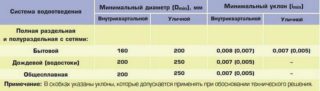
Wastewater treatment plants are designed for different degrees of pollution, so the design features of each of them depend on what substances you have to work with and how difficult it is to remove them from the liquid so that it meets all sanitary standards.
Purpose and principle of operation
 There are several types of wastewater - domestic, storm and industrial. Each of these species is dangerous in its own way and requires a number of measures to remove harmful substances to the required level.
There are several types of wastewater - domestic, storm and industrial. Each of these species is dangerous in its own way and requires a number of measures to remove harmful substances to the required level.
Industrial effluents are characterized by the presence of chemicals that can cause mass poisoning and even lead to the death of people, animals, fish in a pond. To clean chemical effluents, reagents are used that neutralize and neutralize the liquid. Acids, alkalis, radioactive elements, and mechanical particles can be in the drains of chemical plants. The treatment plant should take into account the composition of the wastewater and apply those methods that correspond to the nature of the pollution.
Surface water treatment facilities are designed to remove mechanical particles from rainwater, as well as petroleum products, gasoline, diesel fuel, various oils. Before it enters the sewer system, rainwater flushes the remnants of these substances from highways and parking lots, where they fall from faulty engines, gas tanks, and oil tanks.
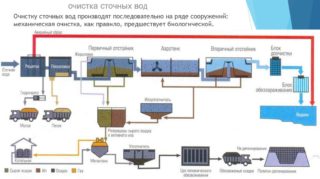
The complex of treatment facilities for domestic wastewater should include several stages of the release of liquids from organic residues and particulate matter. Useful microorganisms participate in the decomposition of organics - aerobic and anaerobic - this is the most effective way, which gives an almost one hundred percent result. In addition to bacteria, biological treatment plants use mechanical devices - sand traps, grease traps, filters and devices for the final disinfection of clean water - ultraviolet radiation or chlorination.
After carrying out all the measures, the liquid is checked by a laboratory method for the presence of toxins, pathogens and suspended particles. If the parameters correspond to the norm, water is sent for reuse in the city water supply network or discharged into natural water bodies.
Types and structure of treatment facilities
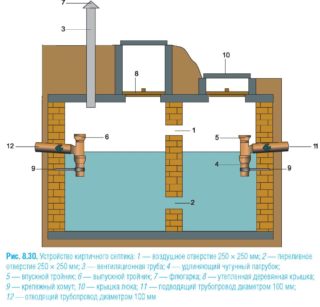 Autonomous treatment facilities are installed in private homes or in summer cottages. These are the simplest devices - septic tanks, in which bacterial concentrates are periodically added to eliminate odor and process organics, in order to subsequently use it to fertilize the soil on the site.
Autonomous treatment facilities are installed in private homes or in summer cottages. These are the simplest devices - septic tanks, in which bacterial concentrates are periodically added to eliminate odor and process organics, in order to subsequently use it to fertilize the soil on the site.
There are sewage treatment plants that accept sewage from the whole village or district. These are larger structures with a full range of equipment. Organizing such a station by joint efforts is much cheaper.
Industrial effluents enter separate storage facilities where hazardous substances and compounds are removed from them. Typically, they try not to mix chemical waste with household waste, since they need completely different technologies and reagents.
Storm sewage is considered the cleanest of all, but many foreign objects enter the sewer that need to be separated and disposed of - plastic bottles, paper, plastic bags, large stones and sand.
The structure distinguishes between surface and underground sewage treatment plants. Surface stations occupy large areas, so they are placed outside the city or village.In servicing, such facilities are more convenient, since all nodes are within the reach of station staff. The downside is the presence of an unpleasant odor, but there are special technologies for this that can avoid it.
In private areas, it is more advantageous to use underground septic tanks so as not to occupy the usable area and not spoil the appearance of the site with plastic containers. In cottage villages, both ground and underground biological treatment plants are used, since the effluents are mainly domestic or surface.
The design of the biological treatment plant
 The advantage of biological stations over septic tanks is that the effect is achieved naturally without the use of chemicals, and the degree of purification is very high - 98%. Such a liquid can be easily pumped into water bodies, and they will not harm nature.
The advantage of biological stations over septic tanks is that the effect is achieved naturally without the use of chemicals, and the degree of purification is very high - 98%. Such a liquid can be easily pumped into water bodies, and they will not harm nature.
