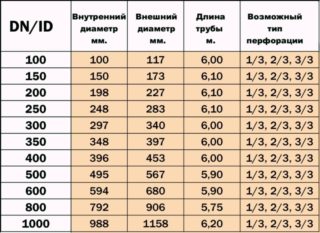
Plots with a large amount of groundwater are subject to mandatory drainage. For this purpose, a special drainage system is mounted. Its design includes perforated sleeves and polymer wells: viewing, storage, rotary, filtering. The entire system is mounted on a slope for better gravity flow of water. In private ownership, pipes with a cross section of 11 cm are mainly used. This diameter is most optimal for the average monthly volume of effluents. Prices for 110 mm drainage pipes in a geotextile filter depend on the manufacturer and the inner cross-section of the sleeve.
Application area
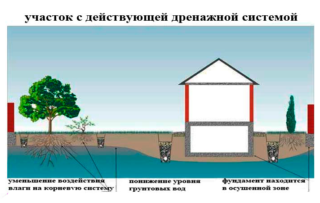 Drainage pipes in a geotextile filter are used in such cases:
Drainage pipes in a geotextile filter are used in such cases:
- moisture removal from the roadway in order to prevent its subsidence;
- high-quality drainage of soil around buildings: cottages, log houses, other private / public houses;
- soil preparation for further productive planting of fruit or vegetable crops;
- drainage of sports grounds;
- water drainage from flooded / swampy pastures and other agricultural land.
Often use such pipes on loamy, clay and sandy soils of medium and high moisture.
Types of pipes in geotextiles
 The finished drain pipe, packaged in a filter made of geotextiles, has a specific configuration:
The finished drain pipe, packaged in a filter made of geotextiles, has a specific configuration:
- sleeve made of polymer;
- geotextile outer sheath;
- special couplings for laying an extended system.
The drainage pipes in the filter are classified by strength and density:
- Single layer. It looks like a regular corrugated sleeve. The stiffeners of the product allow it to be laid to a depth of 4.5-5 meters. The top layer is geotextile filtering.
- Two-layer. It has in its composition the first layer in the form of corrugations and the inner one in the form of a smooth sleeve. Due to this, from the inside, the walls of the drainage pipe remain smooth and do not contribute to the subsidence of silt on them. And the sleeve itself can be laid at an angle, without fear of damage to the corrugation.
Drains are made from the following polymers:
- Polyvinyl chloride. The material is characterized by absolute inertness to aggressive environments. It is resistant to temperature extremes and does not change its structure even in severe frosts. However, you should be careful with the pipes when laying the system in cold. At minus temperatures, polyvinyl chloride becomes brittle and any mechanical impact on it can deform the product. The weight of the PVC pipe is negligible, which allows the site owner to lay the system on their own. With linear expansion, the material is highly ductile. A corrugated PVC sleeve can be laid at an angle of 90 degrees without risking damage to its outside.
- Polypropylene. Resistant to frost and more plastic. It is able to freeze and thaw without losing its elasticity. Polypropylene pipes are in special demand in regions with a cold climate.
- Polyethylene. No less plastic, lightweight and at the same time cheap type of polymer. Polyethylene sleeves can be laid to a depth of 3 meters.
The type of pipe and its cross section are selected depending on the climatic conditions in the region and the monthly volume of groundwater in the area.
Drain pipe sizes
Pipes in a geotextile filter are sold per meter. In one roll 40-50 m. The buyer has the opportunity to purchase the length of the sleeve necessary for installation of the system without the use of additional connections. Distinguish drains by the size of the internal section:
- 63 mm - designed for small garden areas with a small amount of groundwater;
- 90 mm - used in private estates to remove moisture from the foundation of the building;
- 110 mm - ideal for the installation of a drainage system in areas up to 200 m2;
- 160 mm - maximally suitable for the installation of a drainage structure on a site whose area exceeds 200 m2;
- 200 mm is a good option for a sloping terrain, especially if its decrease is observed from a hill towards a given object.
A geotextile filter prevents small debris from entering the drains - sand, earth. On insufficiently smooth surfaces of the sleeves, they can provoke siltation. As a result, the system can become seriously clogged over time.
