the room air (up to 10%) and releases it to the street, providing forced exhaust ventilation. When oxygen is taken from the street, the system begins to make increased noise and to cool the air flow worse. In fact, the air conditioner begins to function as an exhaust fan.
Split system It supports the indoor temperature and air velocity settings. Consists of external and internal blocks.The split system takes air for cooling in an air-conditioned room and transfers it to the street.
The split system has a heating function: the process of freon movement is reversed, which allows the device to return heated air to the room.
Air conditioning unit
The basic and running models of air conditioners are arranged according to the principle of coordinated work of the following main components:
- The compressor compresses the refrigerant (freon) and supports its movement along the refrigeration circuit. Refrigerant is a working substance of refrigerators that takes away heat from a refrigerated object during boiling.
- The air heat exchanger of the outdoor unit provides the process of converting the refrigerant into a liquid (condensation), as well as its cooling.
- The air heat exchanger of the indoor unit contributes to the process of evaporation of freon.
- The capillary tube is responsible for the timely increase / decrease of refrigerant pressure in the air heat exchangers of the outdoor and indoor units.
- The fan provides a continuous flow of air to the condenser.
Air Conditioners
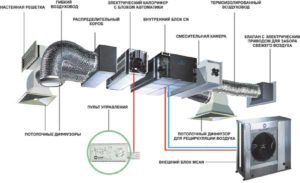
The supply of oxygen from the street is performed by channel and cassette-type air conditioners. Structurally, the possibility of supplying air ducts to the devices for intake of fresh, clean air from the outside is provided. The price of such cooling systems starts at 30 thousand rubles. and varies depending on the required functionality. Air conditioning with ventilation has a significant drawback - the low volume of air that is supplied or removed from the room per unit time.
The channel oxygen supply system shows a higher rate of air exchange, but its installation is complicated by the design features of an ordinary apartment or house. For residential equipment, it is necessary to install a hidden air supply system through the installation of indoor units built into the ceiling. The inconvenience is added by a high-power fan, which is installed externally above the air exchange grill. Its noise level is several times higher than the volume of standard household cooling devices.
An air conditioner with a flow of air from the street has a high oxygen supply capacity and cleans it of impurities and unpleasant odors.
A cooling device with ventilation has a structure similar to standard split systems, with the exception of:
- The indoor unit is equipped with an additional filtration system and an electronic control unit.
- The external unit is supplemented by a suction turbine and a mixing chamber.
The cooling process, supplemented by the flow of oxygen, is as follows:
- The air conditioner takes air from the street with a fan and directs it to the indoor unit through the duct.
- Oxygen taken from the outside is mixed in a separate chamber with room air.
- Filtration, cooling / heating, dehumidification / humidification processes take place.
- Air masses enter the room according to the mode set on the device.
Types of air conditioners with air flow
Cooling devices with a ventilation system differ in the structure of the duct channel:
- Membrane the air conditioner is equipped with a thin flexible plate responsible for the operation of the channel. The permeability of oxygen through the membrane is higher than the permeability of other gases. Devices are expensive, which is why they are rarely found in the consumer market.
- Modular The system is distinguished by the presence of a recuperator installed outside the room next to the air conditioner. The module is equipped with tubes, with the help of which the air is exchanged and thermoregulated. Sellers of HVAC equipment rarely offer such designs, since they are significantly inferior to analogues.
- Modified The air conditioner is equipped with an external cooling and ventilation unit.Between the external and internal parts of the air conditioner, a duct channel for oxygen supply is installed. Cooling systems differ from analogues in their high cost and average air exchange (the amount of ventilated oxygen is calculated for the presence of only one person in the room).
If there are drawbacks: high cost, installation complexity, noise - air conditioners with air intake have a number of useful options: cleaning the room from unpleasant odors, filtering the incoming stream from dust and bacteria. More expensive models have a built-in pollution analyzer that provides information on freshness and purity of air, as well as automatic temperature and humidity settings.