Sewer fittings are important parts of the sewage system. They are used for joining pipe sections into a single network and when assembling plumbing equipment at the time of connection to the sewer line.
Scope and materials
Previously, the installation of sewage was carried out on the basis of pipes made of cast iron with metal fittings. For assembly, the use of various types of welding was required.
Modern hozfekalny pipelines inside and outside buildings, as well as drainage lines are equipped with plastic parts.
Polymer products are resistant to almost all types of aggressive environments, are lightweight, have a long service life and are easy to install. Their use significantly increases the operational performance of engineering communications, reduces the cost of their arrangement.
Polyvinyl chloride products are popular due to their low weight and budget cost. PVC shaped elements are used for abduction:
- permanent wastewater in sewers with a temperature not exceeding 80 degrees;
- short-term drains with a temperature of 95 degrees;
- chemical liquids with a pH value of from two to twelve.
Fitting elements made of polypropylene and polyethylene are more durable, flexible and less susceptible to temperature extremes compared to polyvinyl chloride counterparts. Pipes from these materials can be used for any type of sewage installation, including hidden under plaster. PPRC high-strength fittings are allowed to operate under pressure up to 25 MPa, which is important for pressure sewers.
Types of Sewer Fittings
 The piping in the building is made using fittings designed for internal sewage. The most commonly used tees, single-plane and double-plane crosses, couplings and knees. The first two types of fittings are used to connect additional bends to the pipeline. They are made with an angle of inclination of 45, 65 and 90 degrees. Elbows connect various bends and are installed on the turns of the highway. They can end with a bell from one or both ends. Pieces of pipes of equal cross section are joined by couplings, and repair couplings are used to eliminate damage to the line.
The piping in the building is made using fittings designed for internal sewage. The most commonly used tees, single-plane and double-plane crosses, couplings and knees. The first two types of fittings are used to connect additional bends to the pipeline. They are made with an angle of inclination of 45, 65 and 90 degrees. Elbows connect various bends and are installed on the turns of the highway. They can end with a bell from one or both ends. Pieces of pipes of equal cross section are joined by couplings, and repair couplings are used to eliminate damage to the line.
For internal pipelines, other types of fittings are used:
- Branches - for arranging turns during the installation of nearby branches of the highway.
- Reduction - for the transition between sections of sewers of different diameters, as well as for the joint of cast iron and polymer pipes.
- Compensation pipes - to eliminate breakdowns by replacing the damaged part of the pipeline.
- Revision - to clean clogged pipes. They are equipped with a screw cap and are mounted in easily accessible places.
- Nurses - when connecting an additional branch to an already operating trunk. They sit on the glue, grasping the main pipe, and an outlet is connected to the socket.
- Plugs - for blocking transported wastewater during repairs or revisions.
An aerator or sewer valve is necessary to block the entry of gases into the sanitary room through the toilet due to rarefaction of air in the fan pipe, which leads to the pulling of the water seal from the siphon.
Shaped parts for external sewage in design and purpose are similar to analogues mounted inside the building. But they are much stronger and painted, like pipes for external work, in red color.This allows you to quickly detect the highway against the background of dark earth.
When arranging the external pipeline, check valves and double-knee siphons are used. The first element is necessary to block the return of effluents and is always mounted on pipe lines laid with a slope of less than two centimeters. The siphon acts as a connector for two parallel pipe sections. The bend resulting from the docking area prevents the gases from escaping to the bathroom.
Dimensions of fittings
 The section of the laid pipe segments and connecting shaped elements usually coincides. In transition fittings, the diameters of the outlet openings may vary, but the size of the inlet is always the same as the corresponding line segment.
The section of the laid pipe segments and connecting shaped elements usually coincides. In transition fittings, the diameters of the outlet openings may vary, but the size of the inlet is always the same as the corresponding line segment.
