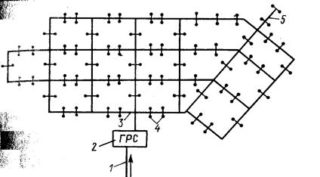
The flow resistance in the manifold acts on the design of the pipeline in the places of narrowing and expansion of the diameter, connecting and rotary nodes, due to which the pressure in the line is lost. The hydraulic calculation of the pipeline is carried out at the design stage to ensure the normal operation of consumers and the supply of the required gas volume.
Definition and need for hydraulic calculation
Resistance includes linear obstruction along the entire length and local obstructions at each structural element of the system at the speed change section. Hydraulic calculation determines the parameters of the gas pipeline. The procedure is a mandatory step in the preparatory phase for the construction of the pipeline.
As a result, a pipe diameter acceptable for highly stable gas transmission over a distance is adopted. The calculation determines the magnitude of the pressure losses and their permissibility during the transfer of fuel.
State standards regulate the calculation procedure for any type of gas pipeline systems, because the processes at gas supply are characterized by identity.
The pipelines are checked for pressure loss:
- low pressure;
- medium head;
- high.
Low-pressure pipelines transport fuel to residential buildings, household enterprises, and public significance, the pressure at the level of 3-5 kPa is considered normal. High and medium pressure highways include branches for mass deliveries, industrial networks, and common pipelines for regions and cities.
Basic input
The initial parameters depend on the gas pipeline scheme, which can be mixed, annular and deadlock. The pressure in the network decreases with distance from the point of insertion or distribution.
Initial parameters are presented by information:
- pressure at the insertion point;
- Consumer information, such as number, location, required nominal flow rate and pressure;
- gas pipeline scheme.
Dead-end sections branch from the main one to consumers and belong to areas with low reliability and difficult recovery during an accident, but require less installation costs. The ring system works more reliably, but installation requires increased costs.
Calculation Schemes
Pressure is determined taking into account the diameter of the pipes, taking into account the influence of internal corrosion, the material of the collectors, the geometric shape of the cross section. The shell of the pipe is destroyed when the voltage in the walls reaches the allowable tensile strength.
During hydraulic testing, a liquid with a temperature of +5 to + 40 ° C is used, unless the technical specification for the test recommends another parameter. When calculating the strength, the temperature of the test and the environment does not drop below + 5 ° C.
The exposure time under the design pressure is indicated by the designer, but always takes more than 5 minutes. In the absence of recommendations, the duration of high pressure is set according to the normative tables and depends on the thickness of the tube shell.
Methodologies
The procedure for selecting the diameter and design scheme of a low pressure gas pipeline is given in the relevant Code of Rules 42. 101 - 2003.Computer programs are used to find the magnitude of the estimated pressure losses between sections of the pipeline, the diameter of the collectors.
Methods applied:
- calculation according to the formulas from the joint venture (complex process);
- calculation by nomograms is simpler, the method of selecting from tables with the substitution of the required parameters is used.
Any method leads to the same results to ensure uninterrupted transportation of gas fuel to consumers.
The influence of pipe material on the calculation
Gas pipelines are built of steel, polyethylene, copper is used in critical areas. Metal-plastic constructions conquer the consumer market. The information in professional tables and collections applies only to plastic and metal pipes, so calculations are carried out for highways made of such materials.
Gas supply pipes are calculated taking into account the roughness coefficient:
- polyethylene (new and old) - 0.007 cm;
- steel, previously in operation - 0.1 cm;
- metal new - 0.01 cm.
If the pipeline is made of another material, gas specialists will not accept the calculation for metal and plastic, an adjustment will be necessary, which will entail additional costs.
Special programs
Branched sections of the gas pipeline with different initial data are calculated separately, but the procedure is performed similarly for each region. The flow velocity changes in places of resistance and change of direction. Linear indicators are calculated on the estimated lengths of the segments of the highway.
The direction is selected depending on the difference in pressure at the end and at the beginning of the study area. The flow goes from a point with more pressure to a place with less resistance. Programs help reduce the efforts of designers in that the initial indicators are introduced into the program, and the electronics perform calculations.
Nomograms are intended to obtain summary information by using tables where each line corresponds to the specified network parameters.
Professional
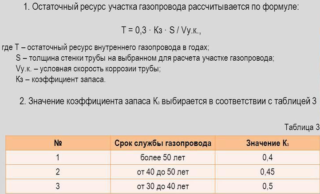 Calculations using formulas are done only by professional engineers and technical workers. A large amount of data is used in the calculations, specific coefficients are used. It is difficult for an unprepared user to take into account all the nuances, to conduct many intermediate calculations to obtain the final result.
Calculations using formulas are done only by professional engineers and technical workers. A large amount of data is used in the calculations, specific coefficients are used. It is difficult for an unprepared user to take into account all the nuances, to conduct many intermediate calculations to obtain the final result.
Professional calculation involves not only the use of formulas and numerical expressions, but also the possession of special knowledge. Skills will not come in handy when using the free settlement software that can be found on the Internet.
Free
Programs are put for use on personal gadgets. The methods determine the diameter, cross-sectional shape of the gas pipeline taking into account allowable losses and flow rate. The user will need the total gas consumption, which is given in the technical documents for the boiler, gas stoves, columns and other equipment.
Then, places with a possible decrease in pressure are determined. Characteristic figures are in the table of the passport, they show a decrease in pressure at the highest consumption. The reduction value is found at the point of incision. The simultaneity coefficient takes into account the joint operation of devices and is contained in the tables.
The diameter of the pipes and the roughness coefficient are indicated at the last stage. The program provides for dissimilar calculations for different pressure in the pipes, which must be taken into account when including data.
Free online software
In this case, the user substitutes the required information in the table columns for online calculations.The hydraulic calculation of a low pressure gas pipeline lasts several minutes and no professional knowledge or computational skills are required from the consumer.
From the technical data are taken:
- gas mixture density;
- kinetic viscosity index;
- climatic temperature range of the region of residence.
Technical conditions are issued by the gas service of the village, the preparation of project documentation begins with the receipt of this task.
Examples of performing hydraulic calculation of the pipeline
The exact number of burners of the connected equipment for selecting the simultaneity factor is given. The numbering of the pipeline segments is not chosen arbitrarily, but is taken from the technical scheme.
The actual length of the highway is indicated and the estimated length is given, which is longer. In the calculation, this parameter increases by 7% due to the presence of resistance regions. The table shows all the structural elements of the pipeline, where pressure losses are assumed.
Calculation of a low pressure gas pipeline
When calculating the gas pipeline inside the house, the amount of boiler equipment is multiplied by the production of each unit. The result is multiplied by an indicator of the simultaneous operation of the units, which is determined by the corresponding table in the directory.
The number of plates in all apartments is multiplied by the productivity of each, the product of the result obtained and the simultaneity coefficient for the connected devices is found. In conclusion, the total pressure for heating units and connected gas stoves is summarized.
Calculation of a high pressure gas pipeline
The calculation is made on the basis of the distribution scheme, taking into account branches to consumer sites. The source of separation is a gas distribution substation. The diameter of the common gas pipeline and branches is located by the gas pressure at the end of the path when introduced to the consumer.
The estimated length of each branch is determined, the pressure is found taking into account losses and resistance in some places. Dead ends are calculated according to their length, gas flow rate and estimated fuel pressure at the point of insertion to the consumer.
The calculation is considered satisfactory if the calculated values of consumer pressure do not exceed the pressure of the network.