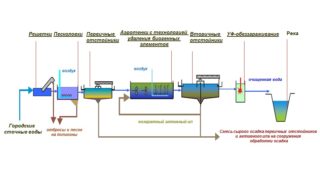
Wastewater treatment plants are devices representing a set of technical equipment for purifying drainage liquids to acceptable levels with further discharge into water bodies, soil or a central sewage system. Their reuse for technological and irrigation needs is possible.
Types of sewage treatment plants
Cleaning devices are divided into urban and local. The former take a mixture of hozfekalny drains from city dwellers, industrial liquid waste from industrial facilities, as well as rain and melt water.
Local OSK are mounted on industrial facilities for purification of drains of the main polluting impurities before dumping in the central sewerage or secondary use. Local autonomous cleaners are installed in personal plots.
The design of sewage treatment plants is diverse and depends on the type of wastewater and the degree of pollution. The complex may consist of the following blocks:
- mechanical components;
- bio-purification plants;
- devices for ion exchange;
- oxygen saturating devices;
- filters for adsorption;
- equipment for electrochemical and physico-chemical cleaning;
- installations for disinfection.
The cleaning equipment includes tanks for the accumulation, storage, processing of filtered sludge.
The principle of operation of the treatment facilities of the centralized city sewage system:
- Wastewater treatment is carried out mechanically. Contaminants are retained thanks to special grilles and sand traps.
- The membrane device performs a more thorough cleaning. Suspensions are separated in the sump and mineral impurities are removed.
- For further purification, biological agents are used. Under the action of active bacteria, the decomposition of organic compounds in the composition of the contaminated liquid occurs. Drains pass through a biological filter. As a result, sludge and gaseous compounds appear.
At the final stage of disinfection, additional chemicals are used. The resulting water can be used for technical purposes.
Storm sewer
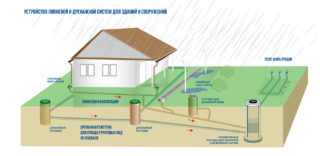 It is intended for the collection and transfer of surface water resulting from precipitation. The main task of stormwater is to remove moisture from the base and walls of houses, green spaces, road surfaces.
It is intended for the collection and transfer of surface water resulting from precipitation. The main task of stormwater is to remove moisture from the base and walls of houses, green spaces, road surfaces.
The storm sewage treatment system includes:
- roof drainage;
- funnels and drains that direct and transport moisture to the storm inlet;
- a system of pipe sections and trays that transfer water to the drive or a nearby ravine.
In various parts of the transportation system, sand traps with garbage containers are placed. They serve as a filter and require systematic cleaning.
Local facilities
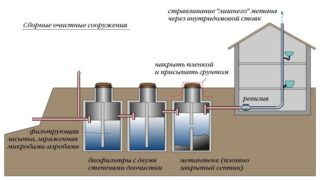 The design is diverse: from the cesspool to the deep sewage treatment plant. At home, most often used:
The design is diverse: from the cesspool to the deep sewage treatment plant. At home, most often used:
- Cesspools. These are the simplest VOCs; they can be airtight or drained. Allowed only for small houses and cottages.
- Septic tanks are hermetic tanks into which sewage is discharged. Anaerobic microorganisms that process sludge and contribute to the purification of water live there. The liquid after the septic tank requires additional purification, for example, using a biofilter, before it is discharged into a reservoir or soil.
- Aerotanks.These are hermetically sealed installations with forced aeration. To process the liquid more efficiently, use activated sludge containing the necessary microorganisms.
For deep cleaning, sewer stations and bioreactors consisting of blocks and modules are mounted. Installations of this type reduce the concentration of sludge in water after treatment and protect the environment and human health. They bring the purity of the waste fluid to 98 percent, which suggests its secondary use. Buildings are mounted at production facilities or at sites near residential complexes and large cottages.
Installation Choice
When choosing a suitable purification system, consider:
- total daily water use;
- type and principle of operation of the sewer installation;
- location of the facility.
The functioning of some installations may be carried out in full autonomy. For the work of others, you will need electricity or other types of energy. There are devices, the use of which is unacceptable with the close location of groundwater.
Design Features
When creating a layout of treatment facilities, it is required to consider the risks of operating the installation. Each type of treatment design has its pros and cons. When selecting, it is necessary to proceed from the application parameters:
- the likely volume of wastewater that will flow daily into the treatment tank;
- use of the facility - on an ongoing or seasonal basis, or only on weekends;
- system performance;
- geological conditions of the site;
- level of subsoil sources and freezing points of the soil.
If you plan to build a large house for a large family with the equipment of several sanitary facilities, it is recommended to build an autonomous sewer system. If you select the installation for a summer residence or a small house - just a normal septic tank is enough.
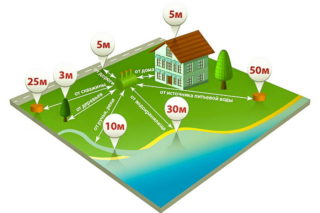
Sanitary and building regulations
The rules for the placement of treatment facilities are specified in SNiP 2.04.03-85 and SanPiN 2.2.1. In order to avoid a conflict with sanitary and other supervisory services, it is necessary to take into account the requirements prescribed in these regulatory codes, as well as prepare a package of documents:
- agreement on ownership or lease;
- location scheme of the point where the installation of the treatment plant is planned;
- compliance with existing sanitary standards;
- technical conditions for the use of water resources;
- information about the volume of used and utilized water;
- design documents;
- description of the filtration system and the disposal of sewage.
Also, permission from the sanitary and epidemiological station will be required. In case of violation of sanitary norms, the owner may be held administratively liable.
Installation work
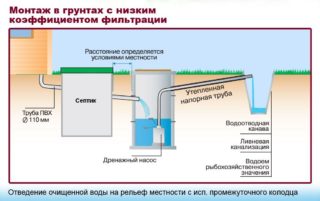 Arrangement of a sewage treatment plant consists of six stages:
Arrangement of a sewage treatment plant consists of six stages:
- Create a project.
- Site inspection and determination of its readiness for installation.
- The construction of the device.
- Connection of installations to communication networks.
- Start-up and commissioning works, adjustment and tuning of automatic equipment.
- Testing and commissioning.
Determination of the full amount of installation work depends on the terrain and the design of the treatment plant.
When drawing up the device diagram and subsequent installation, they are guided by sanitary and construction standards.
If you have to use a sewage machine to pump out the waste, you will need to arrange a free access to the storage tank.
Modern sewer systems are convenient devices for the effective treatment of wastewater. When used correctly, they will provide comfort to residents of houses and owners of enterprises and will prevent environmental pollution of the area.