Inside the building, pipes of the following diameters are used for drainage:
- from a shower, washbasin, bidet, sink, bathtub - 40 mm;
- from the toilet and the central riser - 110 mm;
- from the main riser - 60 mm.
The combined drain combining the bath, shower and sink is equipped with 50 mm parts.
For laying communication networks outside the building, fittings with a diameter of 160-200 mm are chosen.
The aspect ratio of commonly used fittings for PVC sewer pipes is clearly shown in the table:
| Element | Diameter (mm) | Length (mm) |
| Coupling | 110–400 | 120–330 |
| Audit | 50–315 | 167–500 |
| Challenge | 110–400 | 15–90 |
| Expansion joint | 50–500 | 170–320 |
| Check valve | 110–250 | 300–520 |
| Two-knee siphon | 110–200 | 510–820 |
Tees with an angle of 45 degrees produce a diameter of 110–400 mm, the length of their side sockets is 140–530 mm, and the height from the end to the socket ledge is 140–500 mm.
Selection rules
When choosing shaped elements, it is worth considering the following points:
- Before buying, you should create a project with a mark of all points of the spillway and plumbing fixtures. It will help determine the necessary number of fitting parts.
- The material of the connecting elements should be similar to that of which the sewer pipes are made.
- For joining the metal part of the pipeline with a polymer branch, shaped parts for a threaded connection from one edge will be needed.
- It is advisable to purchase fittings from the same manufacturer as the pipe sections. When purchasing products, you should pay attention to exact coincidence in size.
With the increase in the number of fittings installed on the pipeline, the likelihood of congestion increases. Try to simplify the main geometry as much as possible, and install the fittings so that there is free water drainage.
Installation Recommendations
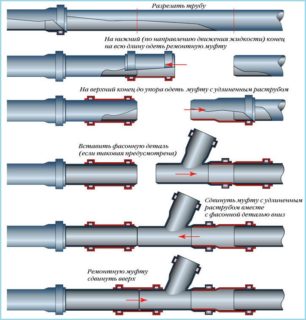 To equip the sewage system from plastic, it is enough to use bell-shaped or glued shaped elements without the use of expensive equipment for gas and electric welding works. In this case, certain nuances must be taken into account:
To equip the sewage system from plastic, it is enough to use bell-shaped or glued shaped elements without the use of expensive equipment for gas and electric welding works. In this case, certain nuances must be taken into account:
- Cut polymer parts using a saw with a fine tooth or a piece of cable. Such a tool allows you to leave minimal scuffs on the edge of the cut.
- After cutting, cut the edge of the saw. Eliminating burrs helps prevent clogging and ensures a tight fit.
- If voids have formed at the junction, glue them using a brush.
When using glued fitting elements, the connected areas are first degreased, and then glue is applied. The composition is evenly smeared with a brush, excess wiped with a rag.
If parts with a rubber seal are purchased, silicone sealant is applied to the joined surfaces before assembly, which will reduce the risk of leaks.
The pipe must not be inserted all the way, but so that a centimeter compensation gap is formed. Prior to this, make a preliminary connection and mark the depth of entry on the pipe.
Shaped parts for polyethylene and polypropylene sewer pipes can be connected to the highway not only by the bell-shaped method, but also by hot welding. It has its own characteristics:
- If the cross section of pipe segments and fittings is less than 50 mm, you can use a household soldering apparatus.
- For the installation of large diameter pipes, you will need a centering unit.
- Prior to welding, aluminum sections reinforced with aluminum are trimmed with a trimming tool or a shaver to the soldering depth.
The ends are heated with a soldering apparatus, which leads to their softening. The parts to be welded are pressed against each other by end surfaces, gradually increasing pressure. Until the seam is cooled, it is important not to move the pipes and fittings to prevent movement. The connection is obtained as strong as possible, since the connection of parts occurs at the molecular level.
The right choice of fittings and competent installation of the pipeline is a guarantee of a long service life of both the fittings themselves and the entire system.



