According to the definition given by GOST, wastewater is a liquid that contains pollutants in the form of household and industrial waste. In order to clean them and remove them from urban, settlement territories and areas of enterprises, sewer systems and treatment facilities are equipped.
Wastewater classification and composition
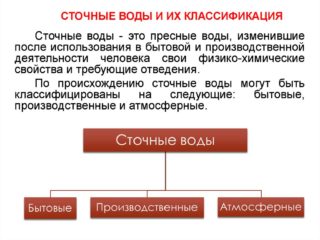 Effluents are divided into three types according to composition, origin and quality characteristics:
Effluents are divided into three types according to composition, origin and quality characteristics:
- Household (hozfekalny). Get into the sewer network from plumbing fixtures. The formation of such effluents occurs both in residential, public and industrial premises in the process of human life. They pose the greatest danger, since they contain a significant amount of organic impurities that are prone to decay. These include feces, urine and a variety of microorganisms, including pathogens.
- Rain or surface. Appear on roads, squares, roofs after precipitation. This category also includes sewage arising after watering gardens and lawns. They are considered the cleanest and contain a small amount of organic matter and mineral suspensions.
- Production. They arise during the implementation of various processes of the technological plan with the use of water at industrial facilities.
The latter category is divided into two types: contaminated effluents, for which treatment is required before reuse or release into water bodies, and relatively clean ones that do not need preliminary treatment. Hazardous substances in the composition vary and depend entirely on the industry and technological features of production.
Another classification of wastewater is based on the concentration of harmful impurities, aggressiveness and toxicity. According to it, sewage is divided into four types:
- slightly contaminated;
- medium contaminated;
- heavily contaminated
- dangerous.
The main evaluation criterion is the pH value. Mildly aggressive liquids include slightly acidic with pH = 6–6.5 and slightly alkaline compositions with pH = 8–9. Liquid media with a strongly acidic (pH <6) or strongly alkaline (pH> 9) composition are highly aggressive.
Contaminated waters are also divided according to phase dispersion composition into suspensions, colloidal, molecular and ionic solutions.
Classifications are regulated by SanPiNov and federal laws, in particular the Water Code.
Pollution assessment
 Calculation of the degree of contamination of sewage effluents depends on the abundance of impurities contained in them and is reflected in the mass per unit volume (g / m3 or mg / l). The density of water is also taken into account, based on the criterion of pure liquid - 999 kg / m3 at a temperature of 15 degrees.
Calculation of the degree of contamination of sewage effluents depends on the abundance of impurities contained in them and is reflected in the mass per unit volume (g / m3 or mg / l). The density of water is also taken into account, based on the criterion of pure liquid - 999 kg / m3 at a temperature of 15 degrees.
Since industrial and household effluents have a complex composition, it is extremely difficult to quickly identify and evaluate the concentration of each of the pollutants.
In this regard, when conducting urgent analyzes, those criteria are selected that are capable of characterizing the total properties of water without separately recognizing impurities. For example, when assessing organoleptic data, the selection of each of the impurities that stain or give an odor is not performed. To determine the composition, apply the total sanitary-chemical study of sewage wastewater. It includes chemical, physico-chemical and microbiological tests.
When performing a full sanitary-chemical analysis, an assessment is carried out according to the following indicators:
- level of acidity (pH), solids, the presence of suspensions;
- temperature, smell, color, transparency;
- biochemical oxygen demand (BOD5) - the consumption of this element for five days;
- the presence of heavy metals, radioactive and toxic substances;
- the presence of petroleum products, surfactants, dissolved oxygen;
- concentration of phosphates, sulfides, nitrogen compounds, chlorides;
- determination of the microbial number, microorganisms of the group of Escherichia coli, parasites.
Also used is the method of measuring the mass concentration of ethylene glycol and diethylene glycol in samples of natural and sewage liquids by gas chromatography.
Studies allow us to evaluate the runoff by the maximum permissible indicators. Their meanings are as follows:
- the number of notified substances - 500;
- BOD - 500;
- COD - 800;
- the remainder of dense matter - 2000;
- ether-containing impurities - 20.
In addition to standard tests at citywide treatment facilities, additional tests can be carried out. They allow you to determine the composition and degree of contamination of industrial wastewater that is discharged from local production facilities.
The main types of pollutants
The composition of wastewater is determined by the presence of pollutants in them:
- biological;
- chemical;
- mineral.
The first include microbes (viruses and bacteria), yeast and algae cultures, fungi and vegetation. Oil products, surfactants, pesticides, heavy metals, dioxins, phenols, nitrogen compounds become polluting chemical impurities. Earth, slag, sand, silt are admixtures of mineral nature.
The composition of the liquids also emit conservative and non-conservative contaminants. The former do not enter into chemical reactions, do not decompose during biological treatment. Non-conservative impurities are removed from effluents through self-cleaning bioprocesses.
Hazardous Raw Wastewater
 To date, the discharge of sewage is one of the most important problems of water resources. Pollution of seas, rivers and lakes occurs as a result of the lack of purification of waste liquids that contain a significant amount of harmful microorganisms, aggressive chemistry and toxic substances. At the moment they enter the water body, a violation of the natural regime occurs, which is expressed in a negative and even fatal effect on water resources. Pollution causes:
To date, the discharge of sewage is one of the most important problems of water resources. Pollution of seas, rivers and lakes occurs as a result of the lack of purification of waste liquids that contain a significant amount of harmful microorganisms, aggressive chemistry and toxic substances. At the moment they enter the water body, a violation of the natural regime occurs, which is expressed in a negative and even fatal effect on water resources. Pollution causes:
- absorption of the oxygen component;
- significant decrease in water quality;
- sedimentation of hazardous components to the bottom;
- the impossibility of using water even for technical purposes;
- death of aquatic inhabitants due to the destruction of their natural habitat.
All types of sewage liquids reduce the functionality of natural and man-made sources. For this reason, in most of them you can’t swim, they are not suitable for recreation or water use. To prevent problems, it is important to treat wastewater from contaminants.
Industrial effluents can carry not only chemical, but also bacteriological hazards. This is possible if the discharge comes from leather processing enterprises, slaughterhouses, and medical facilities. Even anthrax bacteria, glanders, can enter the water. Also, without purification, production drains are a source of aggressive chemistry.
Among domestic sewage liquids, black wastewater is considered the most dangerous. They account for approximately 25 percent of the total volume of household sewage, they include a lot of organic matter, bio-pollutants. These sewage fluids contain more than half of the total amount of phosphorus, about 80 percent of nitrogenous compounds (including urea) and almost all fecal bacteria. It is these constituents of plums, in addition to aggressive chemistry, that are the main threat to water resources.
Substances of a biological and chemical nature must not enter the soil or a body of water.If your pipeline is connected to a citywide sewage system, domestic wastewater treatment is a public utility problem. If the connection is not made, you are responsible for the safety of the faecal discharges or for the removal of liquid waste to municipal wastewater treatment plants. It is for these purposes that septic tanks and bio-purification stations are equipped.
Septic devices are not always able to completely disinfect hozfekalny drains. For antibacterial effects on liquids, irradiation with ultraviolet rays or ozonation are used. Such disinfection is required if the water is supposed to be reused for technical needs. Industrial effluents may require the use of physico-chemical and chemical treatment methods.