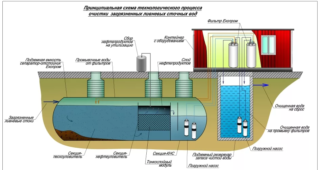
The system consists of four stages, each of which is important:
- Prior to wastewater, a preliminary decontamination is carried out. To do this, gratings are required that retain plastic, cardboard, and clothing. All this is collected and disposed of in a landfill.
- Once in the first tank, the liquid settles, large particles settle to the bottom. Here, organic matter is processed by bacteria, or activated sludge. For the multiplication of microorganisms, a large amount of oxygen is necessary, therefore it is additionally supplied from below.
- After the primary sump, the purified liquid is sent for further treatment to the secondary tank. There, bacterial colonies settle to the bottom, from where they are disposed of with special scrapers that periodically pass along the bottom of the sump.
- Next, a practically pure liquid is irradiated with ultraviolet light or chlorinated in a separate container and sent back to the water intake system.
The technological scheme of treatment facilities for domestic wastewater is the most environmentally friendly of all, since it does not require the use of chemicals. The disadvantages of the system include the dependence on electricity, as well as the lengthy process of processing organics by microorganisms.
Closed surface runoff facilities
 Designed to separate oil products, grease and garbage. The first step is rough cleaning. In this case, synthetic materials - plastic and other substances are removed from the sewer. Then reagents, for example, aluminum oxide, are used, as a result of mixing with storm drains an insoluble precipitate is formed, which is collected and disposed of.
Designed to separate oil products, grease and garbage. The first step is rough cleaning. In this case, synthetic materials - plastic and other substances are removed from the sewer. Then reagents, for example, aluminum oxide, are used, as a result of mixing with storm drains an insoluble precipitate is formed, which is collected and disposed of.
There are special filters that trap large oil molecules, remove manganese and iron ions. The most famous substance is activated carbon. There are more modern methods, expensive and so far inaccessible to most sewage treatment plants.
Surface runoff stations are part of urban wastewater treatment plants that operate faster, since the chemical treatment method allows you to remove contaminants in a short time - less than a day. Such treatment plants are used at gas stations, car washes, oil refineries.
Design of treatment systems
Storm sewage can be combined with domestic, especially in private autonomous systems. But experts do not recommend doing this, since with a large amount of precipitation, the septic tank can fill up very quickly and sewage will spill onto the site.
A more expensive, but practical option is to use separate pipes and containers for rain and melt water. In the event of an overflow, nothing bad will happen, but you can provide an additional channel through which water can go outside the site.
All design issues are best solved with specialists. They will help to correctly calculate the volume of the septic tank and the diameter of the pipes, as well as make a preliminary marking of the sewage system on the site. Typically, stormwater is laid next to or under a sewer pipe.
Installation of installations
The installation of wastewater treatment plants for storm water in terms of scope of work is similar to a household sewer system, therefore it is better to install these two septic tanks at the same time - at the stage of laying the foundation.
The slope of the pipes is taken into account, as when laying the sewer line. Plastic products are additionally insulated and sprinkled with sand so that the joints are not deformed during operation. In places of bends or drops in the level of the pipe, an inspection well is installed for the convenience of eliminating blockages and checking the condition of the internal walls.
When installing plastic pipes, they rarely have to be cleaned, provided that the installation was carried out in accordance with all the rules.
Due to the large amount of dirt and debris - leaves, branches, stones - it is advisable to install sand traps and gratings with large openings for stormwater to prevent debris from entering the pipes and forming a cork.
Maintenance of treatment facilities
Maintenance of biological treatment plants consists in timely pumping of spent activated sludge and organic sludge. Periodically, it is necessary to wash the walls of the septic tanks with a powerful stream of water.
Preventive measures at city stations are carried out by staff, at home you can do it yourself or conclude an agreement with the company that installed the system. Unfortunately, the maintenance of such facilities is not cheap. In urban sewerage is carried out at the expense of the city, autonomous - at the expense of the owners. If a full-scale sewage treatment plant is operating on the site, it requires counting the amount of sludge, its growth and removal. If it is incorrect to calculate the required number of bacteria for the current volume of effluents, the treatment will not be of high quality and organic substances can get back into the water supply system, which is dangerous for the health of the residents of the house.