Advantages and disadvantages
Important advantages of drainage pipes in the filter are:
- Excellent durability of products. The stiffness of the corrugation rings (stiffeners) is 4kN / m2. This allows you to withstand severe loads, even with moving soils.
- Long term of operation. Compared to ceramic or concrete pipes, polymer products last 70 years or more.
- Low mass of products. Even one master can cope with them without involving special equipment. In addition, such drains can also be transported by car.
- High resistance to temperature changes. Polymeric sleeves for drainage can be used in the range of -40 - +90 degrees. And they will not change their original properties.
- The smoothest inner surface of the pipes. Thanks to this, water glides more easily, debris on the walls of the system does not stop.
- The presence of a filter made of geotextiles, which does not allow small debris to penetrate into the drainage collector.
- Acceptable cost - saving the family budget for the installation of a sewage system.
The disadvantages of polymer pipes in geotextiles include the thickness of the filter. It is only 1.7 mm. When installing the system, you should be extremely careful so as not to damage the filter layer. Otherwise, you will have to change the drainage area and use additional connections / couplings.
Features of installation and installation
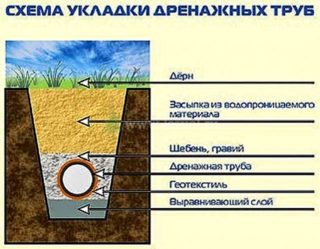 To properly lay the drainage polymer pipes in the geotextile filter, you must first prepare trenches. They are digging around the perimeter of the site in accordance with the project. The depth of the trenches should exceed the level of the groundwater by 20 cm. This will allow the fluid to freely pass through the drains. When preparing and laying pipes, you should adhere to such recommendations:
To properly lay the drainage polymer pipes in the geotextile filter, you must first prepare trenches. They are digging around the perimeter of the site in accordance with the project. The depth of the trenches should exceed the level of the groundwater by 20 cm. This will allow the fluid to freely pass through the drains. When preparing and laying pipes, you should adhere to such recommendations:
- The width of the trench should exceed the sleeve section by 40-50 cm. The spare space is further used for fixing sprinkling. Accordingly, for a pipe with a cross section of 110 mm, a trench width of about 50-60 cm should be made.
- A cushion of coarse sand or fine gravel is poured into prepared ditches. At this stage, a plane slope is formed for the system at the rate of 5-7 mm for each meter of pipeline length. The pillow is carefully rammed.
- All sleeves are laid on the finished base. Joints, if necessary, are connected with fittings. To do this, use couplings for a straight collector, tees or crosses for branching, swivel fittings when changing the trajectory of the system.
- The finished structure is covered from all sides with a mixture of sand and gravel. In this case, there is no need to ram.
- The upper part of the trenches is covered with soil with a protrusion above the surface of the site. This is necessary so that over time the embankment itself settles under the influence of precipitation.
In no case should tamping the upper layers of the backfill. The risk of damaging pipes in the ground is too high.
When carrying out work, it is advisable to avoid dragging the sleeve on the ground. Careless handling of drains can damage a thin layer of the filter, which will require further unnecessary financial costs.
Prices for pipes in a geotextile filter
The cost of drainage hoses depends on its internal section and manufacturer. Estimated prices are as follows:
| Manufacturer | Pipe cross section (mm) | Price (rub / m running) |
| Sibur | 63 mm | 47 RUB |
| Sibur | 110 mm | 60 rub |
| Sibur | 160 mm | 115 rub |
| Sibur | 200 mm | 195 rub |
| Typar | 63 mm | 51 rub |
| Typar | 110 mm | 70 rub |
| Typar | 160 mm | 125 rub |
| Typar | 200 mm | 210 rub |
All drainage pipes with a cross section of 200 mm are sold in rolls of 40 m each. Double-layer sleeves have the corresponding prices:
- 110 mm - 145 rubles / running meter;
- 160 mm - 240 rubles / meter;
- 200 mm - 370 rubles / meter.
When buying drainage pipes in geotextiles, immediately purchase the necessary number of couplings. You can find out the required number of elements from the design documentation / drawing.